Abstract
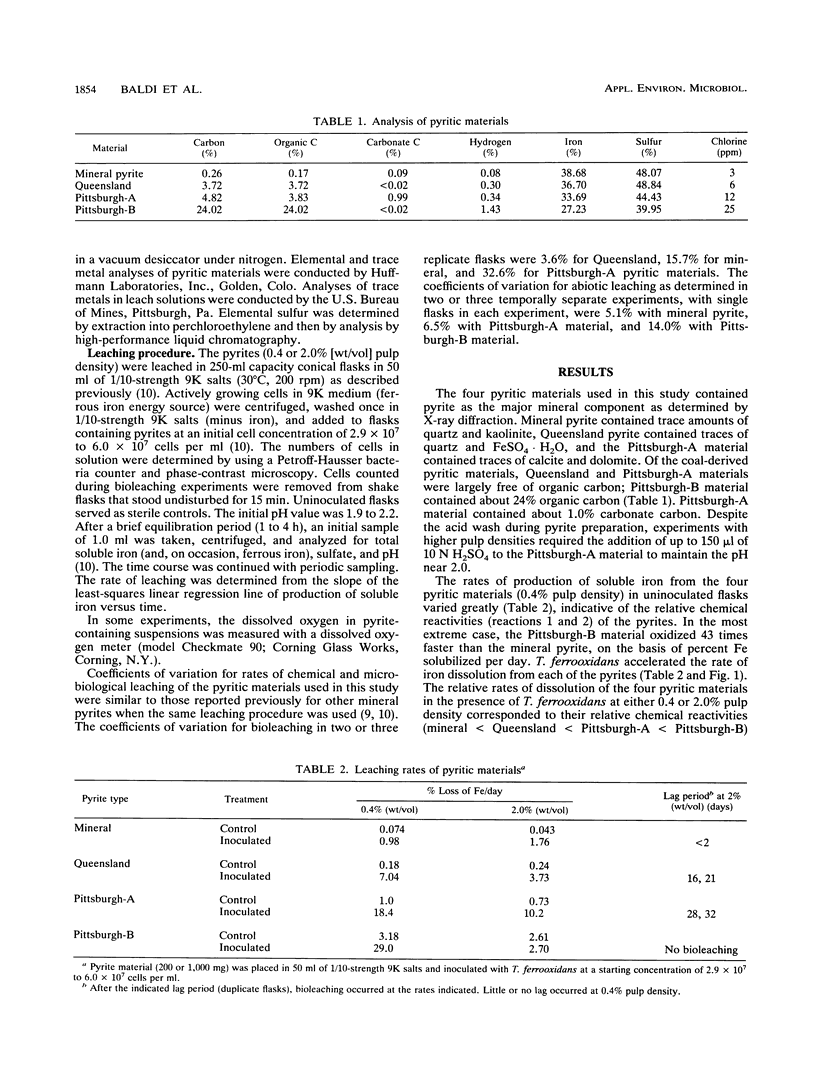
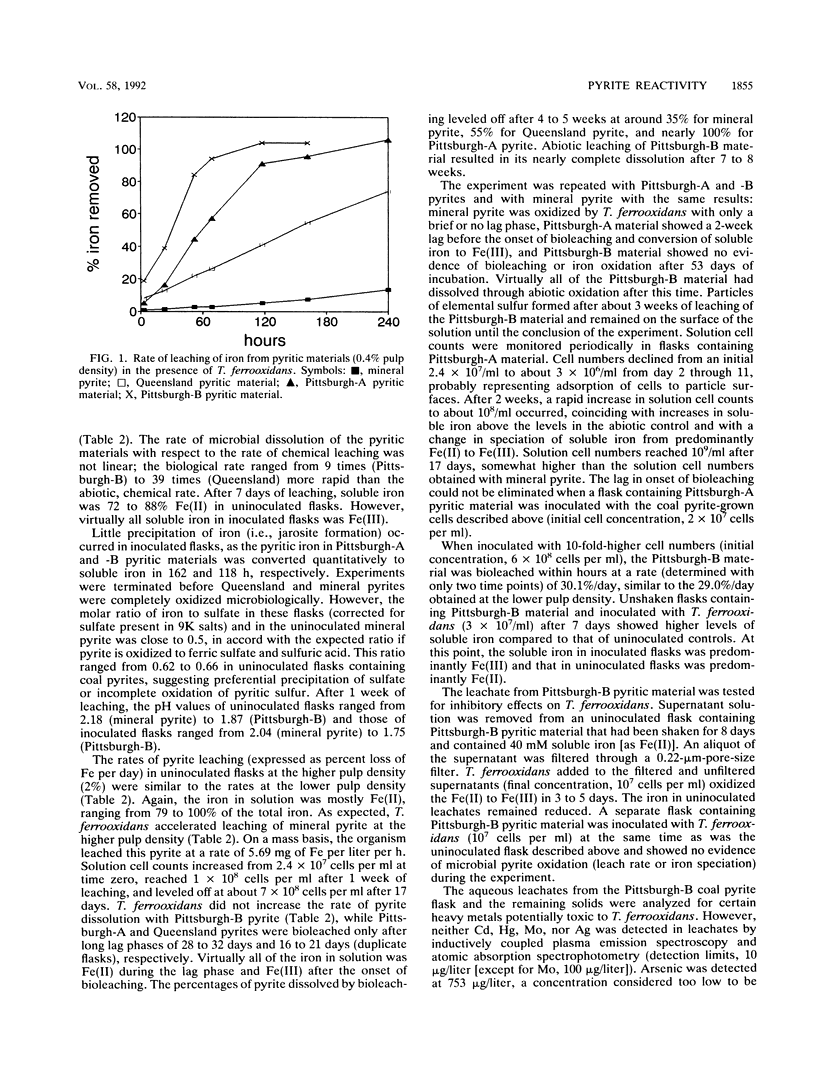
Wide variations were found in the rate of chemical and microbiological leaching of iron from pyritic materials from various sources. Thiobacillus ferrooxidans accelerated leaching of iron from all of the pyritic materials tested in shake flask suspensions at loadings of 0.4% (wt/vol) pulp density. The most chemically reactive pyrites exhibited the fastest bioleaching rates. However, at 2.0% pulp density, a delay in onset of bioleaching occurred with two of the pyrites derived from coal sources. T. ferrooxidans was unable to oxidize the most chemically reactive pyrite at 2.0% pulp density. No inhibition of pyrite oxidation by T. ferrooxidans occurred with mineral pyrite at 2.0% pulp density. Experiments with the most chemically reactive pyrite indicated that the leachates from the material were not inhibitory to iron oxidation by T. ferrooxidans.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Olson G. J. Rate of Pyrite Bioleaching by Thiobacillus ferrooxidans: Results of an Interlaboratory Comparison. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Mar;57(3):642–644. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.3.642-644.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SILVERMAN M. P., LUNDGREN D. G. Studies on the chemoautotrophic iron bacterium Ferrobacillus ferrooxidans. I. An improved medium and a harvesting procedure for securing high cell yields. J Bacteriol. 1959 May;77(5):642–647. doi: 10.1128/jb.77.5.642-647.1959. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer P. C., Stumm W. Acidic mine drainage: the rate-determining step. Science. 1970 Feb 20;167(3921):1121–1123. doi: 10.1126/science.167.3921.1121. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TEMPLE K. L., DELCHAMPS E. W. Autotrophic bacteria and the formation of acid in bituminous coal mines. Appl Microbiol. 1953 Sep;1(5):255–258. doi: 10.1128/am.1.5.255-258.1953. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


