Abstract
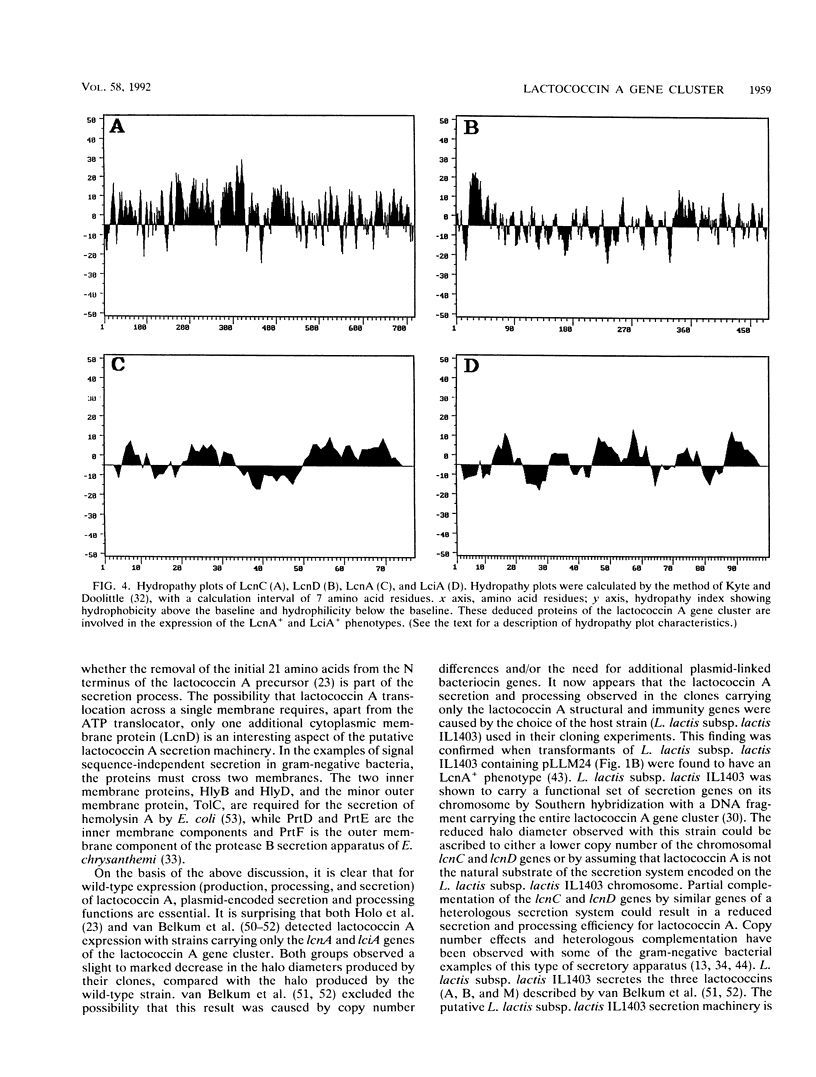
The genes responsible for bacteriocin production and immunity in Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis biovar diacetylactis WM4 were localized and characterized by DNA restriction fragment deletion, subcloning, and nucleotide sequence analysis. The nucleotide sequence of a 5.6-kb AvaII restriction fragment revealed a cluster with five complete open reading frames (ORFs) in the same orientation. DNA and protein homology analyses, combined with deletion and Tn5 insertion mutagenesis, implicated four of the ORFs in the production of and immunity to lactococcin A. The last two ORFs in the cluster were the lactococcin A structural and immunity genes, lcnA and lciA. The two ORFs immediately upstream of lcnA and lciA were designated lcnC and lcnD, and the proteins that they encoded showed similarities to proteins of signal sequence-independent secretion systems. lcnC encodes a protein of 716 amino acids that could belong to the HlyB family of ATP-dependent membrane translocators. LcnC contains an ATP binding domain in a conserved C-terminal stretch of approximately 200 amino acids and three putative hydrophobic segments in the N terminus. The lcnD product, LcnD, of 474 amino acids, is essential for lactococcin A expression and shows structural similarities to HlyD and its homologs. On the basis of these results, a secretion apparatus that is essential for the full expression of active lactococcin A is postulated.
Full text
PDF








Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson D. G., McKay L. L. Simple and rapid method for isolating large plasmid DNA from lactic streptococci. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Sep;46(3):549–552. doi: 10.1128/aem.46.3.549-552.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behnke D., Gilmore M. S., Ferretti J. J. Plasmid pGB301, a new multiple resistance streptococcal cloning vehicle and its use in cloning of a gentamicin/kanamycin resistance determinant. Mol Gen Genet. 1981;182(3):414–421. doi: 10.1007/BF00293929. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blight M. A., Holland I. B. Structure and function of haemolysin B,P-glycoprotein and other members of a novel family of membrane translocators. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Jun;4(6):873–880. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00660.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchman G. W., Banerjee S., Hansen J. N. Structure, expression, and evolution of a gene encoding the precursor of nisin, a small protein antibiotic. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 5;263(31):16260–16266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1141–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1141-1156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung Y. J., Steen M. T., Hansen J. N. The subtilin gene of Bacillus subtilis ATCC 6633 is encoded in an operon that contains a homolog of the hemolysin B transport protein. J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(4):1417–1422. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.4.1417-1422.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DE KLERK H. C., COETZEE J. N. Antibiosis among lactobacilli. Nature. 1961 Oct 28;192:340–341. doi: 10.1038/192340a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dao M. L., Ferretti J. J. Streptococcus-Escherichia coli shuttle vector pSA3 and its use in the cloning of streptococcal genes. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Jan;49(1):115–119. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.1.115-119.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davey G. P., Richardson B. C. Purification and Some Properties of Diplococcin from Streptococcus cremoris 346. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jan;41(1):84–89. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.1.84-89.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies J. K., Reeves P. Genetics of resistance to colicins in Escherichia coli K-12: cross-resistance among colicins of group A. J Bacteriol. 1975 Jul;123(1):102–117. doi: 10.1128/jb.123.1.102-117.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delepelaire P., Wandersman C. Protein secretion in gram-negative bacteria. The extracellular metalloprotease B from Erwinia chrysanthemi contains a C-terminal secretion signal analogous to that of Escherichia coli alpha-hemolysin. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 5;265(28):17118–17125. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dodd H. M., Horn N., Gasson M. J. Analysis of the genetic determinant for production of the peptide antibiotic nisin. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Mar;136(3):555–566. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-3-555. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Froseth B. R., McKay L. L. Molecular characterization of the nisin resistance region of Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis biovar diacetylactis DRC3. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Mar;57(3):804–811. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.3.804-811.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geis A., Singh J., Teuber M. Potential of lactic streptococci to produce bacteriocin. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Jan;45(1):205–211. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.1.205-211.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilson L., Mahanty H. K., Kolter R. Genetic analysis of an MDR-like export system: the secretion of colicin V. EMBO J. 1990 Dec;9(12):3875–3884. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07606.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harmon K. S., McKay L. L. Restriction enzyme analysis of lactose and bacteriocin plasmids from Streptococcus lactis subsp. diacetylactis WM4 and cloning of BclI fragments coding for bacteriocin production. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 May;53(5):1171–1174. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.5.1171-1174.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmes D. S., Quigley M. A rapid boiling method for the preparation of bacterial plasmids. Anal Biochem. 1981 Jun;114(1):193–197. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90473-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holo H., Nilssen O., Nes I. F. Lactococcin A, a new bacteriocin from Lactococcus lactis subsp. cremoris: isolation and characterization of the protein and its gene. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(12):3879–3887. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.12.3879-3887.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaletta C., Entian K. D. Nisin, a peptide antibiotic: cloning and sequencing of the nisA gene and posttranslational processing of its peptide product. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1597–1601. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1597-1601.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaenhammer T. R. Bacteriocins of lactic acid bacteria. Biochimie. 1988 Mar;70(3):337–349. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90206-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein C., Kaletta C., Schnell N., Entian K. D. Analysis of genes involved in biosynthesis of the lantibiotic subtilin. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jan;58(1):132–142. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.1.132-142.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kondo J. K., McKay L. L. Plasmid transformation of Streptococcus lactis protoplasts: optimization and use in molecular cloning. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Aug;48(2):252–259. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.2.252-259.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kékessy D. A., Piguet J. D. New method for detecting bacteriocin production. Appl Microbiol. 1970 Aug;20(2):282–283. doi: 10.1128/am.20.2.282-283.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Létoffé S., Delepelaire P., Wandersman C. Protease secretion by Erwinia chrysanthemi: the specific secretion functions are analogous to those of Escherichia coli alpha-haemolysin. EMBO J. 1990 May;9(5):1375–1382. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08252.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masure H. R., Au D. C., Gross M. K., Donovan M. G., Storm D. R. Secretion of the Bordetella pertussis adenylate cyclase from Escherichia coli containing the hemolysin operon. Biochemistry. 1990 Jan 9;29(1):140–145. doi: 10.1021/bi00453a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntyre D. A., Harlander S. K. Improved electroporation efficiency of intact Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis cells grown in defined media. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Oct;55(10):2621–2626. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.10.2621-2626.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKay L. L., Baldwin K. A., Efstathiou J. D. Transductional evidence for plasmid linkage of lactose metabolism in streptococcus lactis C2. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1976 Jul;32(1):45–52. doi: 10.1128/aem.32.1.45-52.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randall L. L., Hardy S. J., Thom J. R. Export of protein: a biochemical view. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1987;41:507–541. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.41.100187.002451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simon D., Chopin A. Construction of a vector plasmid family and its use for molecular cloning in Streptococcus lactis. Biochimie. 1988 Apr;70(4):559–566. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90093-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathdee C. A., Lo R. Y. Cloning, nucleotide sequence, and characterization of genes encoding the secretion function of the Pasteurella haemolytica leukotoxin determinant. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):916–928. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.916-928.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagg J. R., Dajani A. S., Wannamaker L. W. Bacteriocins of gram-positive bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Sep;40(3):722–756. doi: 10.1128/br.40.3.722-756.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terzaghi B. E., Sandine W. E. Improved medium for lactic streptococci and their bacteriophages. Appl Microbiol. 1975 Jun;29(6):807–813. doi: 10.1128/am.29.6.807-813.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Toneguzzo F., Glynn S., Levi E., Mjolsness S., Hayday A. Use of a chemically modified T7 DNA polymerase for manual and automated sequencing of supercoiled DNA. Biotechniques. 1988 May;6(5):460–469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wagner W., Vogel M., Goebel W. Transport of hemolysin across the outer membrane of Escherichia coli requires two functions. J Bacteriol. 1983 Apr;154(1):200–210. doi: 10.1128/jb.154.1.200-210.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang L. M., Weber D. K., Johnson T., Sakaguchi A. Y. Supercoil sequencing using unpurified templates produced by rapid boiling. Biotechniques. 1988 Oct;6(9):839, 841-3. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Whitehead H. R. A substance inhibiting bacterial growth, produced by certain strains of lactic streptococci. Biochem J. 1933;27(6):1793–1800. doi: 10.1042/bj0271793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zajdel J. K., Ceglowski P., Dobrazański W. T. Mechanism of action of lactostrepcin 5, a bacteriocin produced by Streptococcus cremoris 202. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Apr;49(4):969–974. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.4.969-974.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Bruijn F. J., Lupski J. R. The use of transposon Tn5 mutagenesis in the rapid generation of correlated physical and genetic maps of DNA segments cloned into multicopy plasmids--a review. Gene. 1984 Feb;27(2):131–149. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90135-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Belkum M. J., Hayema B. J., Geis A., Kok J., Venema G. Cloning of two bacteriocin genes from a lactococcal bacteriocin plasmid. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 May;55(5):1187–1191. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.5.1187-1191.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Belkum M. J., Hayema B. J., Jeeninga R. E., Kok J., Venema G. Organization and nucleotide sequences of two lactococcal bacteriocin operons. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Feb;57(2):492–498. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.2.492-498.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Belkum M. J., Kok J., Venema G. Cloning, sequencing, and expression in Escherichia coli of lcnB, a third bacteriocin determinant from the lactococcal bacteriocin plasmid p9B4-6. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Feb;58(2):572–577. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.2.572-577.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



