Abstract
Reductive dechlorination of tetrachloroethene (perchloroethylene; PCE) was observed at 20 degrees C in a fixed-bed column, filled with a mixture (3:1) of anaerobic sediment from the Rhine river and anaerobic granular sludge. In the presence of lactate (1 mM) as an electron donor, 9 microM PCE was dechlorinated to ethene. Ethene was further reduced to ethane. Mass balances demonstrated an almost complete conversion (95 to 98%), with no chlorinated compounds remaining (less than 0.5 micrograms/liter). When the temperature was lowered to 10 degrees C, an adaptation of 2 weeks was necessary to obtain the same performance as at 20 degrees C. Dechlorination by column material to ethene, followed by a slow ethane production, could also be achieved in batch cultures. Ethane was not formed in the presence of bromoethanesulfonic acid, an inhibitor of methanogenesis. The high dechlorination rate (3.7 mumol.l-1.h-1), even at low temperatures and considerable PCE concentrations, together with the absence of chlorinated end products, makes reductive dechlorination an attractive method for removal of PCE in bioremediation processes.
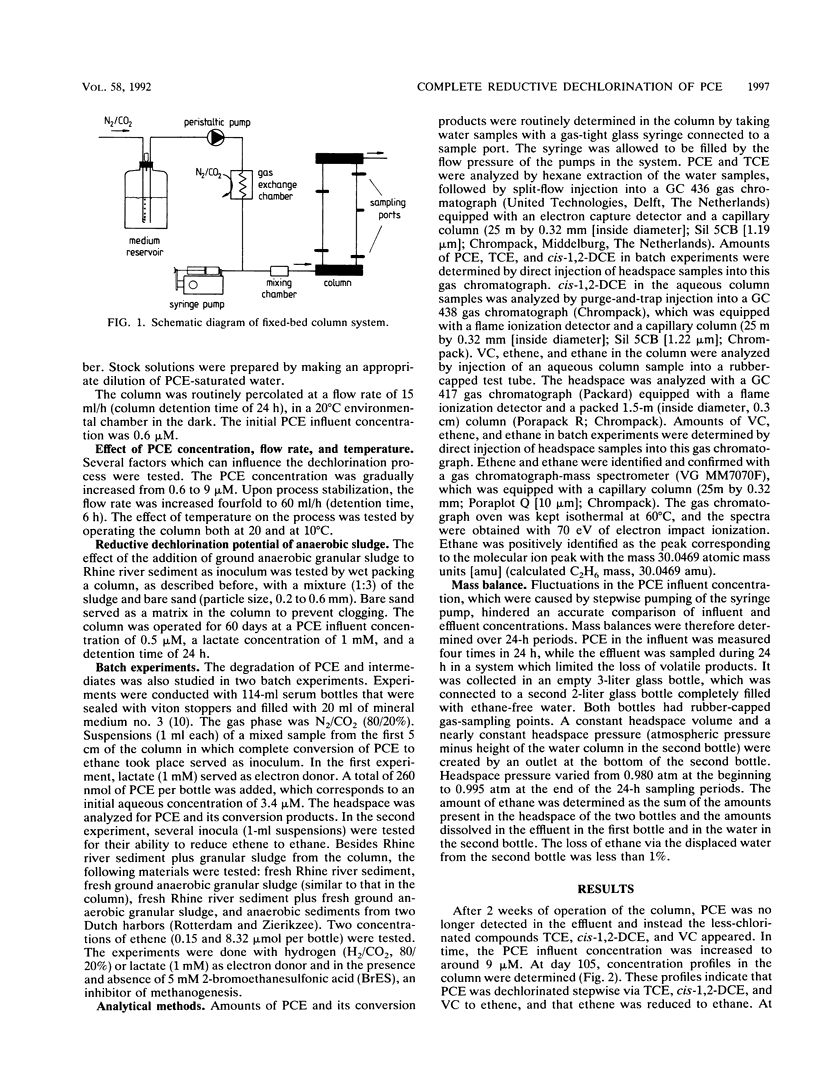
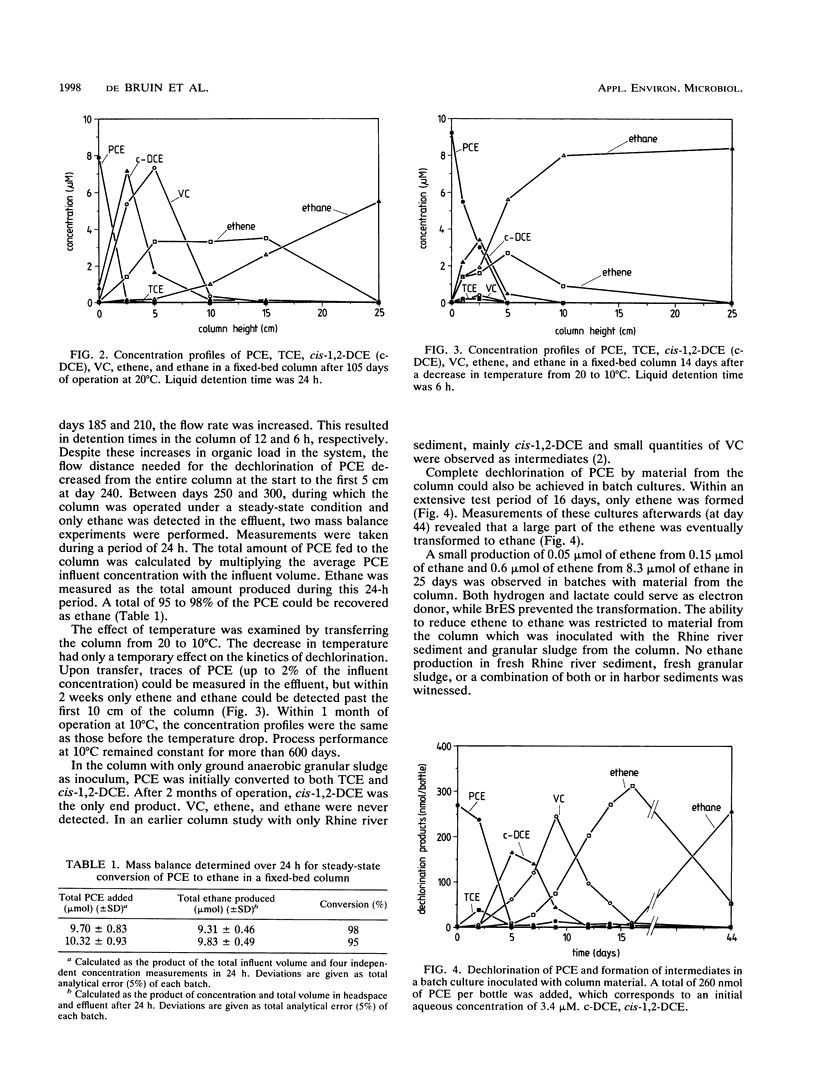
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bagley D. M., Gossett J. M. Tetrachloroethene transformation to trichloroethene and cis-1,2-dichloroethene by sulfate-reducing enrichment cultures. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Aug;56(8):2511–2516. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.8.2511-2516.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bouwer E. J., McCarty P. L. Transformations of 1- and 2-carbon halogenated aliphatic organic compounds under methanogenic conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1983 Apr;45(4):1286–1294. doi: 10.1128/aem.45.4.1286-1294.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DiStefano T. D., Gossett J. M., Zinder S. H. Reductive dechlorination of high concentrations of tetrachloroethene to ethene by an anaerobic enrichment culture in the absence of methanogenesis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Aug;57(8):2287–2292. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.8.2287-2292.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fathepure B. Z., Boyd S. A. Dependence of tetrachloroethylene dechlorination on methanogenic substrate consumption by Methanosarcina sp. strain DCM. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Dec;54(12):2976–2980. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.12.2976-2980.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fathepure B. Z., Nengu J. P., Boyd S. A. Anaerobic bacteria that dechlorinate perchloroethene. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Nov;53(11):2671–2674. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.11.2671-2674.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freedman D. L., Gossett J. M. Biological reductive dechlorination of tetrachloroethylene and trichloroethylene to ethylene under methanogenic conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Sep;55(9):2144–2151. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.9.2144-2151.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oremland R. S. Microbial formation of ethane in anoxic estuarine sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Jul;42(1):122–129. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.1.122-129.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scholz P. M., Kedem J., Sideman S., Beyar R., Weiss H. R. Effect of hyper- and hypovolaemia on regional myocardial oxygen consumption. Cardiovasc Res. 1990 Feb;24(2):81–86. doi: 10.1093/cvr/24.2.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogel T. M., McCarty P. L. Biotransformation of tetrachloroethylene to trichloroethylene, dichloroethylene, vinyl chloride, and carbon dioxide under methanogenic conditions. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 May;49(5):1080–1083. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.5.1080-1083.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zehnder A. J., Huser B. A., Brock T. D., Wuhrmann K. Characterization of an acetate-decarboxylating, non-hydrogen-oxidizing methane bacterium. Arch Microbiol. 1980 Jan;124(1):1–11. doi: 10.1007/BF00407022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zeyer J., Kuhn E. P., Schwarzenbach R. P. Rapid microbial mineralization of toluene and 1,3-dimethylbenzene in the absence of molecular oxygen. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Oct;52(4):944–947. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.4.944-947.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


