Abstract
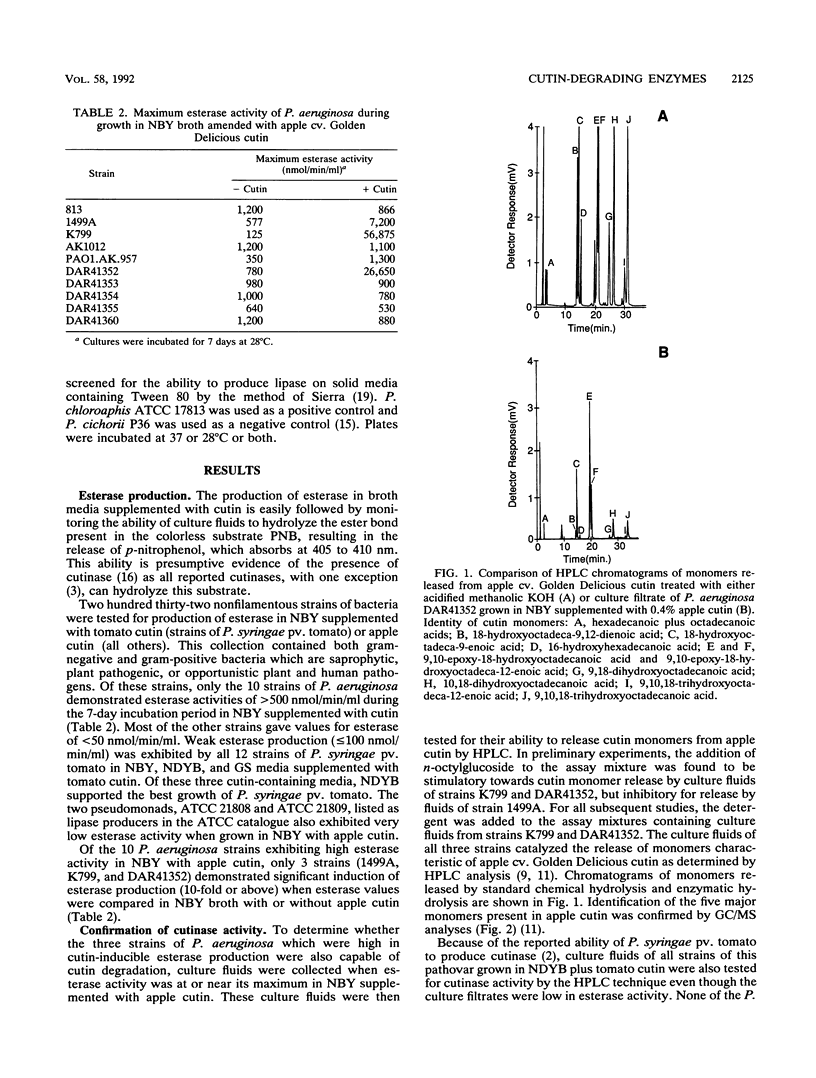
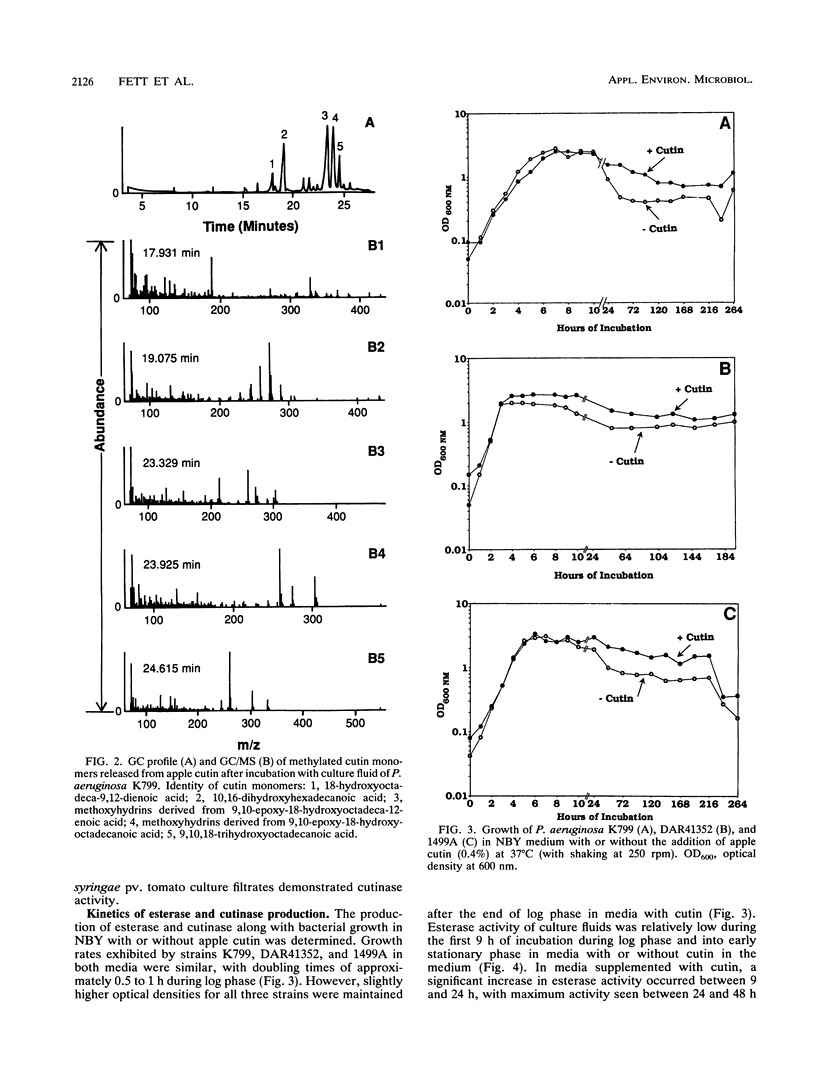
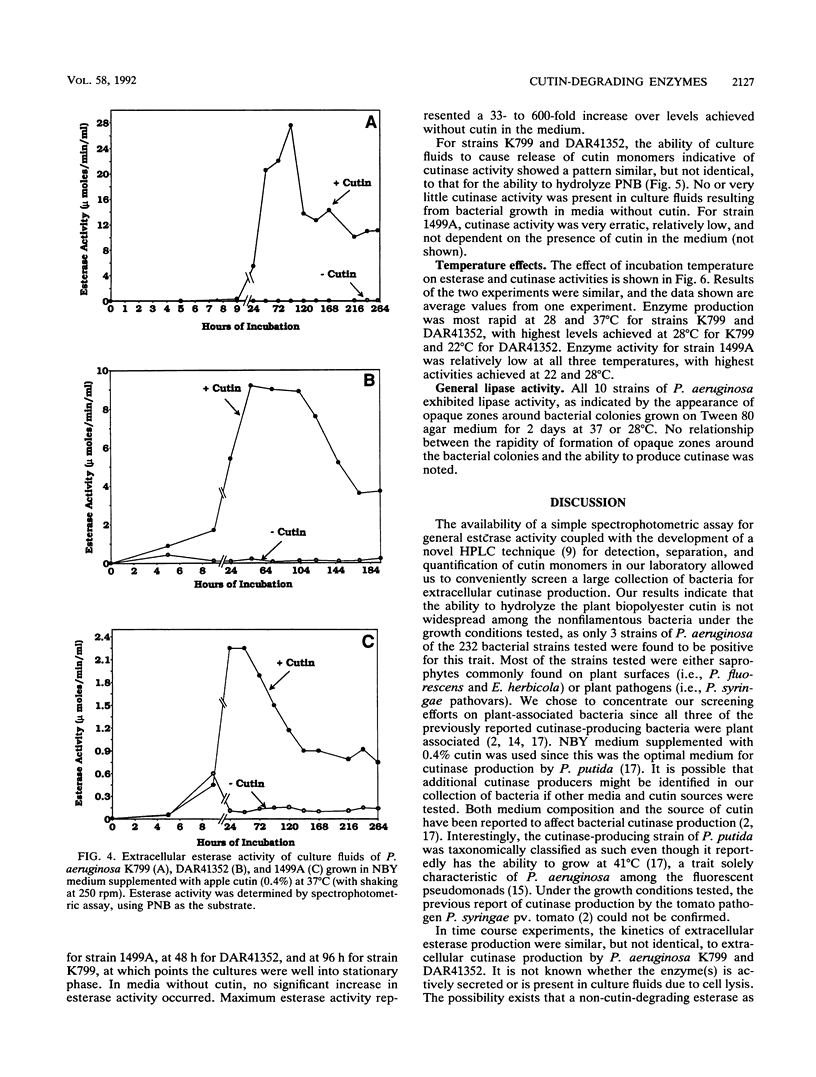
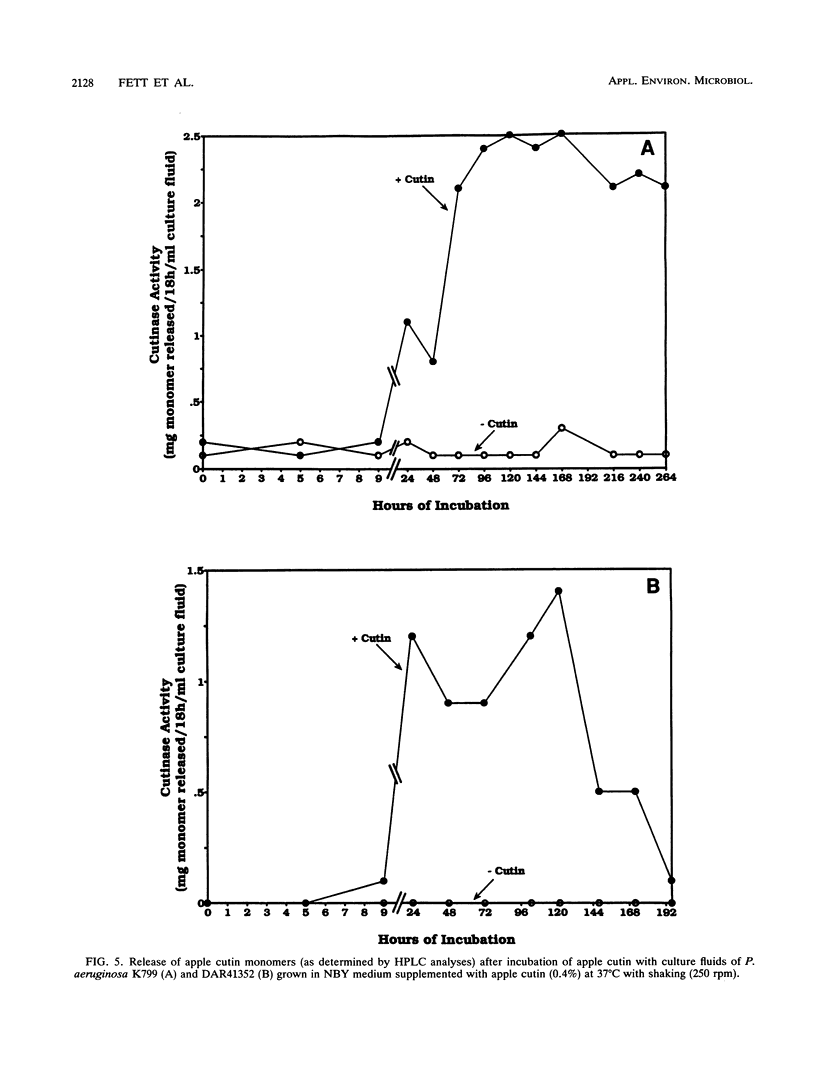
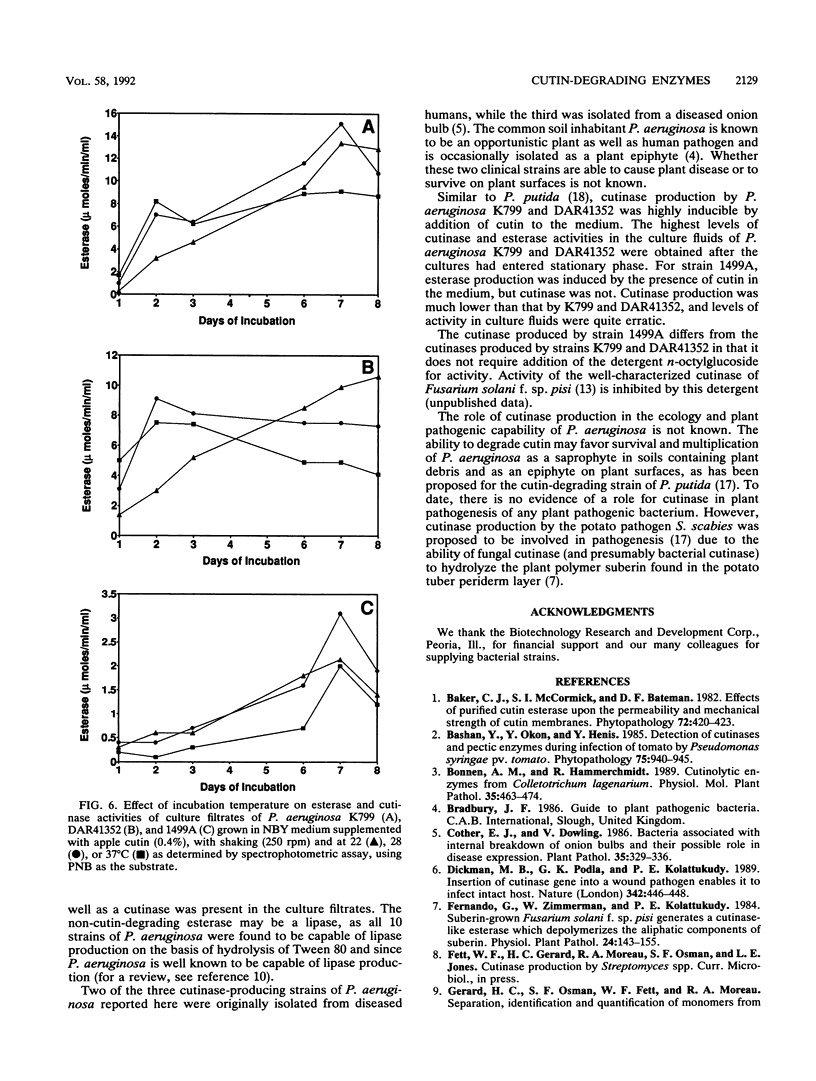
Two hundred thirty-two nonfilamentous bacterial strains, including saprophytes, plant pathogens, and opportunistic plant and human pathogens, were screened for the ability to produce cutinases (cutin-degrading esterases). Initially, esterase activity of culture filtrates of strains grown in nutrient broth-yeast extract medium supplemented with 0.4% apple or tomato cutin was determined by a spectrophotometric assay utilizing the model substrate p-nitrophenyl butyrate. The culture filtrates of the 10 Pseudomonas aeruginosa strains tested exhibited the highest esterase activity, with values of >500 nmol/min/ml. Of these 10 strains, 3 (K799, 1499A, and DAR41352) demonstrated significant induction (10-fold or above) of esterase activity by addition of cutin to nutrient broth-yeast extract medium. The ability of culture filtrates of the three strains to cause release of apple cutin monomers was confirmed by a novel high-performance liquid chromatography technique. Monomer identification was confirmed by gas chromatography-mass spectroscopy analyses. Addition of the nonionic detergent n-octylglucoside stimulated cutinase activity of culture filtrates from strains K799 and DAR41352, but not that of filtrates from strain 1499A. Time course studies in nutrient broth-yeast extract medium supplemented with apple cutin indicated maximal levels of cutinase in the culture fluids after cultures entered stationary phase. Incubation temperatures below the optimal temperature for growth (37°C) led to maximal production of cutinase.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Hull H. M. Leaf structure as related to absorption of pesticides and other compounds. Residue Rev. 1970;31:1–150. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purdy R. E., Kolattukudy P. E. Depolymerization of a hydroxy fatty acid biopolymer, cutin, by an extracellular enzyme from Fusarium solani f. pisi: isolation and some properties of the enzyme. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1973 Nov;159(1):61–69. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(73)90429-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SIERRA G. A simple method for the detection of lipolytic activity of micro-organisms and some observations on the influence of the contact between cells and fatty substrates. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1957;23(1):15–22. doi: 10.1007/BF02545855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebastian J., Chandra A. K., Kolattukudy P. E. Discovery of a cutinase-producing Pseudomonas sp. cohabiting with an apparently nitrogen-fixing Corynebacterium sp. in the phyllosphere. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):131–136. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.131-136.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sebastian J., Kolattukudy P. E. Purification and characterization of cutinase from a fluorescent Pseudomonas putida bacterial strain isolated from phyllosphere. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1988 May 15;263(1):77–85. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(88)90615-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walton T. J., Kolattukudy P. E. Determination of the structures of cutin monomers by a novel depolymerization procedure and combined gas chromatography and mass spectrometry. Biochemistry. 1972 May 9;11(10):1885–1896. doi: 10.1021/bi00760a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


