Abstract
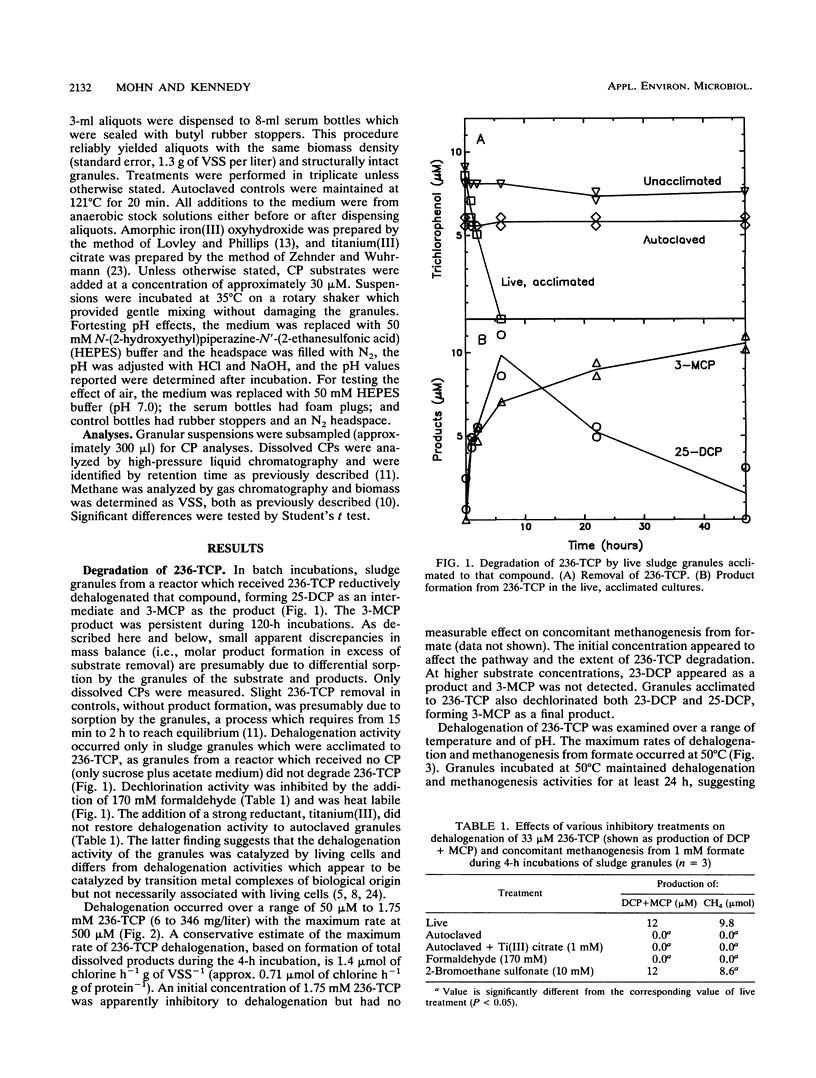
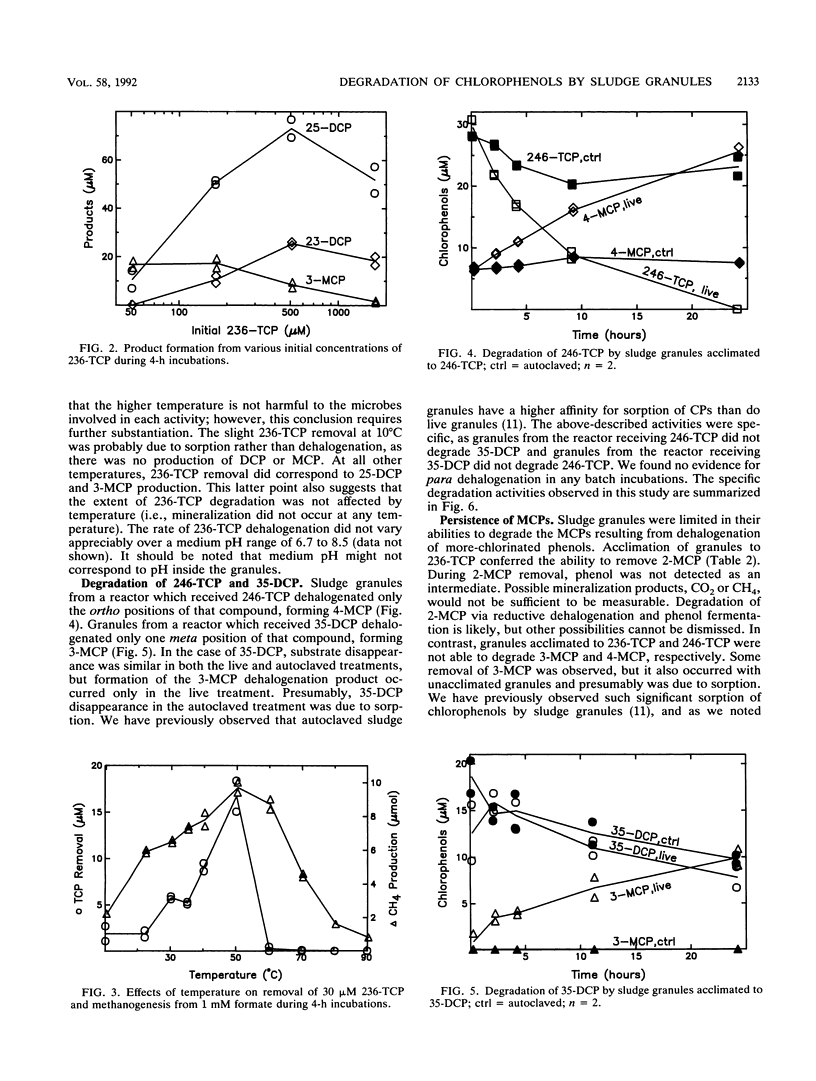
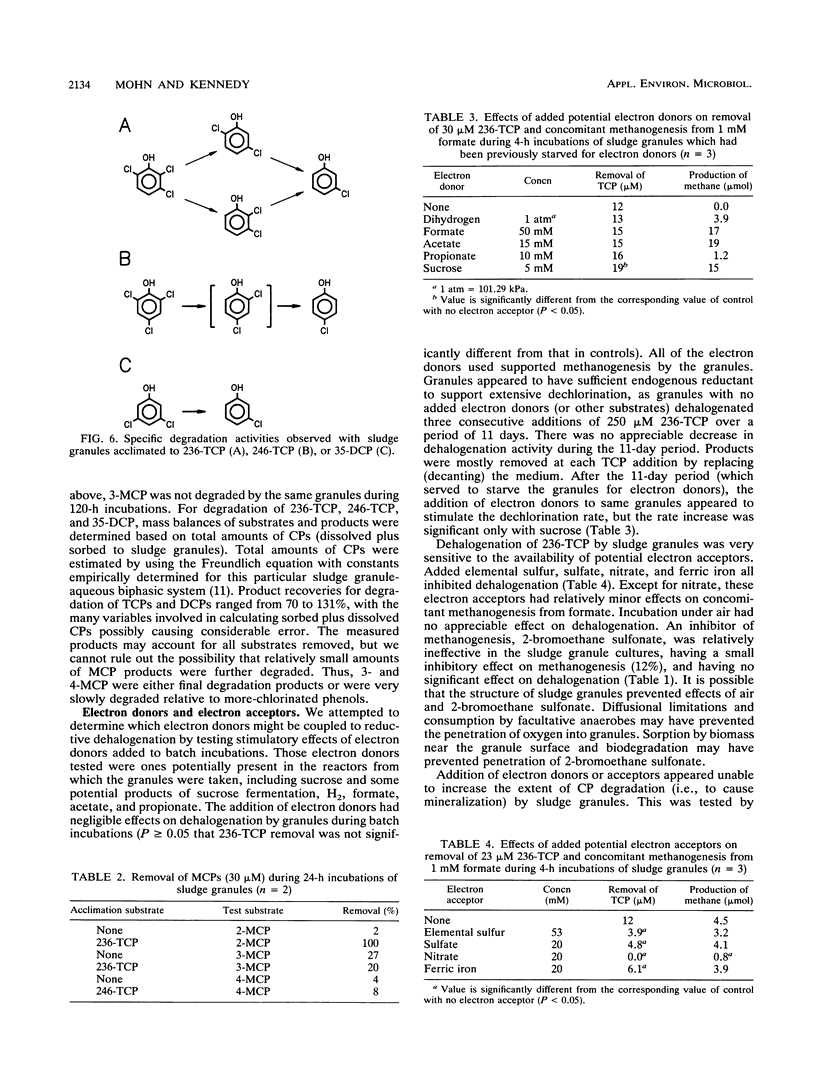
To better understand the fate of chlorophenols treated in upflow anaerobic sludge bed reactors, we examined the ability of sludge granules from such bioreactors to degrade two trichlorophenols and one dichlorophenol in batch incubations under controlled conditions. Biodegradation was primarily limited to two distinct activities, reductive dehalogenation of ortho- and of meta-chlorine substituents. Both 3- and 4-monochlorophenol were persistent degradation products, while 2-monochlorophenol was further degraded. We also examined factors potentially affecting the rate and extent of 2,3,6-trichlorophenol degradation. An initial concentration of up to 1.75 mM (346 mg/liter) was dehalogenated. At that concentration, dehalogenation was partially inhibited but methanogenesis from formate was not. The initial concentration affected both the extent of dehalogenation and which products were detected. The maximum dechlorination rate observed was 1.4 mumol of Cl- h-1 g of volatile suspended solids-1. Dechlorination had a temperature optimum of 50 degrees C, was inhibited by added electron acceptors, and was not appreciably affected by added electron donors. The availability of electron acceptors and electron donors did not affect the extent of chlorophenol degradation. These particular sludge granules do not appear to be capable of mineralizing phenols with meta- or para-chlorine substituents.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Boyd S. A., Shelton D. R. Anaerobic biodegradation of chlorophenols in fresh and acclimated sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Feb;47(2):272–277. doi: 10.1128/aem.47.2.272-277.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolfing J. Reductive dechlorination of 3-chlorobenzoate is coupled to ATP production and growth in an anaerobic bacterium, strain DCB-1. Arch Microbiol. 1990;153(3):264–266. doi: 10.1007/BF00249079. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dolfing J., Tiedje J. M. Growth yield increase linked to reductive dechlorination in a defined 3-chlorobenzoate degrading methanogenic coculture. Arch Microbiol. 1987;149(2):102–105. doi: 10.1007/BF00425073. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fathepure B. Z., Vogel T. M. Complete degradation of polychlorinated hydrocarbons by a two-stage biofilm reactor. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Dec;57(12):3418–3422. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.12.3418-3422.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genthner B. R., Price W. A., Pritchard P. H. Characterization of anaerobic dechlorinating consortia derived from aquatic sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jun;55(6):1472–1476. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.6.1472-1476.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendriksen H. V., Larsen S., Ahring B. K. Influence of a supplemental carbon source on anaerobic dechlorination of pentachlorophenol in granular sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Jan;58(1):365–370. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.1.365-370.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovley D. R., Phillips E. J. Competitive mechanisms for inhibition of sulfate reduction and methane production in the zone of ferric iron reduction in sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Nov;53(11):2636–2641. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.11.2636-2641.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mikesell M. D., Boyd S. A. Complete reductive dechlorination and mineralization of pentachlorophenol by anaerobic microorganisms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Oct;52(4):861–865. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.4.861-865.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohn W. W., Kennedy K. J. Reductive dehalogenation of chlorophenols by Desulfomonile tiedjei DCB-1. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Apr;58(4):1367–1370. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.4.1367-1370.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohn W. W., Tiedje J. M. Strain DCB-1 conserves energy for growth from reductive dechlorination coupled to formate oxidation. Arch Microbiol. 1990;153(3):267–271. doi: 10.1007/BF00249080. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zehnder A. J., Wuhrmann K. Titanium (III) citrate as a nontoxic oxidation-reduction buffering system for the culture of obligate anaerobes. Science. 1976 Dec 10;194(4270):1165–1166. doi: 10.1126/science.793008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zoro J. A., Hunter J. M., Eglinton G., Ware G. C. Degradation of p,p'-DDT in reducing environments. Nature. 1974 Jan 25;247(5438):235–237. doi: 10.1038/247235a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



