Abstract
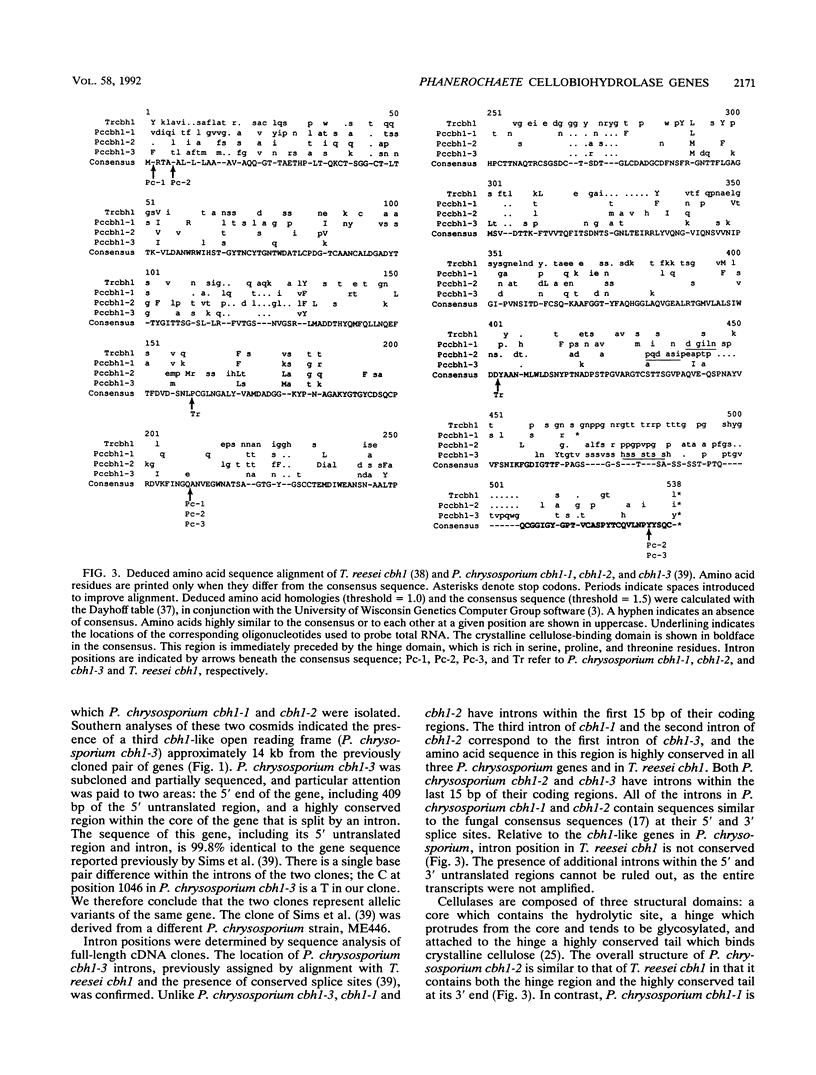
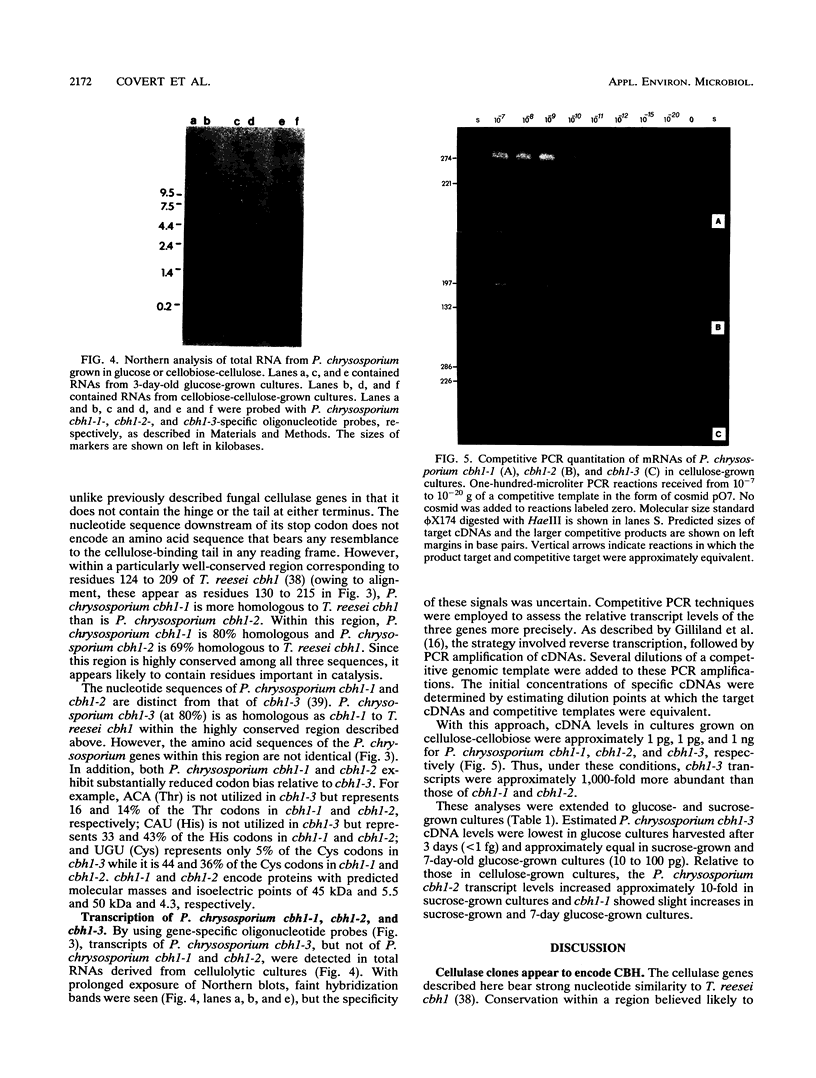
Restriction mapping and sequence analysis of cosmid clones revealed a cluster of three cellobiohydrolase genes in Phanerochaete chrysosporium. P. chrysosporium cbh1-1 and cbh1-2 are separated by only 750 bp and are located approximately 14 kb upstream from a cellulase gene previously cloned from P. chrysosporium (P. Sims, C. James, and P. Broda, Gene 74:411-422, 1988). Within a well-conserved region, the deduced amino acid sequences of P. chrysosporium cbh1-1 and cbh1-2 are, respectively, 80 and 69% homologous to that of the Trichoderma reesei cellobiohydrolase I gene. The conserved cellulose-binding domain typical of microbial cellulases is absent from cbh1-1. Transcript levels of the three P. chrysosporium genes varied substantially, depending on culture conditions. cbh1-1 and cbh1-2 were not induced in the presence of cellulose, nor did they appear to be subject to glucose repression. Therefore, aspects of the chromosomal organization, structure, and transcription of these genes are unlike those of any previously described cellulase genes.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azevedo M. de O., Felipe M. S., Astolfi-Filho S., Radford A. Cloning, sequencing and homologies of the cbh-1 (exoglucanase) gene of Humicola grisea var. thermoidea. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Dec;136(12):2569–2576. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-12-2569. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deshpande V., Eriksson K. E., Pettersson B. Production , purification and partial characterization of 1,4-beta-glucosidase enzymes from Sporotrichum pulverulentum. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Sep 15;90(1):191–198. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12590.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dosoretz C. G., Chen H. C., Grethlein H. E. Effect of Environmental Conditions on Extracellular Protease Activity in Lignolytic Cultures of Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Feb;56(2):395–400. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.2.395-400.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Díez B., Gutiérrez S., Barredo J. L., van Solingen P., van der Voort L. H., Martín J. F. The cluster of penicillin biosynthetic genes. Identification and characterization of the pcbAB gene encoding the alpha-aminoadipyl-cysteinyl-valine synthetase and linkage to the pcbC and penDE genes. J Biol Chem. 1990 Sep 25;265(27):16358–16365. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson K. E., Hamp S. G. Regulation of Endo-1,4-beta-glucanase production in Sporotrichum pulverulentum. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Sep 15;90(1):183–190. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12589.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson K. E., Pettersson B. Extracellular enzyme system utilized by the fungus Sporotrichum pulverulentum (Chrysosporium lignorum) for the breakdown of cellulose. 1. Separation, purification and physico-chemical characterization of five endo-1,4-beta-glucanases. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Feb 3;51(1):193–206. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb03919.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson K. E., Pettersson B. Extracellular enzyme system utilized by the fungus Sporotrichum pulverulentum (Chrysosporium lignorum) for the breakdown of cellulose. 3. Purification and physico-chemical characterization of an exo-1,4-beta-glucanase. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Feb 3;51(1):213–218. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb03921.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksson K. E., Pettersson B. Purification and partial characterization of two acidic proteases from the white-rot fungus Sporotrichum pulverulentum. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Jun;124(3):635–642. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb06641.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaskell J., Dieperink E., Cullen D. Genomic organization of lignin peroxidase genes of Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Feb 11;19(3):599–603. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.3.599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geever R. F., Huiet L., Baum J. A., Tyler B. M., Patel V. B., Rutledge B. J., Case M. E., Giles N. H. DNA sequence, organization and regulation of the qa gene cluster of Neurospora crassa. J Mol Biol. 1989 May 5;207(1):15–34. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90438-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilkes N. R., Henrissat B., Kilburn D. G., Miller R. C., Jr, Warren R. A. Domains in microbial beta-1, 4-glycanases: sequence conservation, function, and enzyme families. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Jun;55(2):303–315. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.2.303-315.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilkes N. R., Warren R. A., Miller R. C., Jr, Kilburn D. G. Precise excision of the cellulose binding domains from two Cellulomonas fimi cellulases by a homologous protease and the effect on catalysis. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10401–10407. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huoponen K., Ollikka P., Kälin M., Walther I., Mäntsälä P., Reiser J. Characterization of lignin peroxidase-encoding genes from lignin-degrading basidiomycetes. Gene. 1990 Apr 30;89(1):145–150. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90218-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnstone I. L., McCabe P. C., Greaves P., Gurr S. J., Cole G. E., Brow M. A., Unkles S. E., Clutterbuck A. J., Kinghorn J. R., Innis M. A. Isolation and characterisation of the crnA-niiA-niaD gene cluster for nitrate assimilation in Aspergillus nidulans. Gene. 1990 Jun 15;90(2):181–192. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(90)90178-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamb H. K., Hawkins A. R., Smith M., Harvey I. J., Brown J., Turner G., Roberts C. F. Spatial and biological characterisation of the complete quinic acid utilisation gene cluster in Aspergillus nidulans. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Aug;223(1):17–23. doi: 10.1007/BF00315792. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacCabe A. P., Riach M. B., Unkles S. E., Kinghorn J. R. The Aspergillus nidulans npeA locus consists of three contiguous genes required for penicillin biosynthesis. EMBO J. 1990 Jan;9(1):279–287. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb08106.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mead D. A., Pey N. K., Herrnstadt C., Marcil R. A., Smith L. M. A universal method for the direct cloning of PCR amplified nucleic acid. Biotechnology (N Y) 1991 Jul;9(7):657–663. doi: 10.1038/nbt0791-657. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mischak H., Hofer F., Messner R., Weissinger E., Hayn M., Tomme P., Esterbauer H., Küchler E., Claeyssens M., Kubicek C. P. Monoclonal antibodies against different domains of cellobiohydrolase I and II from Trichoderma reesei. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Jan 27;990(1):1–7. doi: 10.1016/s0304-4165(89)80003-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyada C. G., Wallace R. B. Oligonucleotide hybridization techniques. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:94–107. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54072-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ooi T., Shinmyo A., Okada H., Hara S., Ikenaka T., Murao S., Arai M. Cloning and sequence analysis of a cDNA for cellulase (FI-CMCase) from Aspergillus aculeatus. Curr Genet. 1990 Oct;18(3):217–222. doi: 10.1007/BF00318384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Penttilä M., Lehtovaara P., Nevalainen H., Bhikhabhai R., Knowles J. Homology between cellulase genes of Trichoderma reesei: complete nucleotide sequence of the endoglucanase I gene. Gene. 1986;45(3):253–263. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90023-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Raeder U., Thompson W., Broda P. RFLP-based genetic map of Phanerochaete chrysosporium ME446: lignin peroxidase genes occur in clusters. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Jul;3(7):911–918. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb00240.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouvinen J., Bergfors T., Teeri T., Knowles J. K., Jones T. A. Three-dimensional structure of cellobiohydrolase II from Trichoderma reesei. Science. 1990 Jul 27;249(4967):380–386. doi: 10.1126/science.2377893. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sims P., James C., Broda P. The identification, molecular cloning and characterisation of a gene from Phanerochaete chrysosporium that shows strong homology to the exo-cellobiohydrolase I gene from Trichoderma reesei. Gene. 1988 Dec 30;74(2):411–422. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90174-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. J., Burnham M. K., Edwards J., Earl A. J., Turner G. Cloning and heterologous expression of the penicillin biosynthetic gene cluster from penicillum chrysogenum. Biotechnology (N Y) 1990 Jan;8(1):39–41. doi: 10.1038/nbt0190-39. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streamer M., Eriksson K. E., Pettersson B. Extracellular enzyme system utilized by the fungus Sporotrichum pulverulentum (Chrysosporium lignorum) for the breakdown of cullulose. Functional characterization of five endo-1,4-beta-glucanases and one exo-1,4-beta-glucanase. Eur J Biochem. 1975 Nov 15;59(2):607–613. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1975.tb02489.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ståhlberg J., Johansson G., Pettersson G. A binding-site-deficient, catalytically active, core protein of endoglucanase III from the culture filtrate of Trichoderma reesei. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Apr 5;173(1):179–183. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13982.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Timberlake W. E., Barnard E. C. Organization of a gene cluster expressed specifically in the asexual spores of A. nidulans. Cell. 1981 Oct;26(1 Pt 1):29–37. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90030-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomme P., Van Tilbeurgh H., Pettersson G., Van Damme J., Vandekerckhove J., Knowles J., Teeri T., Claeyssens M. Studies of the cellulolytic system of Trichoderma reesei QM 9414. Analysis of domain function in two cellobiohydrolases by limited proteolysis. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jan 4;170(3):575–581. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13736.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uzcategui E., Ruiz A., Montesino R., Johansson G., Pettersson G. The 1,4-beta-D-glucan cellobiohydrolases from Phanerochaete chrysosporium. I. A system of synergistically acting enzymes homologous to Trichoderma reesei. J Biotechnol. 1991 Jul;19(2-3):271–285. doi: 10.1016/0168-1656(91)90064-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yelton M. M., Timberlake W. E., Hondel C. A. A cosmid for selecting genes by complementation in Aspergillus nidulans: Selection of the developmentally regulated yA locus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):834–838. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.834. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el-Gogary S., Leite A., Crivellaro O., Eveleigh D. E., el-Dorry H. Mechanism by which cellulose triggers cellobiohydrolase I gene expression in Trichoderma reesei. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Aug;86(16):6138–6141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.16.6138. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





