Abstract
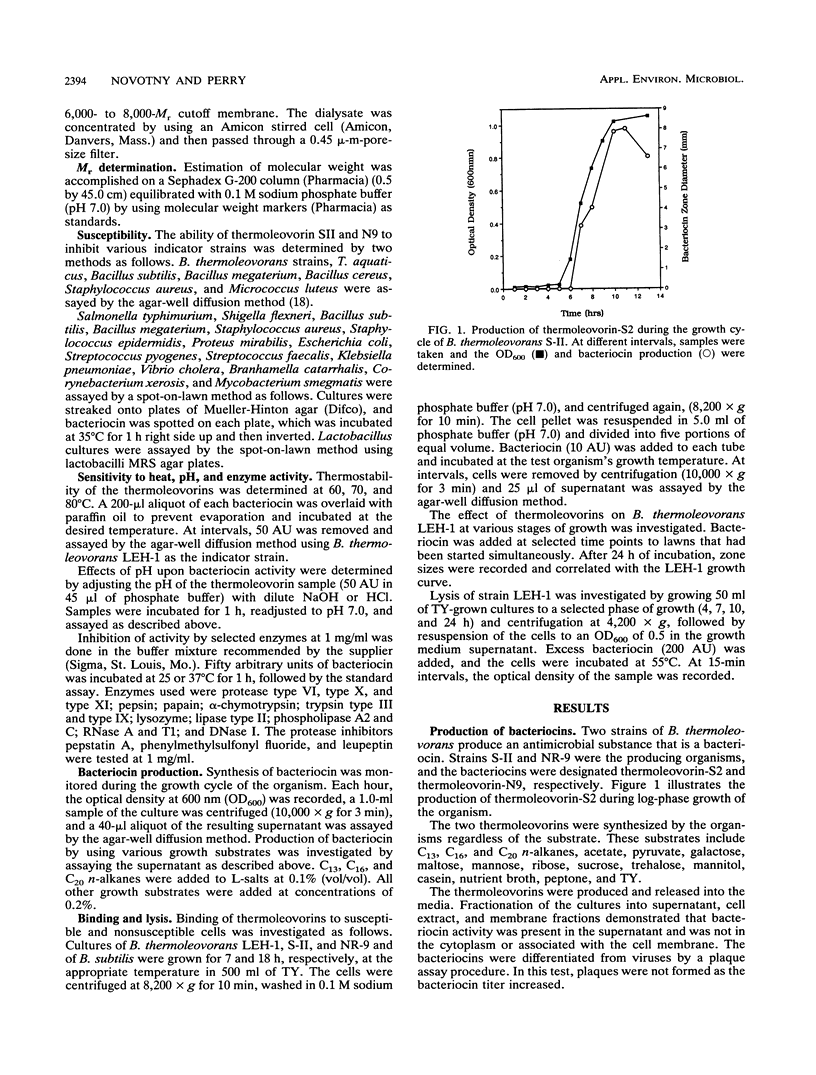
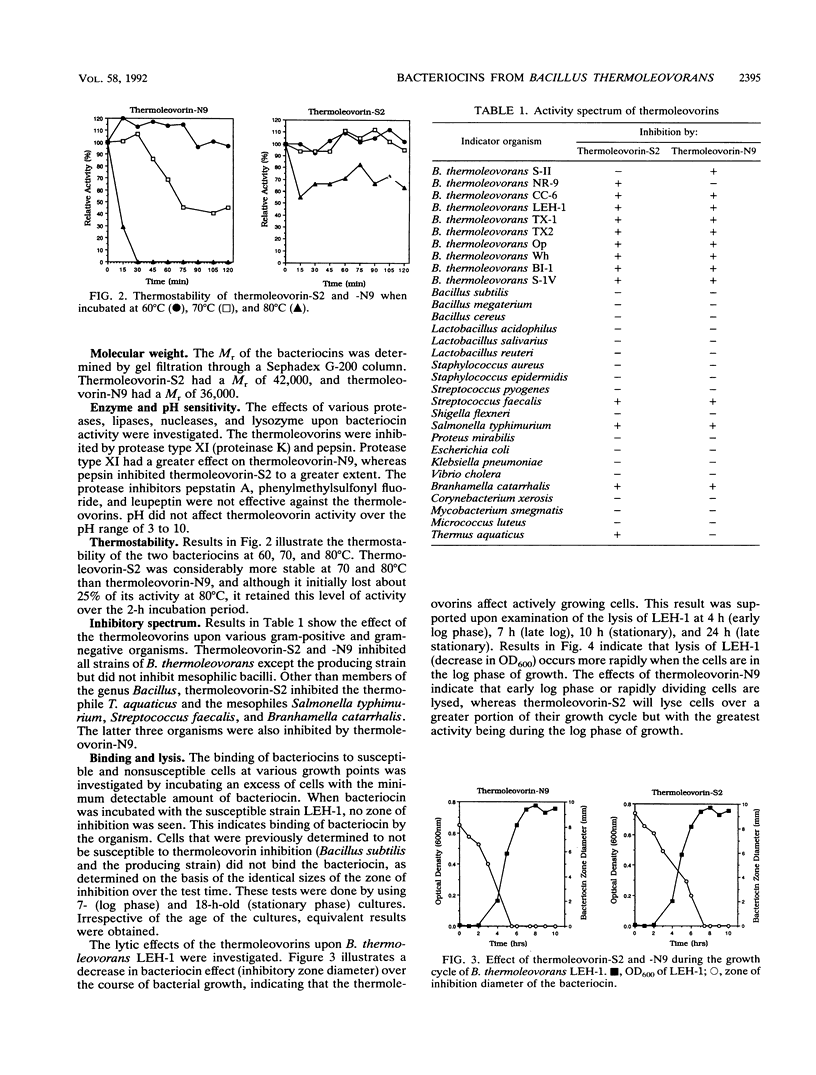
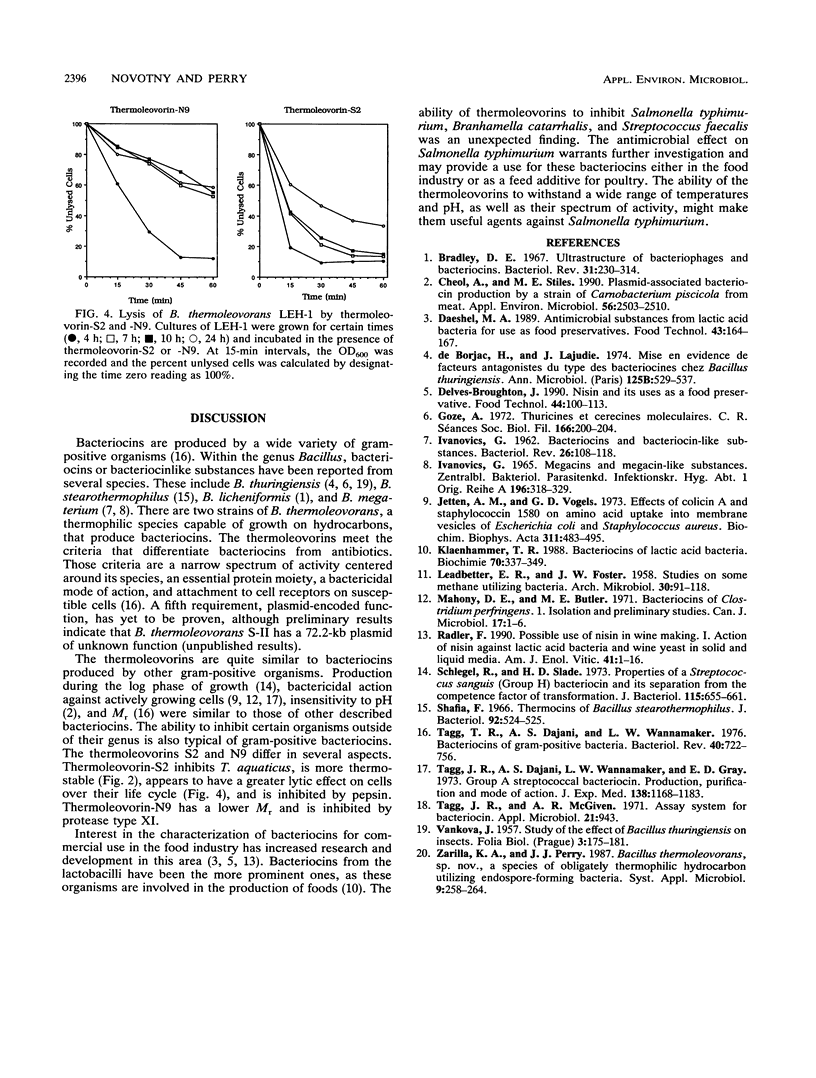
Bacillus thermoleovorans S-II and B. thermoleovorans NR-9 produce bacteriocins, and these bacteriocins are designated thermoleovorin-S2 and thermoleovorin-N9, respectively. The bacteriocins are effective against all but the producing strain of B. thermoleovorans, as well as being effective against Salmonella typhimurium, Branhamella catarrhalis, Streptococcus faecalis, and Thermus aquaticus. Thermoleovorins are produced during log-phase growth and are inhibitory to actively growing cells. The bacteriocins are proteinaceous in nature, being sensitive to selected proteases (protease type XI and pepsin). They are stable at pHs of 3 to 10. Thermoleovorin-S2 was more thermostable than thermoleovorin-N9 at 70 and 80 degrees C. Thermoleovorins-S2 and -N9 apparently act by binding to the susceptible organisms, resulting in lysis of the cell. Thermoleovorins-S2 has an estimated M(r) of 42,000, while thermoleovorin-N9 has a M(r) of 36,000.
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahn C., Stiles M. E. Plasmid-associated bacteriocin production by a strain of Carnobacterium piscicola from meat. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Aug;56(8):2503–2510. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.8.2503-2510.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradley D. E. Ultrastructure of bacteriophage and bacteriocins. Bacteriol Rev. 1967 Dec;31(4):230–314. doi: 10.1128/br.31.4.230-314.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goze A. Thuricines et céréines moléculaires. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1972;166(1):200–204. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ivanovics G. BACTERIOCINS AND BACTERIOCIN-LIKE SUBSTANCES. Bacteriol Rev. 1962 Jun;26(2 Pt 1):108–118. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jetten A. M., Vogels G. D. Effects of colicin A and staphylococcin 1580 on amino acid uptake into membrane vesicles of Escherichia coli and staphylococcus aureus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jul 18;311(4):483–495. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(73)90124-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klaenhammer T. R. Bacteriocins of lactic acid bacteria. Biochimie. 1988 Mar;70(3):337–349. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90206-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LEADBETTER E. R., FOSTER J. W. Studies on some methane-utilizing bacteria. Arch Mikrobiol. 1958;30(1):91–118. doi: 10.1007/BF00509229. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mahony D. E., Butler M. E. Bacteriocins of Clostridium perfringens. 1. Isolation and preliminary studies. Can J Microbiol. 1971 Jan;17(1):1–6. doi: 10.1139/m71-001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schlegel R., Slade H. D. Properties of a Streptococcus sanguis (group H) bacteriocin and its separation from the competence factor of transformation. J Bacteriol. 1973 Aug;115(2):655–661. doi: 10.1128/jb.115.2.655-661.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shafia F. Thermocins of Bacillus stearothermophilus. J Bacteriol. 1966 Aug;92(2):524–525. doi: 10.1128/jb.92.2.524-525.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagg J. R., Dajani A. S., Wannamaker L. W. Bacteriocins of gram-positive bacteria. Bacteriol Rev. 1976 Sep;40(3):722–756. doi: 10.1128/br.40.3.722-756.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagg J. R., Dajani A. S., Wannamaker L. W., Gray E. D. Group A streptococcal bacteriocin. Production, purification, and mode of action. J Exp Med. 1973 Nov 1;138(5):1168–1183. doi: 10.1084/jem.138.5.1168. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tagg J. R., McGiven A. R. Assay system for bacteriocins. Appl Microbiol. 1971 May;21(5):943–943. doi: 10.1128/am.21.5.943-943.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Barjac H., Lajudie J. Mise en évidence de facteurs antagonistes du type des bactériocines chez Bacillus thuringiensis. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1974 Dec;125(4):529–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


