Abstract
Phytopathogenic strains of Pseudomonas syringae are exposed to plant-produced, detrimental levels of hydrogen peroxide during invasion and colonization of host plant tissue. When P. syringae strains were investigated for their capacity to resist H2O2, they were found to contain 10- to 100-fold-higher levels of total catalase activity than selected strains belonging to nonpathogenic related taxa (Pseudomonas fluorescens and Pseudomonas putida) or Escherichia coli. Multiple catalase activities were identified in both periplasmic and cytoplasmic fluids of exponential- and stationary-phase P. syringae cells. Two of these activities were unique to the periplasm of P. syringae pv. glycinea. During the stationary growth phase, the specific activity of cytoplasmic catalases increased four- to eightfold. The specific activities of catalases in both fluids from exponential-phase cells increased in response to treatment with 0.25 to 10 mM H2O2 but decreased when higher H2O2 concentrations were used. In stationary-growth phase cultures, the specific activities of cytoplasmic catalases increased remarkably after treatment with 0.25 to 50 mM H2O2. The growth of P. syringae into stationary phase and H2O2 treatment did not induce synthesis of additional catalase isozymes. Only the stationary-phase cultures of all of the P. syringae strains which we tested were capable of surviving high H2O2 stress at concentrations up to 50 mM. Our results are consistent with the involvement of multiple catalase isozymes in the reduction of oxidative stress during plant pathogenesis by these bacteria.
Full text
PDF


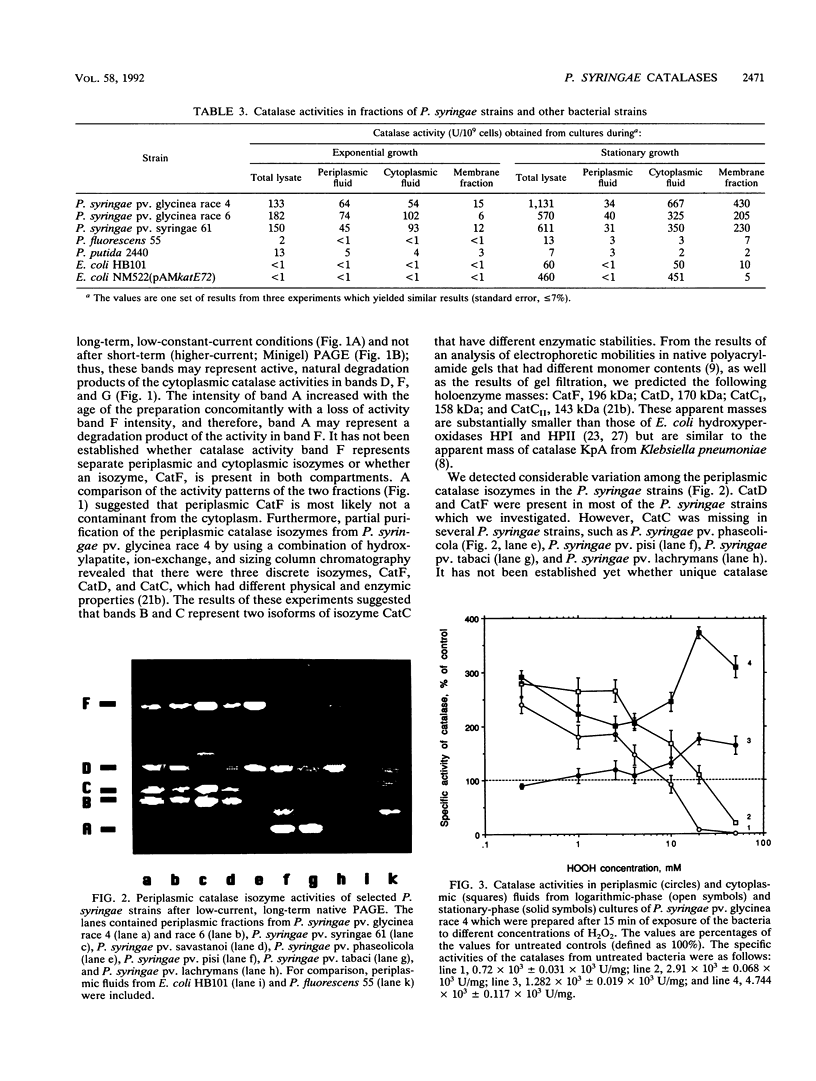
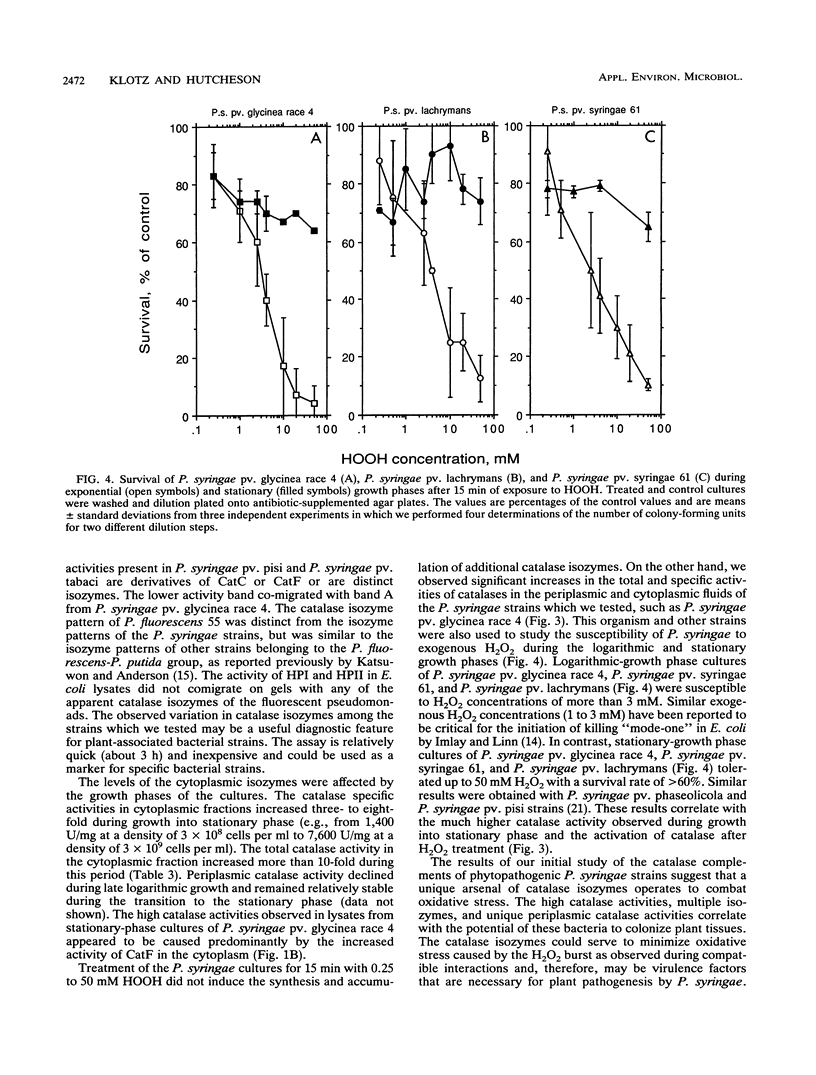

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames G. F., Prody C., Kustu S. Simple, rapid, and quantitative release of periplasmic proteins by chloroform. J Bacteriol. 1984 Dec;160(3):1181–1183. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.3.1181-1183.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Christman M. F., Morgan R. W., Jacobson F. S., Ames B. N. Positive control of a regulon for defenses against oxidative stress and some heat-shock proteins in Salmonella typhimurium. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):753–762. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80056-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Claiborne A., Fridovich I. Purification of the o-dianisidine peroxidase from Escherichia coli B. Physicochemical characterization and analysis of its dual catalatic and peroxidatic activities. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):4245–4252. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Comai L., Kosuge T. Involvement of plasmid deoxyribonucleic acid in indoleacetic acid synthesis in Pseudomonas savastanoi. J Bacteriol. 1980 Aug;143(2):950–957. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.2.950-957.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg I., Hochman A. Purification and characterization of a novel type of catalase from the bacterium Klebsiella pneumoniae. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 May 31;991(2):330–336. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(89)90124-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassan H. M., Fridovich I. Regulation of the synthesis of catalase and peroxidase in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1978 Sep 25;253(18):6445–6420. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hassett D. J., Charniga L., Bean K., Ohman D. E., Cohen M. S. Response of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to pyocyanin: mechanisms of resistance, antioxidant defenses, and demonstration of a manganese-cofactored superoxide dismutase. Infect Immun. 1992 Feb;60(2):328–336. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.2.328-336.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hedrick J. L., Smith A. J. Size and charge isomer separation and estimation of molecular weights of proteins by disc gel electrophoresis. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1968 Jul;126(1):155–164. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(68)90569-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heimberger A., Eisenstark A. Compartmentalization of catalases in Escherichia coli. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Jul 15;154(1):392–397. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90698-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang H. C., Schuurink R., Denny T. P., Atkinson M. M., Baker C. J., Yucel I., Hutcheson S. W., Collmer A. Molecular cloning of a Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae gene cluster that enables Pseudomonas fluorescens to elicit the hypersensitive response in tobacco plants. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4748–4756. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4748-4756.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imlay J. A., Linn S. DNA damage and oxygen radical toxicity. Science. 1988 Jun 3;240(4857):1302–1309. doi: 10.1126/science.3287616. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KING E. O., WARD M. K., RANEY D. E. Two simple media for the demonstration of pyocyanin and fluorescin. J Lab Clin Med. 1954 Aug;44(2):301–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsuwon J., Anderson A. J. Catalase and superoxide dismutase of root-colonizing saprophytic fluorescent pseudomonads. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Nov;56(11):3576–3582. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.11.3576-3582.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewen P. C. Isolation of catalase-deficient Escherichia coli mutants and genetic mapping of katE, a locus that affects catalase activity. J Bacteriol. 1984 Feb;157(2):622–626. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.2.622-626.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewen P. C., Switala J. Multiple catalases in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3601–3607. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3601-3607.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewen P. C., Switala J. Purification and characterization of catalase HPII from Escherichia coli K12. Biochem Cell Biol. 1986 Jul;64(7):638–646. doi: 10.1139/o86-088. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewen P. C., Triggs B. L. Genetic mapping of katF, a locus that with katE affects the synthesis of a second catalase species in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1984 Nov;160(2):668–675. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.2.668-675.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loewen P. C., Triggs B. L., George C. S., Hrabarchuk B. E. Genetic mapping of katG, a locus that affects synthesis of the bifunctional catalase-peroxidase hydroperoxidase I in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):661–667. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.661-667.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulvey M. R., Switala J., Borys A., Loewen P. C. Regulation of transcription of katE and katF in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):6713–6720. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.6713-6720.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- RUDOLPH K., STAHMANN M. A. INTERACTIONS OF PEROXIDASES AND CATALASES BETWEEN PHASEOLUS VULGARIS AND PSEUDOMONAS PHASEOLICOLA (HALO BLIGHT OF BEAN). Nature. 1964 Oct 31;204:474–475. doi: 10.1038/204474a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rorth M., Jensen P. K. Determination of catalase activity by means of the Clark oxygen electrode. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1967 May 16;139(1):171–173. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(67)90124-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schellhorn H. E., Hassan H. M. Transcriptional regulation of katE in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4286–4292. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4286-4292.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Switala J., Triggs-Raine B. L., Loewen P. C. Homology among bacterial catalase genes. Can J Microbiol. 1990 Oct;36(10):728–731. doi: 10.1139/m90-123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodbury W., Spencer A. K., Stahman M. A. An improved procedure using ferricyanide for detecting catalase isozymes. Anal Biochem. 1971 Nov;44(1):301–305. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(71)90375-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



