Abstract
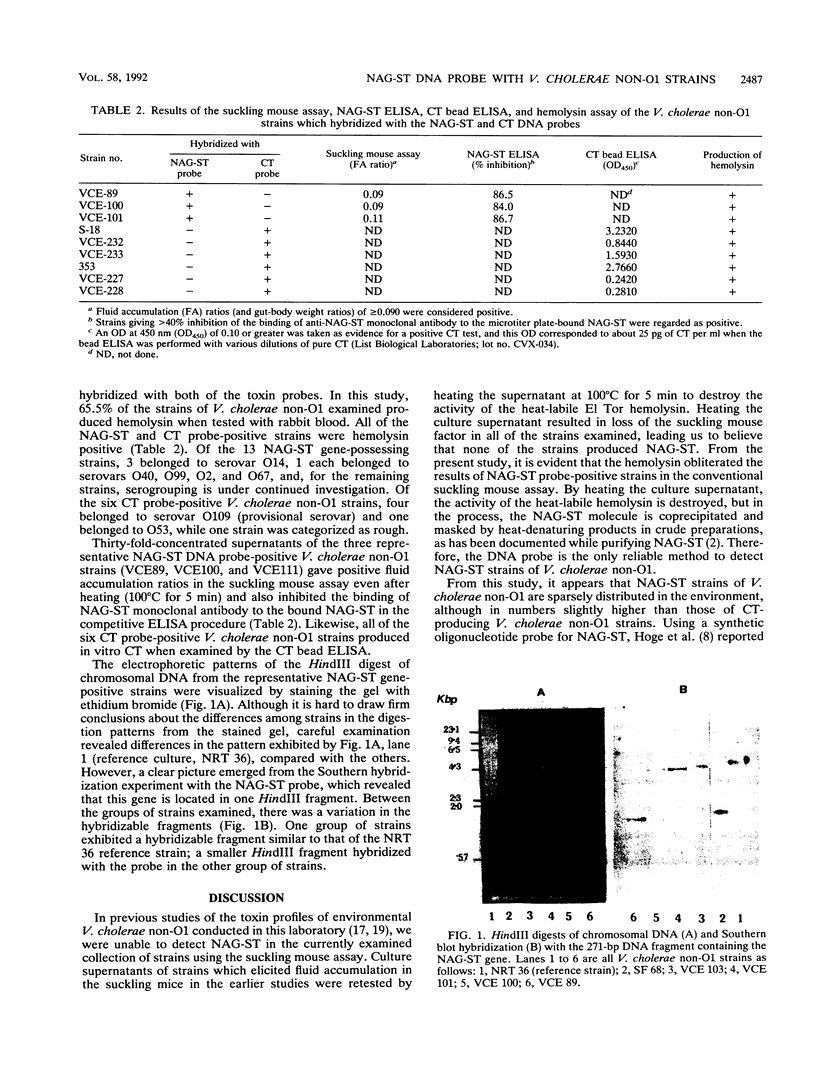
A collection of 521 environmental isolates of Vibrio cholerae which were previously examined by the suckling mouse assay and found to be negative for the heat-stable enterotoxin NAG-ST were reassessed by a recently developed DNA probe for NAG-ST. A total of 12 (2.3%) of the isolates hybridized with the NAG-ST probe. By using a cholera toxin (CT) DNA probe, the CT gene was detected in six of the strains in the collection, although none of the isolates of V. cholerae non-O1 hybridized with both of the toxin probes. All of the NAG-ST and CT probe-positive strains were hemolysin positive. Thirty-fold-concentrated supernatants of the three representative NAG-ST DNA probe-positive V. cholerae non-O1 strains gave positive fluid accumulation ratios in the suckling mouse assay even after heating (100 degrees C for 5 min) and also inhibited the binding of a NAG-ST monoclonal antibody to the bound NAG-ST in a competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA). Likewise, all six CT probe-positive V. cholerae non-O1 strains produced in vitro CT when examined by the CT bead ELISA. HindIII digest patterns of chromosomal DNA from the representative NAG-ST gene-positive strains were visually indistinguishable. Between the groups of NAG-ST probe-positive strains examined, there was a variation in the hybridizable fragments, with one group of strains exhibiting a hybridizable fragment similar to that of the NRT 36 reference strain; a smaller HindIII fragment hybridized with the NAG-ST probe in the other group of strains.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aldová E., Láznicková K., Stepánková E., Lietava J. Isolation of nonagglutinable vibrios from an enteritis outbreak in Czechoslovakia. J Infect Dis. 1968 Feb;118(1):25–31. doi: 10.1093/infdis/118.1.25. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arita M., Takeda T., Honda T., Miwatani T. Purification and characterization of Vibrio cholerae non-O1 heat-stable enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):45–49. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.45-49.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonner J. R., Coker A. S., Berryman C. R., Pollock H. M. Spectrum of Vibrio infections in a Gulf Coast community. Ann Intern Med. 1983 Oct;99(4):464–469. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-99-4-464. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenner D. J., Fanning G. R., Johnson K. E., Citarella R. V., Falkow S. Polynucleotide sequence relationships among members of Enterobacteriaceae. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):637–650. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.637-650.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig J. P., Yamamoto K., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Production of cholera-like enterotoxin by a Vibrio cholerae non-O1 strain isolated from the environment. Infect Immun. 1981 Oct;34(1):90–97. doi: 10.1128/iai.34.1.90-97.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Echeverria P., Seriwatana J., Taylor D. N., Yanggratoke S., Tirapat C. A comparative study of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli, Shigella, Aeromonas, and Vibrio as etiologies of diarrhea in northeastern Thailand. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1985 May;34(3):547–554. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1985.34.547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoge C. W., Sethabutr O., Bodhidatta L., Echeverria P., Robertson D. C., Morris J. G., Jr Use of a synthetic oligonucleotide probe to detect strains of non-serovar O1 Vibrio cholerae carrying the gene for heat-stable enterotoxin (NAG-ST). J Clin Microbiol. 1990 Jun;28(6):1473–1476. doi: 10.1128/jcm.28.6.1473-1476.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoge C. W., Watsky D., Peeler R. N., Libonati J. P., Israel E., Morris J. G., Jr Epidemiology and spectrum of Vibrio infections in a Chesapeake Bay community. J Infect Dis. 1989 Dec;160(6):985–993. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.6.985. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda T., Arita M., Takeda T., Yoh M., Miwatani T. Non-O1 Vibrio cholerae produces two newly identified toxins related to Vibrio parahaemolyticus haemolysin and Escherichia coli heat-stable enterotoxin. Lancet. 1985 Jul 20;2(8447):163–164. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)90277-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichinose Y., Yamamoto K., Nakasone N., Tanabe M. J., Takeda T., Miwatani T., Iwanaga M. Enterotoxicity of El Tor-like hemolysin of non-O1 Vibrio cholerae. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1090–1093. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1090-1093.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaper J., Lockman H., Colwell R. R., Joseph S. W. Ecology, serology, and enterotoxin production of Vibrio cholerae in Chesapeake Bay. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Jan;37(1):91–103. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.1.91-103.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MCINTYRE O. R., FEELEY J. C., GREENOUGH W. B., 3rd, BENENSON A. S., HASSAN S. I., SAAD A. DIARRHEA CAUSED BY NON-CHOLERA VIBRIOS. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1965 May;14:412–418. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1965.14.412. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. G., Jr, Takeda T., Tall B. D., Losonsky G. A., Bhattacharya S. K., Forrest B. D., Kay B. A., Nishibuchi M. Experimental non-O group 1 Vibrio cholerae gastroenteritis in humans. J Clin Invest. 1990 Mar;85(3):697–705. doi: 10.1172/JCI114494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nair G. B., Oku Y., Takeda Y., Ghosh A., Ghosh R. K., Chattopadhyay S., Pal S. C., Kaper J. B., Takeda T. Toxin profiles of Vibrio cholerae non-O1 from environmental sources in Calcutta, India. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Dec;54(12):3180–3182. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.12.3180-3182.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien A. D., Chen M. E., Holmes R. K., Kaper J., Levine M. M. Environmental and human isolates of Vibrio cholerae and Vibrio parahaemolyticus produce a Shigella dysenteriae 1 (Shiga)-like cytotoxin. Lancet. 1984 Jan 14;1(8368):77–78. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)90006-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogawa A., Kato J., Watanabe H., Nair B. G., Takeda T. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of a heat-stable enterotoxin gene from Vibrio cholerae non-O1 isolated from a patient with traveler's diarrhea. Infect Immun. 1990 Oct;58(10):3325–3329. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.10.3325-3329.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oku Y., Uesaka Y., Hirayama T., Takeda Y. Development of a highly sensitive bead-ELISA to detect bacterial protein toxins. Microbiol Immunol. 1988;32(8):807–816. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1988.tb01442.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Safrin S., Morris J. G., Jr, Adams M., Pons V., Jacobs R., Conte J. E., Jr Non-O:1 Vibrio cholerae bacteremia: case report and review. Rev Infect Dis. 1988 Sep-Oct;10(5):1012–1017. doi: 10.1093/clinids/10.5.1012. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakazaki R., Shimada T. Serovars of Vibrio cholerae identified during 1970-1975. Jpn J Med Sci Biol. 1977 Oct;30(5):279–282. doi: 10.7883/yoken1952.30.279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seriwatana J., Echeverria P., Taylor D. N., Sakuldaipeara T., Changchawalit S., Chivoratanond O. Identification of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli with synthetic alkaline phosphatase-conjugated oligonucleotide DNA probes. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Aug;25(8):1438–1441. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.8.1438-1441.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takao T., Hitouji T., Aimoto S., Shimonishi Y., Hara S., Takeda T., Takeda Y., Miwatani T. Amino acid sequence of a heat-stable enterotoxin isolated from enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli strain 18D. FEBS Lett. 1983 Feb 7;152(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80469-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda T., Nair G. B., Suzuki K., Shimonishi Y. Production of a monoclonal antibody to Vibrio cholerae non-O1 heat-stable enterotoxin (ST) which is cross-reactive with Yersinia enterocolitica ST. Infect Immun. 1990 Sep;58(9):2755–2759. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.9.2755-2759.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda T., Peina Y., Ogawa A., Dohi S., Abe H., Nair G. B., Pal S. C. Detection of heat-stable enterotoxin in a cholera toxin gene-positive strain of Vibrio cholerae O1. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 May 1;64(1):23–27. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90203-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y., Takeda T., Yano T., Yamamoto K., Miwatani T. Purification and partial characterization of heat-stable enterotoxin of enterotoxigenic Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1979 Sep;25(3):978–985. doi: 10.1128/iai.25.3.978-985.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uesaka Y., Otsuka Y., Kashida M., Oku Y., Horigome K., Nair G. B., Pal S. C., Yamasaki S., Takeda Y. Detection of cholera toxin by a highly sensitive bead-enzyme linked immunosorbent assay. Microbiol Immunol. 1992;36(1):43–53. doi: 10.1111/j.1348-0421.1992.tb01641.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto K., Takeda Y., Miwatani T., Craig J. P. Evidence that a non-O1 Vibrio cholerae produces enterotoxin that is similar but not identical to cholera enterotoxin. Infect Immun. 1983 Sep;41(3):896–901. doi: 10.1128/iai.41.3.896-901.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimura S., Takao T., Shimonishi Y., Hara S., Arita M., Takeda T., Imaishi H., Honda T., Miwatani T. A heat-stable enterotoxin of Vibrio cholerae non-01: chemical synthesis, and biological and physicochemical properties. Biopolymers. 1986;25 (Suppl):S69–S83. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- el Shawi N., Thewaini A. J. Non-agglutinable vibrios isolated in the 1966 epidemic of cholera in Irag. Bull World Health Organ. 1969;40(1):163–166. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]