Abstract
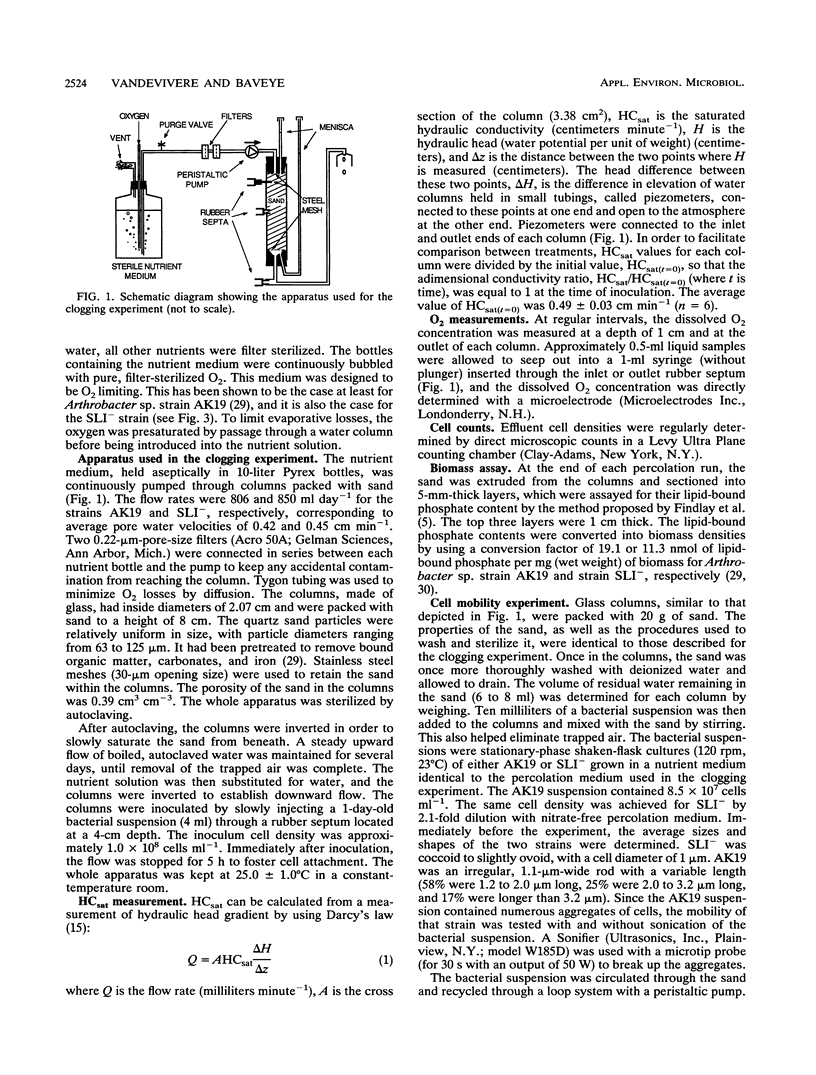
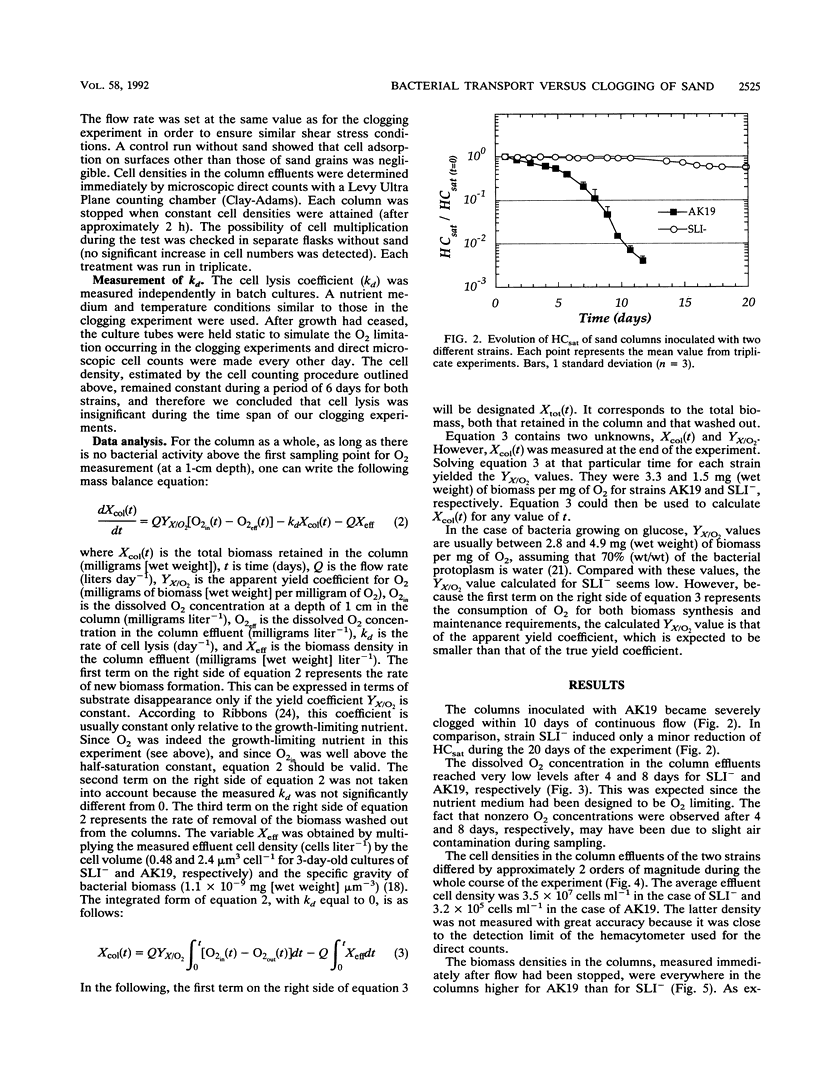
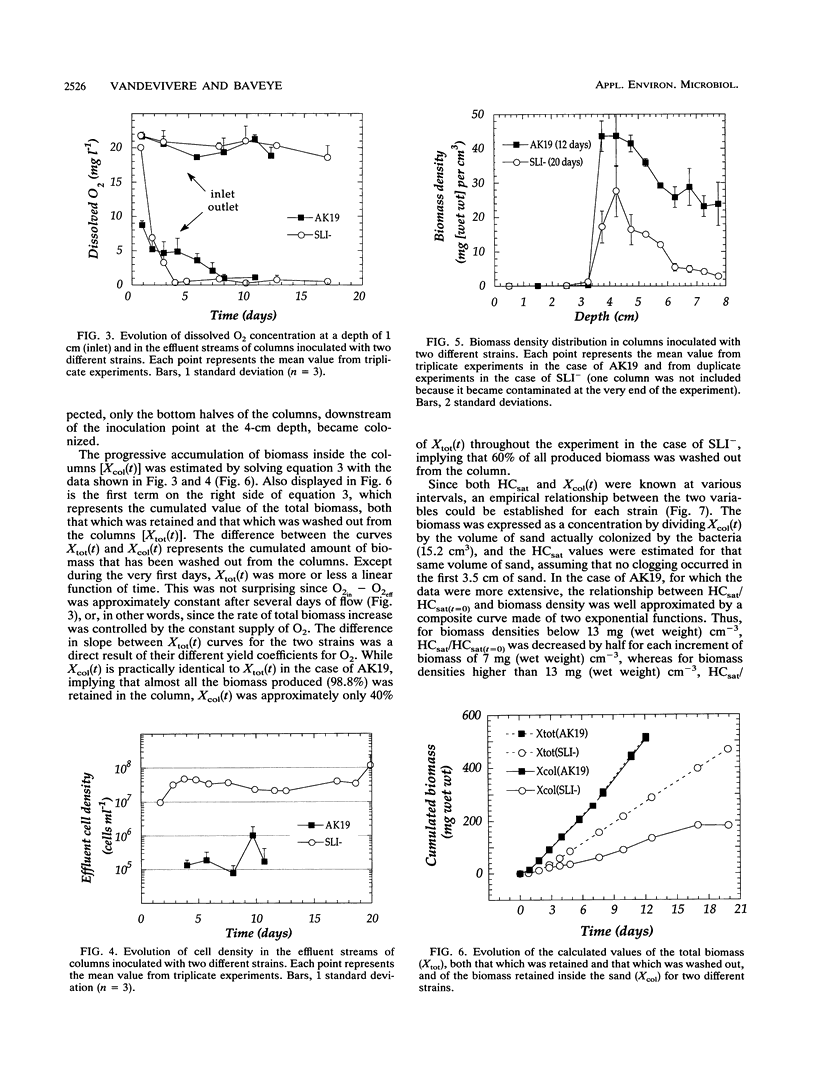
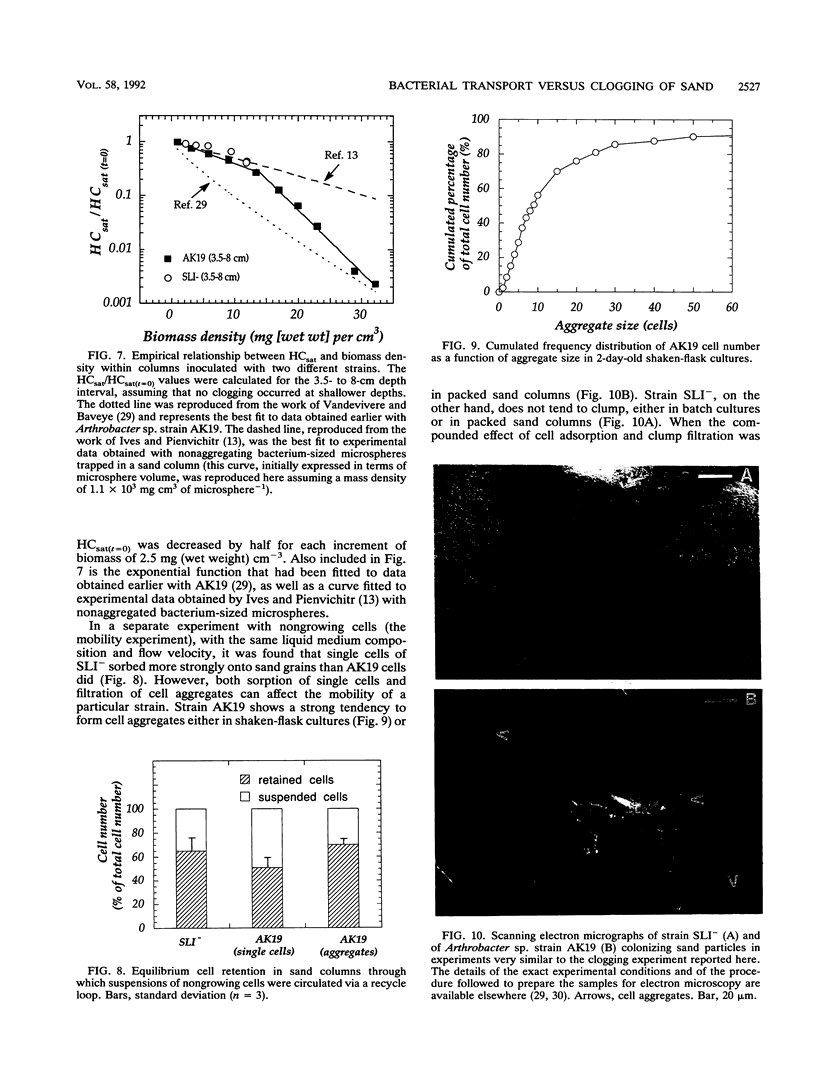
In an earlier article, we reported that, under conditions in which neither exopolymers nor bacterial mats were produced, Arthrobacter sp. strain AK19 was an effective plugging agent in sand columns, whereas the bacterial strain SLI- had no significant effect on the permeability of the medium. A laboratory experiment with sand columns was carried out to elucidate the causes of this difference in behavior. Measured values of the saturated hydraulic conductivity of the sand were explained in terms of biomass accumulation, which was estimated by solving a mass balance equation. The relationship between the saturated hydraulic conductivity and the biomass density within the sand was exponential, although two different exponential coefficients were needed to fit the data for biomass densities above or below 13 mg (wet weight) per cm3, suggesting that two different clogging mechanisms may be involved in different ranges of biomass densities. The experimental results suggest that the SLI- strain was a poor clogging agent partly because of its lower yield coefficient relative to the limiting nutrient (oxygen) and partly because 60% of the biomass produced in situ was washed out from the column, compared with only 1.2% in the case of Arthrobacter sp. strain AK19.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Findlay R. H., King G. M., Watling L. Efficacy of phospholipid analysis in determining microbial biomass in sediments. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Nov;55(11):2888–2893. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.11.2888-2893.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontes D. E., Mills A. L., Hornberger G. M., Herman J. S. Physical and chemical factors influencing transport of microorganisms through porous media. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Sep;57(9):2473–2481. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.9.2473-2481.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon J. T., Manilal V. B., Alexander M. Relationship between Cell Surface Properties and Transport of Bacteria through Soil. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Jan;57(1):190–193. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.1.190-193.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gannon J., Tan Y. H., Baveye P., Alexander M. Effect of sodium chloride on transport of bacteria in a saturated aquifer material. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1991 Sep;57(9):2497–2501. doi: 10.1128/aem.57.9.2497-2501.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macleod F. A., Lappin-Scott H. M., Costerton J. W. Plugging of a model rock system by using starved bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jun;54(6):1365–1372. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.6.1365-1372.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLee A. G., Kormendy A. C., Wayman M. Isolation and characterization of n-butane-utilizing microorganisms. Can J Microbiol. 1972 Aug;18(8):1191–1195. doi: 10.1139/m72-186. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds P. J., Sharma P., Jenneman G. E., McInerney M. J. Mechanisms of microbial movement in subsurface materials. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Sep;55(9):2280–2286. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.9.2280-2286.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw J. C., Bramhill B., Wardlaw N. C., Costerton J. W. Bacterial fouling in a model core system. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Mar;49(3):693–701. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.3.693-701.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vandevivere P., Baveye P. Effect of bacterial extracellular polymers on the saturated hydraulic conductivity of sand columns. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 May;58(5):1690–1698. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.5.1690-1698.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



