Abstract
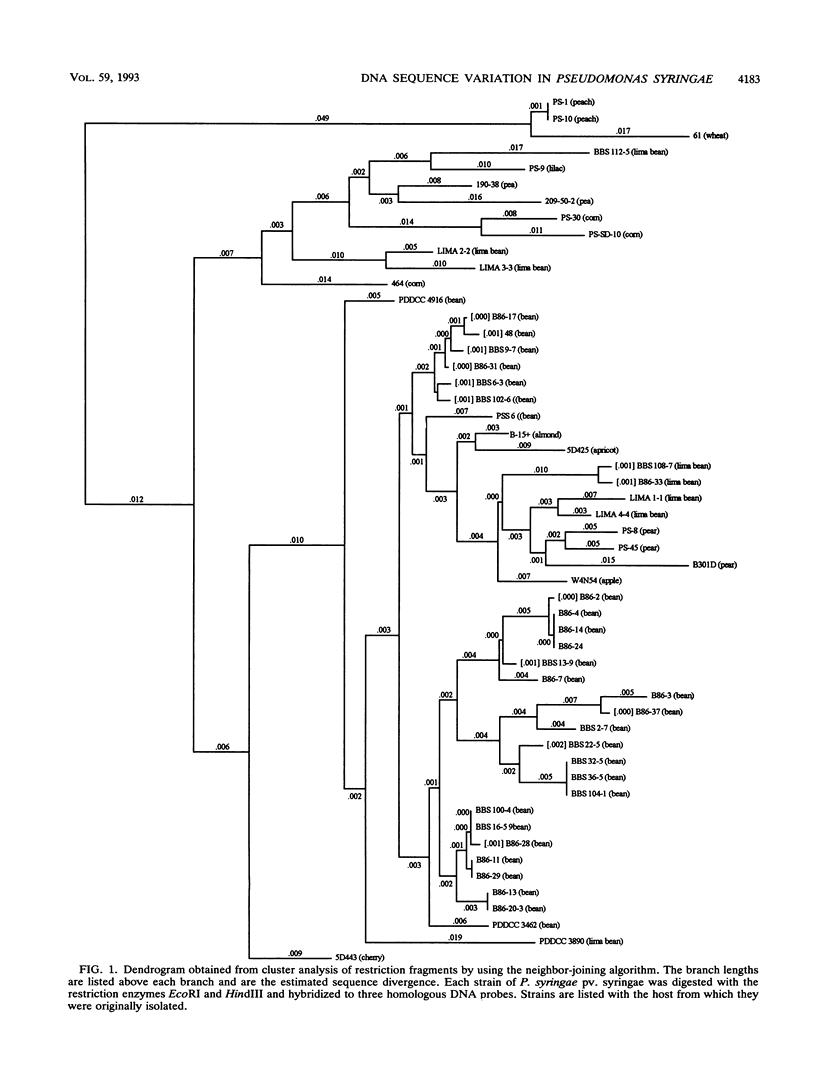
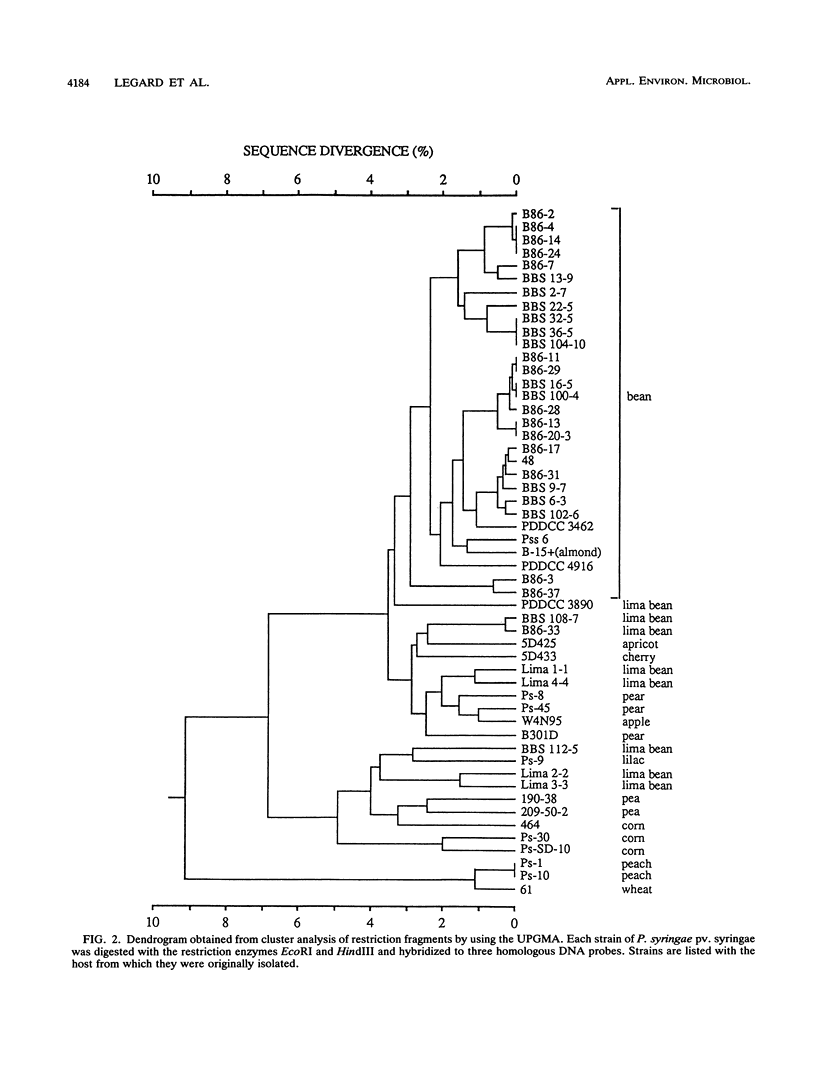
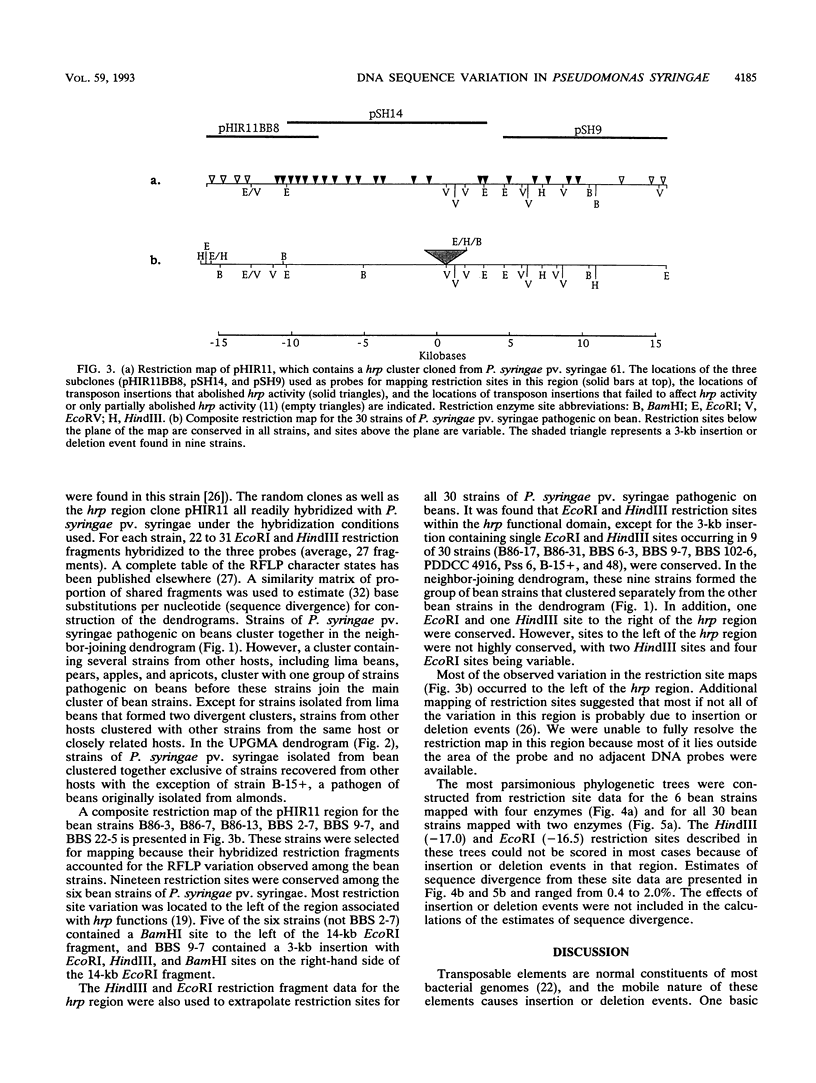
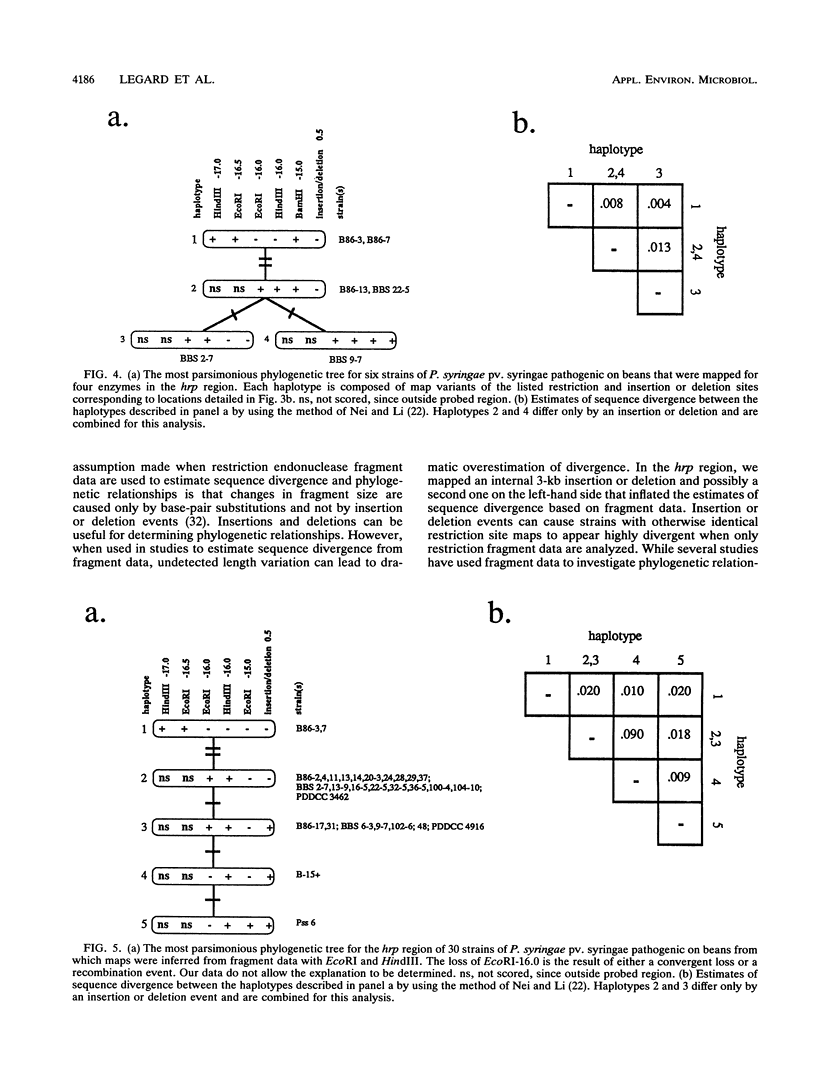
We evaluated the restriction fragment length polymorphism of genomic DNA among 53 strains of the phytopathogenic bacterium Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae. Twenty-nine strains were isolated from beans, and the rest were isolated from 11 other hosts. Southern blots of DNA digested with EcoRI or HindIII were hybridized to two random probes from a cosmid library of P. syringae pv. syringae and a hrp (hypersensitive reaction and pathogenicity) cluster cloned from P. syringae pv. syringae. The size of hybridizing fragments was determined, and a similarity matrix was constructed by comparing strains on a pairwise basis for the presence or absence of fragments. The proportion of shared fragments was then used to estimate sequence divergence. Dendrograms were produced by using the unweighted pair group method with averages and the neighbor-joining method. For the hrp region, BamHI, EcoRI, EcoRV, and HindIII restriction sites were mapped for six representative bean strains and used to construct EcoRI and HindIII restriction maps for all 30 strains pathogenic on beans. Restriction mapping revealed the presence of a 3-kb insertion in nine bean strains and a probable second insertion or deletion event on the left-hand side of the hrp cluster that biased estimates of nucleotide sequence divergence from fragment comparisons. This demonstrated that the determination of phylogenetic relationships among bacteria by using restriction fragment length polymorphism data requires mapping restriction sites to remove the effect of insertion or deletion events on the analysis.(ABSTRACT TRUNCATED AT 250 WORDS)
Full text
PDF




Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birnboim H. C. A rapid alkaline extraction method for the isolation of plasmid DNA. Methods Enzymol. 1983;100:243–255. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)00059-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Denny T. P., Gilmour M. N., Selander R. K. Genetic diversity and relationships of two pathovars of Pseudomonas syringae. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Jul;134(7):1949–1960. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-7-1949. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoitink H. A., Hagedorn D. J., McCoy E. Survival, transmission, and taxonomy of Pseudomonas syringae van Hall, the causal organism of bacterial brown spot of bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Can J Microbiol. 1968 Apr;14(4):437–441. doi: 10.1139/m68-069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang H. C., He S. Y., Bauer D. W., Collmer A. The Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae 61 hrpH product, an envelope protein required for elicitation of the hypersensitive response in plants. J Bacteriol. 1992 Nov;174(21):6878–6885. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.21.6878-6885.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huang H. C., Schuurink R., Denny T. P., Atkinson M. M., Baker C. J., Yucel I., Hutcheson S. W., Collmer A. Molecular cloning of a Pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae gene cluster that enables Pseudomonas fluorescens to elicit the hypersensitive response in tobacco plants. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4748–4756. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4748-4756.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KING E. O., WARD M. K., RANEY D. E. Two simple media for the demonstration of pyocyanin and fluorescin. J Lab Clin Med. 1954 Aug;44(2):301–307. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOVACS N. Identification of Pseudomonas pyocyanea by the oxidase reaction. Nature. 1956 Sep 29;178(4535):703–703. doi: 10.1038/178703a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N. Transposable elements in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Genet. 1981;15:341–404. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.15.120181.002013. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kliman R. M., Hey J. DNA sequence variation at the period locus within and among species of the Drosophila melanogaster complex. Genetics. 1993 Feb;133(2):375–387. doi: 10.1093/genetics/133.2.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindow S. E., Arny D. C., Upper C. D. Distribution of ice nucleation-active bacteria on plants in nature. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1978 Dec;36(6):831–838. doi: 10.1128/aem.36.6.831-838.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nei M., Li W. H. Mathematical model for studying genetic variation in terms of restriction endonucleases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):5269–5273. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.5269. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson K., Whittam T. S., Selander R. K. Nucleotide polymorphism and evolution in the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene (gapA) in natural populations of Salmonella and Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Aug 1;88(15):6667–6671. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.15.6667. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saitou N., Nei M. The neighbor-joining method: a new method for reconstructing phylogenetic trees. Mol Biol Evol. 1987 Jul;4(4):406–425. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.molbev.a040454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



