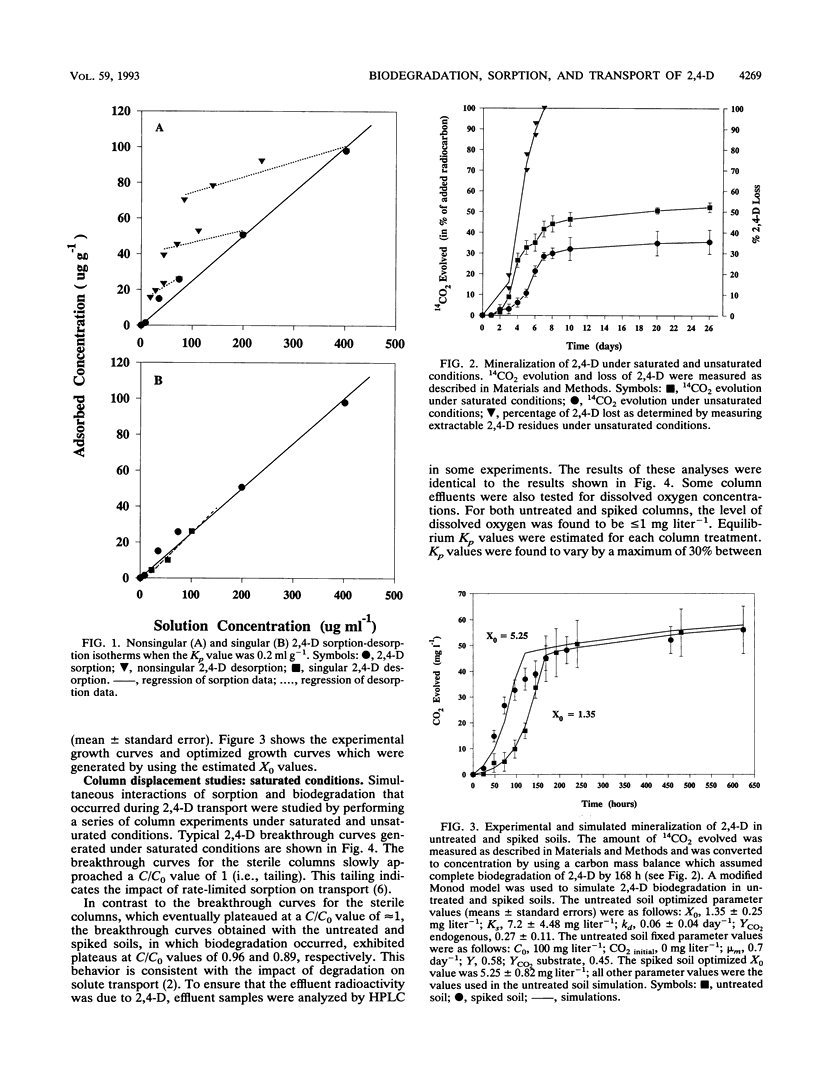
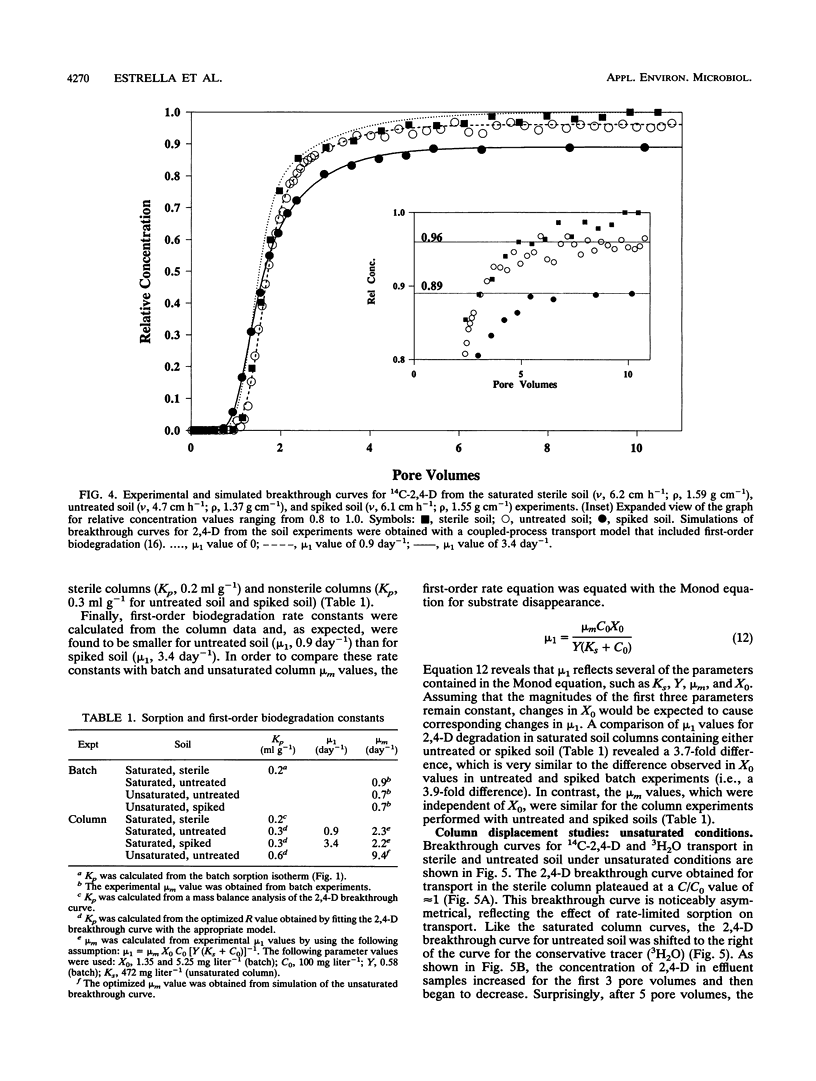
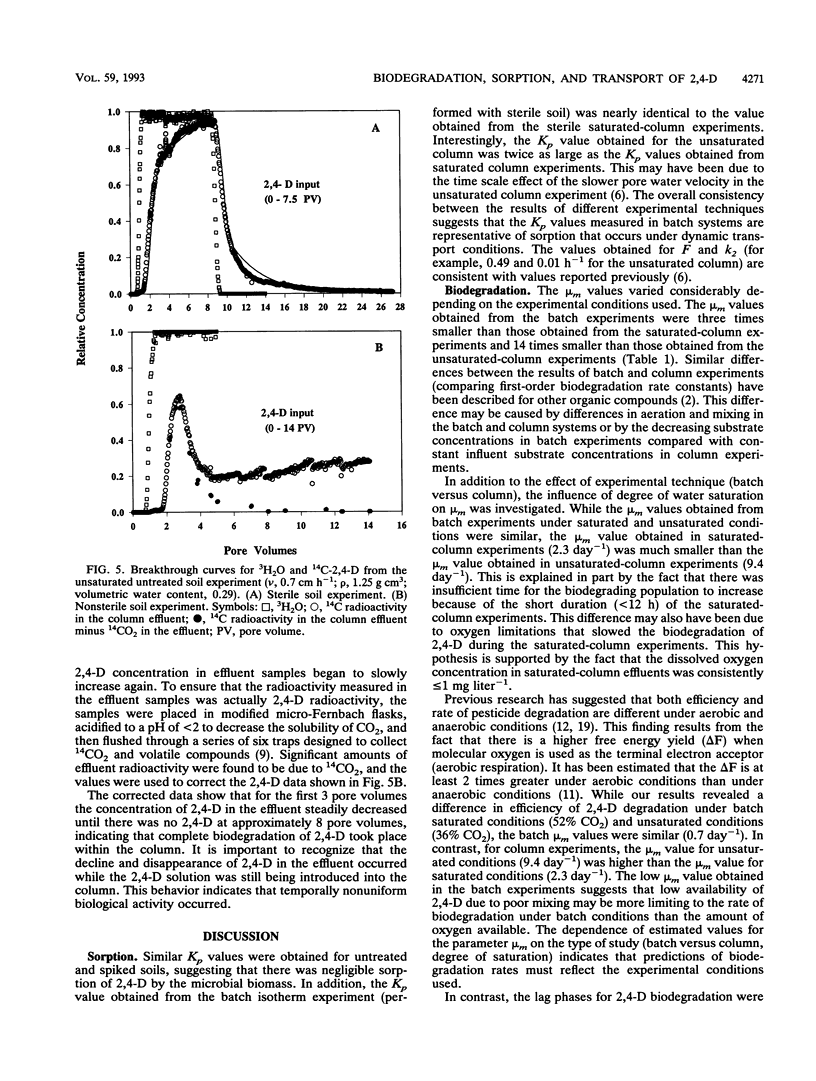
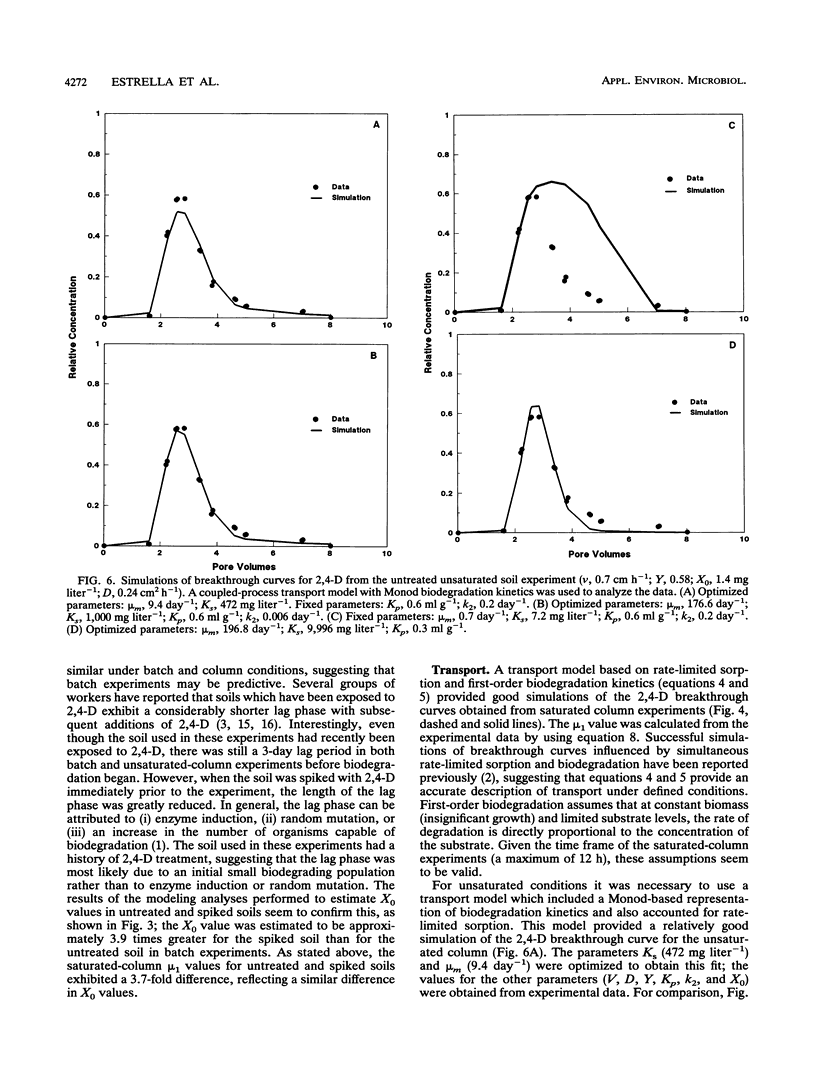
Abstract
The fate of an organic contaminant in soil depends on many factors, including sorption, biodegradation, and transport. The herbicide 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) was used as a model compound to illustrate the impact of these interacting factors on the fate of an organic contaminant. Batch and column experiments performed with a sandy loam soil mixture under saturated and unsaturated conditions were used to determine the effects of sorption and biodegradation on the fate and transport of 2,4-D. Sorption of 2,4-D was found to have a slight but significant effect on transport of 2,4-D under saturated conditions (retardation factor, 1.8) and unsaturated conditions (retardation factor, 3.4). Biodegradation of 2,4-D was extensive under both batch and column conditions and was found to have a significant impact on 2,4-D transport in column experiments. In batch experiments, complete mineralization of 2,4-D (100 mg kg-1) occurred over a 4-day period following a 3-day lag phase under both saturated and unsaturated conditions. The biodegradation rate parameters calculated for batch experiments were found to be significantly different from those estimated for column experiments.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aelion C. M., Swindoll C. M., Pfaender F. K. Adaptation to and biodegradation of xenobiotic compounds by microbial communities from a pristine aquifer. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Sep;53(9):2212–2217. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.9.2212-2217.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greer L. E., Shelton D. R. Effect of inoculant strain and organic matter content on kinetics of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid degradation in soil. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 May;58(5):1459–1465. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.5.1459-1465.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marinucci A. C., Bartha R. Apparatus for monitoring the mineralization of volatile C-labeled compounds. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 Nov;38(5):1020–1022. doi: 10.1128/aem.38.5.1020-1022.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


