Abstract
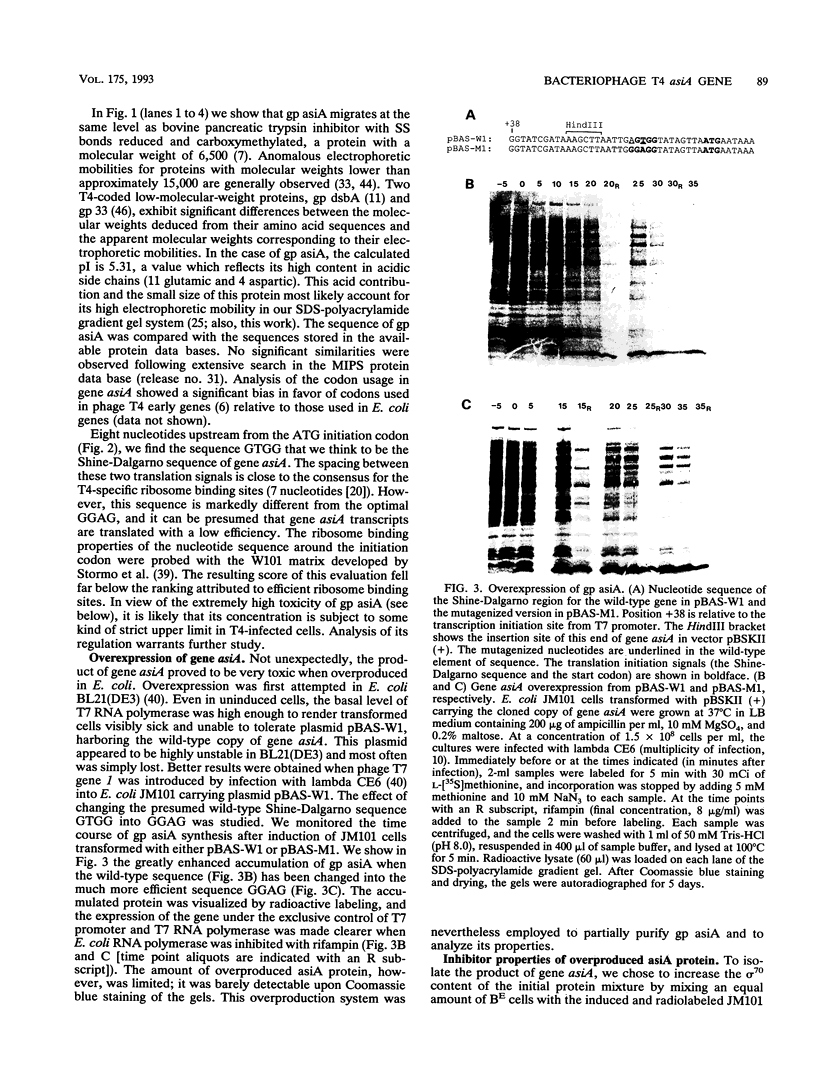
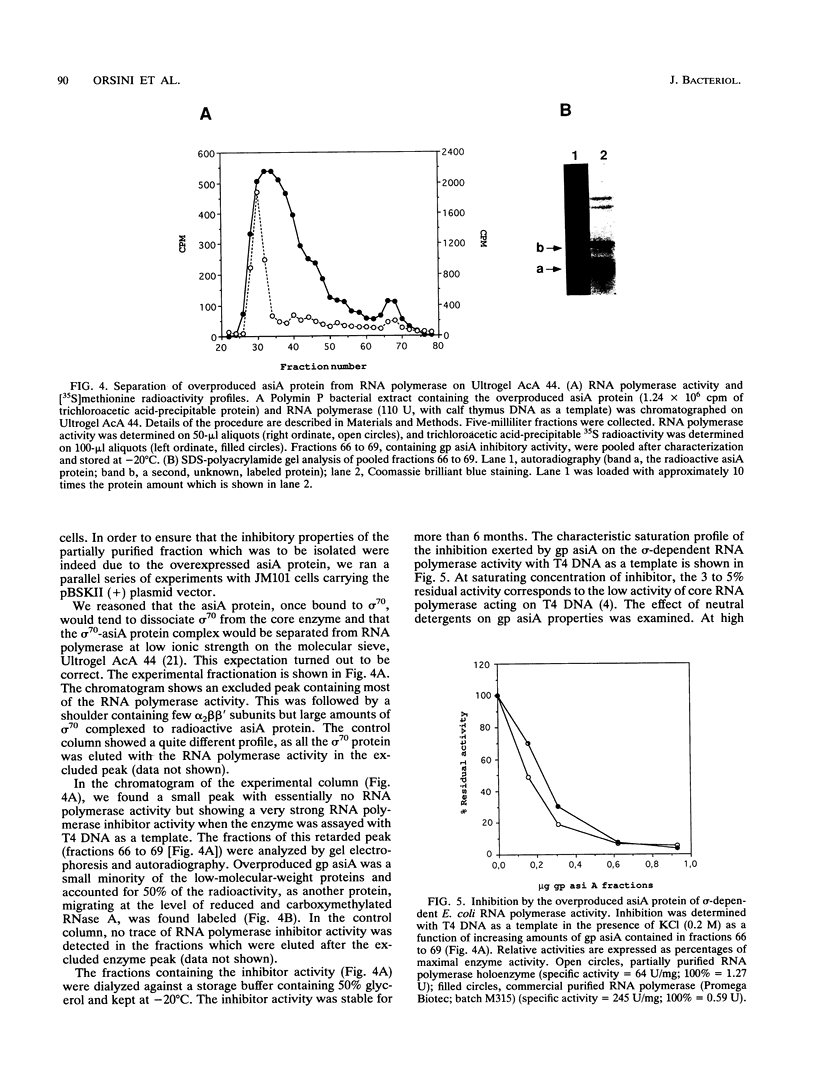
The anti-sigma 70 factor of bacteriophage T4 is a 10-kDa (10K) protein which inhibits the sigma 70-directed initiation of transcription by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase holoenzyme. We have partially purified the anti-sigma 70 factor and obtained the sequence of a C-terminal peptide of this protein. Using reverse genetics, we have identified, at the end of the lysis gene t and downstream of an as yet unassigned phage T4 early promoter, an open reading frame encoding a 90-amino-acid protein with a predicted molecular weight of 10,590. This protein has been overproduced in a phage T7 expression system and partially purified. It shows a strong inhibitory activity towards sigma 70-directed transcription (by RNA polymerase holoenzyme), whereas it has no significant effect on sigma 70-independent transcription (by RNA polymerase core enzyme). At high ionic strength, this inhibition is fully antagonized by the neutral detergent Triton X-100. Our results corroborate the initial observations on the properties of the phage T4 10K anti-sigma 70 factor, and we therefore propose that the gene which we call asiA, identified in the present study, corresponds to the gene encoding this T4 transcriptional inhibitor.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burgess R. R. A new method for the large scale purification of Escherichia coli deoxyribonucleic acid-dependent ribonucleic acid polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1969 Nov 25;244(22):6160–6167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess R. R., Jendrisak J. J. A procedure for the rapid, large-scall purification of Escherichia coli DNA-dependent RNA polymerase involving Polymin P precipitation and DNA-cellulose chromatography. Biochemistry. 1975 Oct 21;14(21):4634–4638. doi: 10.1021/bi00692a011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgess R. R., Travers A. A., Dunn J. J., Bautz E. K. Factor stimulating transcription by RNA polymerase. Nature. 1969 Jan 4;221(5175):43–46. doi: 10.1038/221043a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creighton T. E. Intermediates in the refolding of reduced pancreatic trypsin inhibitor. J Mol Biol. 1974 Aug 15;87(3):579–602. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90105-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daegelen P., Brody E. The rIIA gene of bacteriophage T4. I. Its DNA sequence and discovery of a new open reading frame between genes 60 and rIIA. Genetics. 1990 Jun;125(2):237–248. doi: 10.1093/genetics/125.2.237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gansz A., Kruse U., Rüger W. Gene product dsbA of bacteriophage T4 binds to late promoters and enhances late transcription. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Mar;225(3):427–434. doi: 10.1007/BF00261683. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geiduschek E. P. Regulation of expression of the late genes of bacteriophage T4. Annu Rev Genet. 1991;25:437–460. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.25.120191.002253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn S., Kruse U., Rüger W. The region of phage T4 genes 34, 33 and 59: primary structures and organization on the genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Dec 9;14(23):9311–9327. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.23.9311. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassavetis G. A., Geiduschek E. P. Defining a bacteriophage T4 late promoter: bacteriophage T4 gene 55 protein suffices for directing late promoter recognition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5101–5105. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liebig H. D., Rüger W. Bacteriophage T4 early promoter regions. Consensus sequences of promoters and ribosome-binding sites. J Mol Biol. 1989 Aug 20;208(4):517–536. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90145-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lowe P. A., Hager D. A., Burgess R. R. Purification and properties of the sigma subunit of Escherichia coli DNA-dependent RNA polymerase. Biochemistry. 1979 Apr 3;18(7):1344–1352. doi: 10.1021/bi00574a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthias P. D., Bernard H. U., Scott A., Brady G., Hashimoto-Gotoh T., Schütz G. A bovine papilloma virus vector with a dominant resistance marker replicates extrachromosomally in mouse and E. coli cells. EMBO J. 1983;2(9):1487–1492. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01612.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montag D., Degen M., Henning U. Nucleotide sequence of gene t (lysis gene) of the E. coli phage T4. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 25;15(16):6736–6736. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.16.6736. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., Bloch P. L., Smith D. F. Culture medium for enterobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):736–747. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.736-747.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orsini G., Brody E. N. Phage T4 DNA codes for two distinct 10-kDa proteins which strongly bind to RNA polymerase. Virology. 1988 Feb;162(2):397–405. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(88)90480-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratner D. Letter to the editor: Bacteriophage T4 transcriptional control gene 55 codes for a protein bound to Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1974 Nov 15;89(4):803–807. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90054-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ratner D. The interaction bacterial and phage proteins with immobilized Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Mol Biol. 1974 Sep 15;88(2):373–383. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90488-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruckman J., Parma D., Tuerk C., Hall D. H., Gold L. Identification of a T4 gene required for bacteriophage mRNA processing. New Biol. 1989 Oct;1(1):54–65. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saunders S. E., Burke J. F. Rapid isolation of miniprep DNA for double strand sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Aug 25;18(16):4948–4948. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.16.4948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schägger H., von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1 to 100 kDa. Anal Biochem. 1987 Nov 1;166(2):368–379. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(87)90587-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens A. Deoxyribonucleic acid dependent ribonucleic acid polymerases from two T4 phage-infected systems. Biochemistry. 1974 Jan 29;13(3):493–503. doi: 10.1021/bi00700a015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens A. Inhibition of DNA-enzyme binding by an RNA polymerase inhibitor from T4 phage-infected Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 2;475(1):193–196. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(77)90355-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens A. New small polypeptides associated with DNA-dependent RNA polymerase of Escherichia coli after infection with bacteriophage T4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):603–607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.603. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stevens A., Rhoton J. C. Characterization of an inhibitor causing potassium chloride sensitivity of an RNA polymerase from T4 phage-infected Escherichia coli. Biochemistry. 1975 Nov 18;14(23):5074–5079. doi: 10.1021/bi00694a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stormo G. D., Schneider T. D., Gold L., Ehrenfeucht A. Use of the 'Perceptron' algorithm to distinguish translational initiation sites in E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2997–3011. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uzan M., Brody E., Favre R. Nucleotide sequence and control of transcription of the bacteriophage T4 motA regulatory gene. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Sep;4(9):1487–1496. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb02059.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uzan M., Favre R., Brody E. A nuclease that cuts specifically in the ribosome binding site of some T4 mRNAs. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8895–8899. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. G., Gratzer W. B. Limitations of the detergent-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis method for molecular weight determination of proteins. J Chromatogr. 1971 Apr 22;57(1):121–125. doi: 10.1016/0021-9673(71)80013-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams K. P., Kassavetis G. A., Esch F. S., Geiduschek E. P. Identification of the gene encoding an RNA polymerase-binding protein of bacteriophage T4. J Virol. 1987 Feb;61(2):597–599. doi: 10.1128/jvi.61.2.597-599.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams K. P., Müller R., Rüger W., Geiduschek E. P. Overproduced bacteriophage T4 gene 33 protein binds RNA polymerase. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3579–3582. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3579-3582.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Franciscis V., Brody E. In vitro system for middle T4 RNA. I. Studies with Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 25;257(8):4087–4096. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]