Abstract
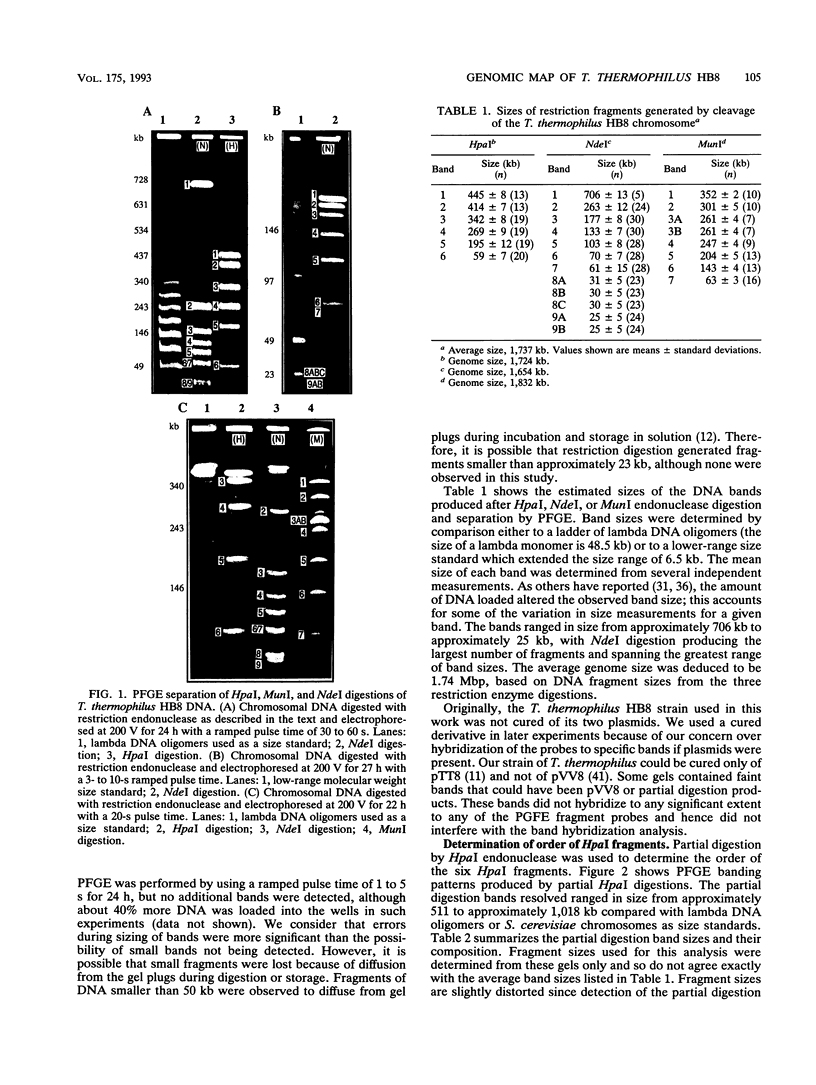
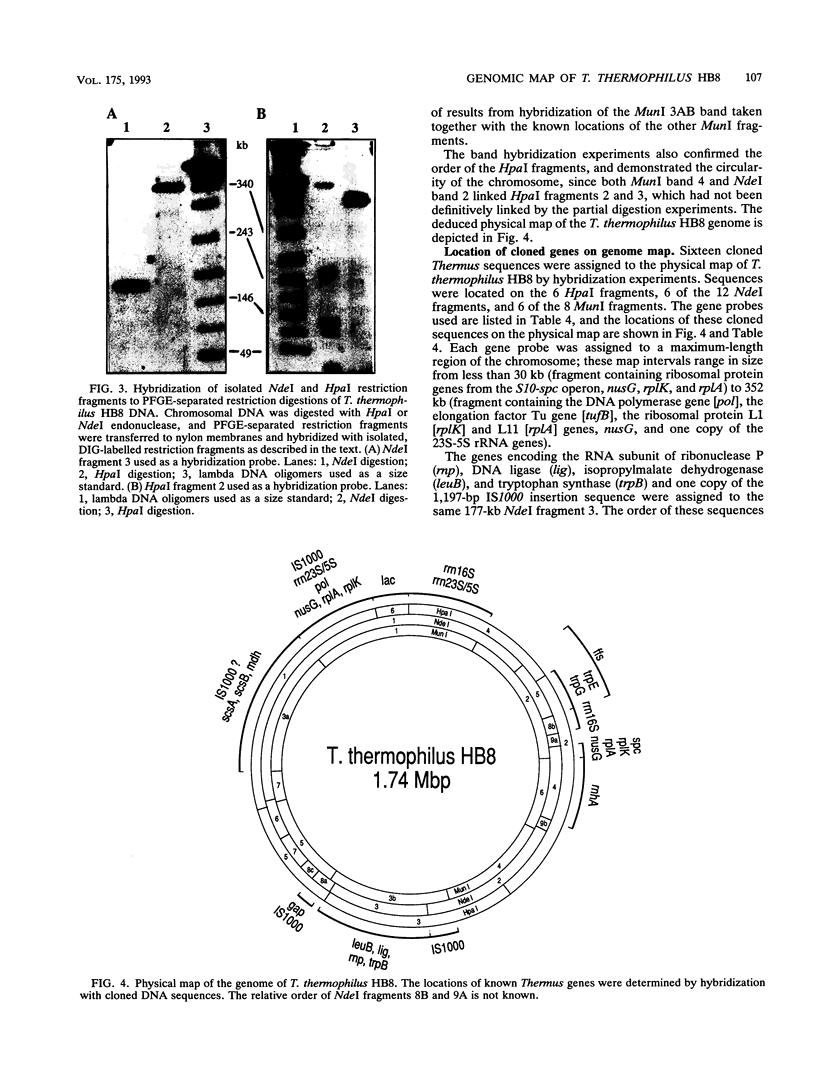
A physical map of the chromosome of the extremely thermophilic eubacterium Thermus thermophilus HB8 has been constructed by using pulsed-field gel electrophoresis techniques. A total of 26 cleavage sites for the rarely cutting restriction endonucleases HpaI, MunI, and NdeI were located on the genome. On the basis of the sizes of the restriction fragments generated, the genome size was estimated to be 1.74 Mbp, which is significantly smaller than the chromosomes of Escherichia coli and other mesophiles. Partial digestion experiments revealed the order of the six HpaI bands on the chromosome. Hybridization of isolated restriction fragments to pulsed-field gel-separated restriction digestions confirmed the deduced order of the HpaI fragments and allowed ordering and alignment of the NdeI and MunI fragments. In addition, 16 genes or gene clusters cloned from several different Thermus strains were located on the T. thermophilus HB8 chromosomal map by hybridization of gene probes to pulsed-field gel-resolved restriction digestions.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ashby M. K., Bergquist P. L. Cloning and sequence of IS1000, a putative insertion sequence from Thermus thermophilus HB8. Plasmid. 1990 Jul;24(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(90)90020-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann B. J. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 8. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Jun;54(2):130–197. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.2.130-197.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Birkelund S., Stephens R. S. Construction of physical and genetic maps of Chlamydia trachomatis serovar L2 by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. J Bacteriol. 1992 May;174(9):2742–2747. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.9.2742-2747.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borges K. M., Bergquist P. L. A rapid method for preparation of bacterial chromosomal DNA in agarose plugs using Thermus Rt41A proteinase. Biotechniques. 1992 Feb;12(2):222–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen H. W., Kuspa A., Keseler I. M., Shimkets L. J. Physical map of the Myxococcus xanthus chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1991 Mar;173(6):2109–2115. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.6.2109-2115.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croft J. E., Love D. R., Bergquist P. L. Expression of leucine genes from an extremely thermophilic bacterium in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Dec;210(3):490–497. doi: 10.1007/BF00327202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degryse E., Glansdorff N., Piérard A. A comparative analysis of extreme thermophilic bacteria belonging to the genus Thermus. Arch Microbiol. 1978 May 30;117(2):189–196. doi: 10.1007/BF00402307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dekker K., Yamagata H., Sakaguchi K., Udaka S. Xylose (glucose) isomerase gene from the thermophile Thermus thermophilus: cloning, sequencing, and comparison with other thermostable xylose isomerases. J Bacteriol. 1991 May;173(10):3078–3083. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.10.3078-3083.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eberhard M. D., Vásquez C., Valenzuela P., Vicuña R., Yudelevich A. Physical characterization of a plasmid (pTT1) isolated from Thermus thermophilus. Plasmid. 1981 Jul;6(1):1–6. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(81)90049-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fritz R. B., Musich P. R. Unexpected loss of genomic DNA from agarose gel plugs. Biotechniques. 1990 Nov;9(5):542, 544, 546-50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann R. K., Erdmann V. A. Analysis of the gene encoding the RNA subunit of ribonuclease P from T. thermophilus HB8. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Nov 11;19(21):5957–5964. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.21.5957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann R. K., Erdmann V. A. Thermus thermophilus 16S rRNA is transcribed from an isolated transcription unit. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):2933–2941. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.2933-2941.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann R. K., Ulbrich N., Erdmann V. A. An unusual rRNA operon constellation: in Thermus thermophilus HB8 the 23S/5S rRNA operon is a separate entity from the 16S rRNA operon. Biochimie. 1987 Oct;69(10):1097–1104. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(87)90009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hecht R. M., Garza A., Lee Y. H., Miller M. D., Pisegna M. A. Nucleotide sequence of the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene from Thermus aquaticus YT1. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Dec 11;17(23):10123–10123. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.23.10123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höpfl P., Ludwig W., Schleifer K. H., Larsen N. The 23S ribosomal RNA higher-order structure of Pseudomonas cepacia and other prokaryotes. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Nov 6;185(2):355–364. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15123.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itaya M., Kondo K. Molecular cloning of a ribonuclease H (RNase HI) gene from an extreme thermophile Thermus thermophilus HB8: a thermostable RNase H can functionally replace the Escherichia coli enzyme in vivo. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Aug 25;19(16):4443–4449. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.16.4443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn O., Hartmann R. K., Erdmann V. A. Analysis of the spc ribosomal protein operon of Thermus aquaticus. Eur J Biochem. 1991 May 8;197(3):733–740. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15965.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyama Y., Arikawa Y., Furukawa K. A plasmid vector for an extreme thermophile, Thermus thermophilus. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Oct;60(1-2):97–101. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90352-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koyama Y., Okamoto S., Furukawa K. Cloning of alpha- and beta-galactosidase genes from an extreme thermophile, Thermus strain T2, and their expression in Thermus thermophilus HB27. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jul;56(7):2251–2254. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.7.2251-2254.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kushiro M., Shimizu M., Tomita K. Molecular cloning and sequence determination of the tuf gene coding for the elongation factor Tu of Thermus thermophilus HB8. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Dec 30;170(1-2):93–98. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb13671.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Bourgeois P., Mata M., Ritzenthaler P. Genome comparison of Lactococcus strains by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1989 May;50(1-2):65–69. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(89)90460-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neimark H. C., Lange C. S. Pulse-field electrophoresis indicates full-length Mycoplasma chromosomes range widely in size. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Sep 25;18(18):5443–5448. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.18.5443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishiyama M., Horinouchi S., Beppu T. Characterization of an operon encoding succinyl-CoA synthetase and malate dehydrogenase from Thermus flavus AT-62 and its expression in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Apr;226(1-2):1–9. doi: 10.1007/BF00273580. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noll K. M. Chromosome map of the thermophilic archaebacterium Thermococcus celer. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6720–6725. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6720-6725.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato S., Nakada Y., Kanaya S., Tanaka T. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of Thermus thermophilus HB8 trpE and trpG. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Sep 7;950(3):303–312. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(88)90126-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. L., Condemine G. New approaches for physical mapping of small genomes. J Bacteriol. 1990 Mar;172(3):1167–1172. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.3.1167-1172.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. L., Econome J. G., Schutt A., Klco S., Cantor C. R. A physical map of the Escherichia coli K12 genome. Science. 1987 Jun 12;236(4807):1448–1453. doi: 10.1126/science.3296194. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Struck J. C., Toschka H. Y., Erdmann V. A. Nucleotide sequence of the 4.5S RNA gene from Thermus thermophilus HB8. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Sep 26;16(18):9042–9042. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.18.9042. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanskanen E. I., Tulloch D. L., Hillier A. J., Davidson B. E. Pulsed-Field Gel Electrophoresis of SmaI Digests of Lactococcal Genomic DNA, a Novel Method of Strain Identification. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Oct;56(10):3105–3111. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.10.3105-3111.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weisburg W. G., Giovannoni S. J., Woese C. R. The Deinococcus-Thermus phylum and the effect of rRNA composition on phylogenetic tree construction. Syst Appl Microbiol. 1989;11:128–134. doi: 10.1016/s0723-2020(89)80051-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woese C. R. Bacterial evolution. Microbiol Rev. 1987 Jun;51(2):221–271. doi: 10.1128/mr.51.2.221-271.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]