Abstract
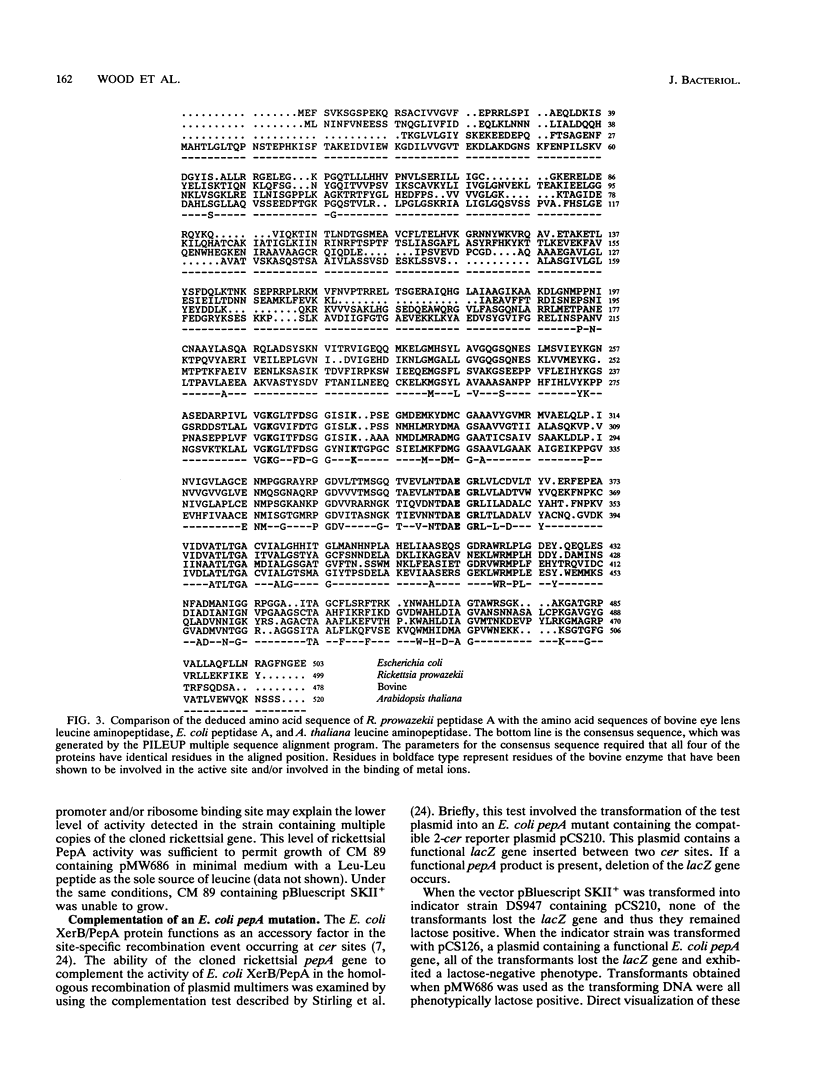
The pepA gene, encoding a protein with leucine aminopeptidase activity, was isolated from Rickettsia prowazekii, an obligate intracellular parasitic bacterium. Nucleotide sequence analysis revealed an open reading frame of 1,502 bp that would encode a protein of 499 amino acids with a calculated molecular weight of 53,892, a size comparable to that of the protein produced in Escherichia coli minicells containing the rickettsial gene. Also, heat-stable leucine aminopeptidase activity was demonstrable in an E. coli peptidase-deficient strain containing R. prowazekii pepA. Comparison of the amino acid sequence of the R. prowazekii PepA with the characterized leucine aminopeptidases from E. coli, Arabidopsis thaliana, and bovine eye lens revealed that 39.8, 34.9, and 34.0% of the residues were identical, respectively. Residues proposed to be part of the active site or involved in the binding of metal ions in the bovine metalloenzyme were all conserved in R. prowazekii PepA. However, despite the structural and enzymatic similarity to E. coli PepA, the R. prowazekii protein was unable to complement the cer site-specific, PepA-dependent recombination system found in E. coli that resolves ColE1-type plasmid multimers into their monomeric forms.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann B. J. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 8. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Jun;54(2):130–197. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.2.130-197.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartling D., Weiler E. W. Leucine aminopeptidase from Arabidopsis thaliana. Molecular evidence for a phylogenetically conserved enzyme of protein turnover in higher plants. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Apr 1;205(1):425–431. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb16796.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolivar F., Rodriguez R. L., Greene P. J., Betlach M. C., Heyneker H. L., Boyer H. W., Crosa J. H., Falkow S. Construction and characterization of new cloning vehicles. II. A multipurpose cloning system. Gene. 1977;2(2):95–113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burley S. K., David P. R., Sweet R. M., Taylor A., Lipscomb W. N. Structure determination and refinement of bovine lens leucine aminopeptidase and its complex with bestatin. J Mol Biol. 1992 Mar 5;224(1):113–140. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90580-d. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carpenter F. H., Vahl J. M. Leucine aminopeptidase (Bovine lens). Mechanism of activation by Mg 2+ and Mn 2+ of the zinc metalloenzyme, amino acid composition, and sulfhydryl content. J Biol Chem. 1973 Jan 10;248(1):294–304. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colloms S. D., Sykora P., Szatmari G., Sherratt D. J. Recombination at ColE1 cer requires the Escherichia coli xerC gene product, a member of the lambda integrase family of site-specific recombinases. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):6973–6980. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.6973-6980.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuypers H. T., van Loon-Klaassen L. A., Egberts W. T., de Jong W. W., Bloemendal H. The primary structure of leucine aminopeptidase from bovine eye lens. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 25;257(12):7077–7085. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen J. B., Abiko Y., Curtiss R., 3rd Characterization of the Streptococcus mutans plasmid pva318 cloned into Escherichia coli. Infect Immun. 1981 Mar;31(3):1034–1043. doi: 10.1128/iai.31.3.1034-1043.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. G., Mackinnon K. Peptidase mutants of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1974 Oct;120(1):355–363. doi: 10.1128/jb.120.1.355-363.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller C. G., Schwartz G. Peptidase-deficient mutants of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1978 Aug;135(2):603–611. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.2.603-611.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stirling C. J., Colloms S. D., Collins J. F., Szatmari G., Sherratt D. J. xerB, an Escherichia coli gene required for plasmid ColE1 site-specific recombination, is identical to pepA, encoding aminopeptidase A, a protein with substantial similarity to bovine lens leucine aminopeptidase. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1623–1627. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03547.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stormo G. D., Schneider T. D., Gold L. M. Characterization of translational initiation sites in E. coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 11;10(9):2971–2996. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.9.2971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TUPPY H., WIESBAUER U., WINTERSBERGER E. [Amino acid-p-nitroanilide as a substrate for aminopeptidases and other proteolytic enzymes]. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1962 Nov 15;329:278–288. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1962.329.1.278. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor A., Surgenor T., Thomson D. K., Graham R. J., Oettgen H. Comparison of leucine aminopeptidase from human lens, beef lens and kidney, and hog lens and kidney. Exp Eye Res. 1984 Mar;38(3):217–229. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(84)90160-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt V. M. Purification and properties of an aminopeptidase from Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1970 Sep 25;245(18):4760–4769. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E., Dobson M. E., Dasch G. A. Biochemistry of rickettsiae: recent advances. Acta Virol. 1987 May;31(3):271–286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss E. The biology of rickettsiae. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1982;36:345–370. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.36.100182.002021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson L. R., Plano G. V., Winkler H. H., Krause D. C., Wood D. O. Nucleotide sequence of the Rickettsia prowazekii ATP/ADP translocase-encoding gene. Gene. 1989 Aug 15;80(2):269–278. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90291-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H. Rickettsia species (as organisms). Annu Rev Microbiol. 1990;44:131–153. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.44.100190.001023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winkler H. H., Wood D. O. Codon usage in selected AT-rich bacteria. Biochimie. 1988 Aug;70(8):977–986. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90262-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood D. O., Williamson L. R., Winkler H. H., Krause D. C. Nucleotide sequence of the Rickettsia prowazekii citrate synthase gene. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3564–3572. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3564-3572.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]