Abstract
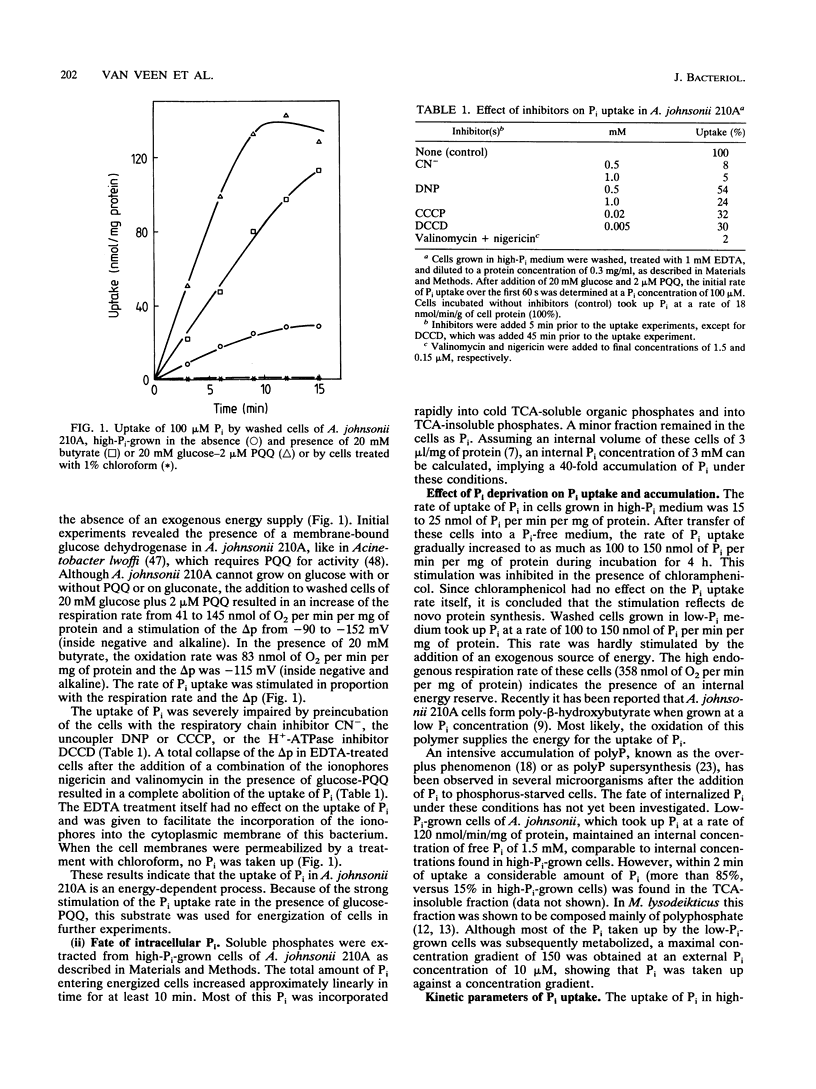
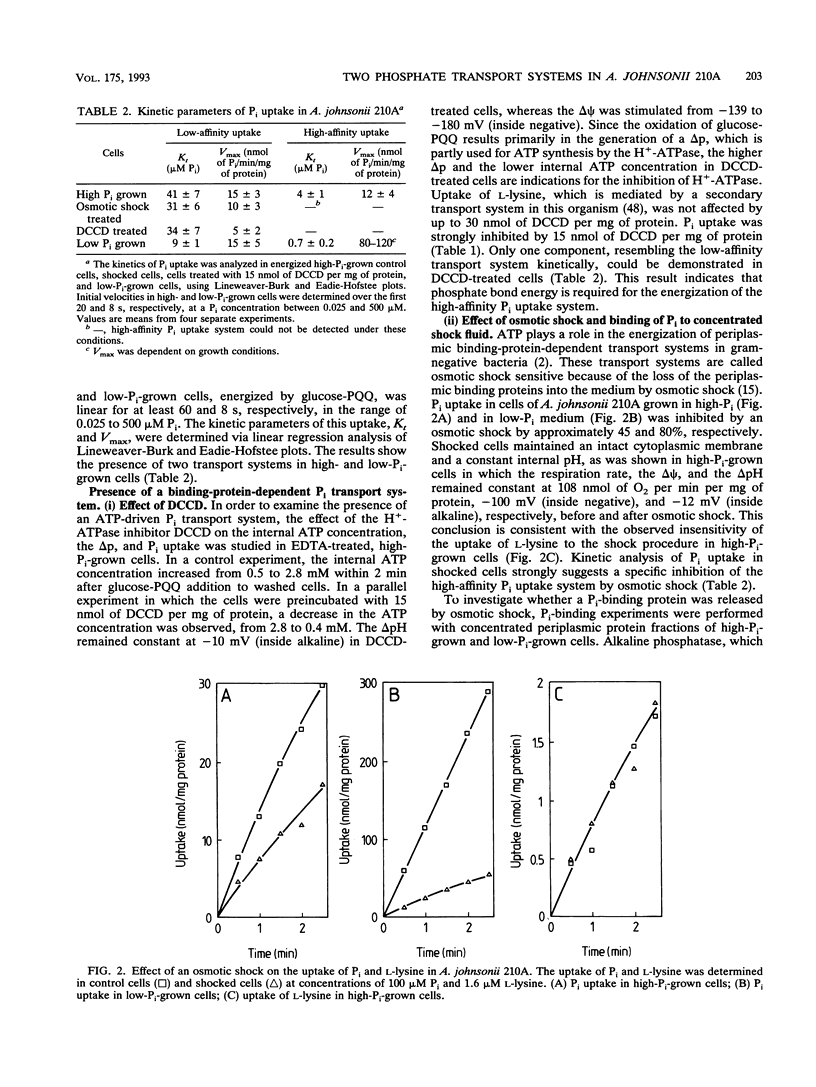
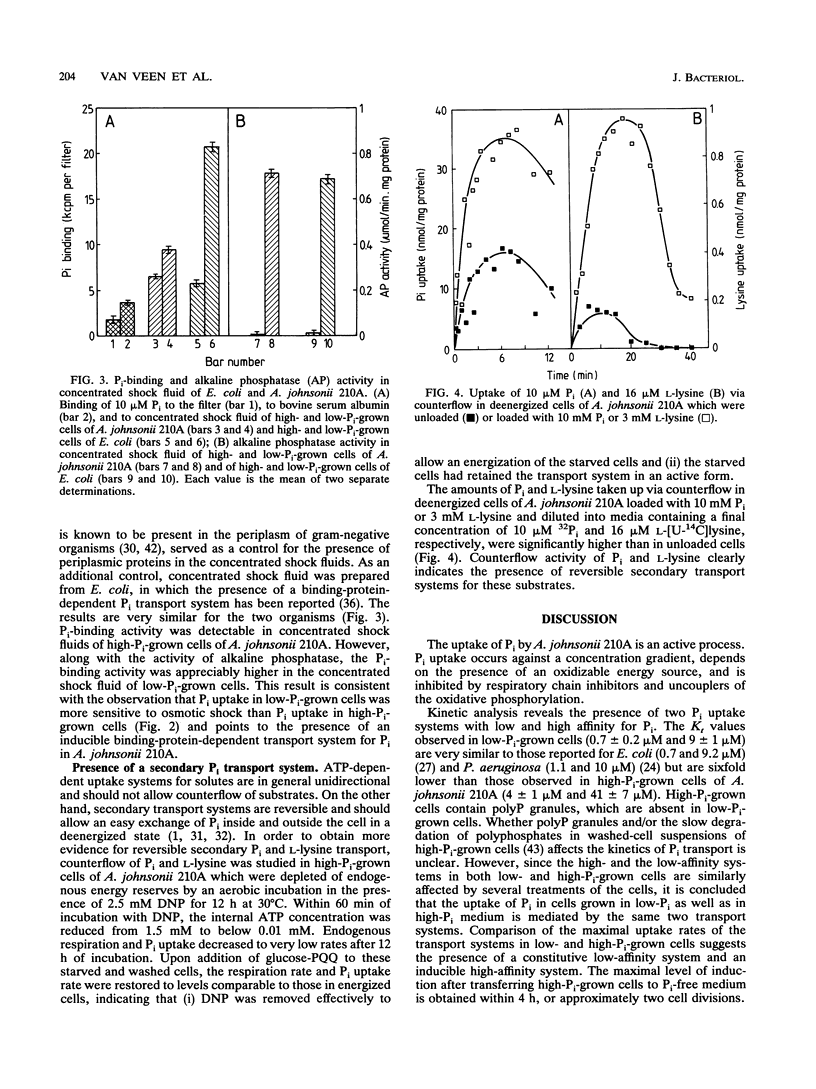
The transport of P(i) was characterized in Acinetobacter johnsonii 210A, which is able to accumulate an excessive amount of phosphate as polyphosphate (polyP) under aerobic conditions. P(i) is taken up against a concentration gradient by energy-dependent, carrier-mediated processes. A. johnsonii 210A, grown under P(i) limitation, contains two uptake systems with Kt values of 0.7 +/- 0.2 microM and 9 +/- 1 microM. P(i) uptake via the high-affinity component is drastically reduced by N,N'-dicyclohexylcarbodiimide, an inhibitor of H(+)-ATPase, and by osmotic shock. Together with the presence of P(i)-binding activity in concentrated periplasmic protein fractions, these results suggest that the high-affinity transport system belongs to the group of ATP-driven, binding-protein-dependent transport systems. Induction of this transport system upon transfer of cells grown in the presence of excess P(i) to P(i)-free medium results in a 6- to 10-fold stimulation of the P(i) uptake rate. The constitutive low-affinity uptake system for P(i) is inhibited by uncouplers and can mediate counterflow of P(i), indicating its reversible, secondary nature. The presence of an inducible high-affinity uptake system for P(i) and the ability to decrease the free internal P(i) pool by forming polyP enable A. johnsonii 210A to reduce the P(i) concentration in the aerobic environment to micromolar levels. Under anaerobic conditions, polyP is degraded again and P(i) is released via the low-affinity secondary transport system.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AVRON M. Photophosphorylation by swiss-chard chloroplasts. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 May 20;40:257–272. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91350-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Abee T., van der Wal F. J., Hellingwerf K. J., Konings W. N. Binding-protein-dependent alanine transport in Rhodobacter sphaeroides is regulated by the internal pH. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):5148–5154. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.5148-5154.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames G. F. Bacterial periplasmic transport systems: structure, mechanism, and evolution. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:397–425. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.002145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames G. F., Joshi A. K. Energy coupling in bacterial periplasmic permeases. J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4133–4137. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4133-4137.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames G. F., Nikaido K., Groarke J., Petithory J. Reconstitution of periplasmic transport in inside-out membrane vesicles. Energization by ATP. J Biol Chem. 1989 Mar 5;264(7):3998–4002. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker E. P., Harold F. M. Energy coupling to potassium transport in Streptococcus faecalis. Interplay of ATP and the protonmotive force. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 25;255(2):433–440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bakker E. P., Mangerich W. E. Interconversion of components of the bacterial proton motive force by electrogenic potassium transport. J Bacteriol. 1981 Sep;147(3):820–826. doi: 10.1128/jb.147.3.820-826.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bonting C. F., Kortstee G. J., Zehnder A. J. Properties of polyphosphate: AMP phosphotransferase of Acinetobacter strain 210A. J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(20):6484–6488. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.20.6484-6488.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driessen A. J., Kodde J., de Jong S., Konings W. N. Neutral amino acid transport by membrane vesicles of Streptococcus cremoris is subject to regulation by internal pH. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2748–2754. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2748-2754.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedberg I., Avigad G. Structures containing polyphosphate in Micrococcus lysodeikticus. J Bacteriol. 1968 Aug;96(2):544–553. doi: 10.1128/jb.96.2.544-553.1968. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedberg I. Phosphate transport in Micrococcus lysodeikticus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 May 2;466(3):451–460. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90338-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerdes R. G., Rosenberg H. The relationship between the phosphate-binding protein and a regulator gene product from Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 May 10;351(1):77–86. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(74)90066-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harold F. M. Inorganic polyphosphates in biology: structure, metabolism, and function. Bacteriol Rev. 1966 Dec;30(4):772–794. doi: 10.1128/br.30.4.772-794.1966. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hellingwerf K. J., Friedberg I., Lolkema J. S., Michels P. A., Konings W. N. Energy coupling of facilitated transport of inorganic ions in Rhodopseudomonas sphaeroides. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jun;150(3):1183–1191. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.3.1183-1191.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F., Hyde S. C., Mimmack M. M., Gileadi U., Gill D. R., Gallagher M. P. Binding protein-dependent transport systems. J Bioenerg Biomembr. 1990 Aug;22(4):571–592. doi: 10.1007/BF00762962. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong J. S., Hunt A. G., Masters P. S., Lieberman M. A. Requirements of acetyl phosphate for the binding protein-dependent transport systems in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1213–1217. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kulaev I. S., Vagabov V. M. Polyphosphate metabolism in micro-organisms. Adv Microb Physiol. 1983;24:83–171. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60385-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medveczky N., Rosenberg H. Phosphate transport in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Aug 13;241(2):494–506. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(71)90048-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neu H. C., Heppel L. A. The release of enzymes from Escherichia coli by osmotic shock and during the formation of spheroplasts. J Biol Chem. 1965 Sep;240(9):3685–3692. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poole K., Hancock R. E. Phosphate transport in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Involvement of a periplasmic phosphate-binding protein. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Nov 2;144(3):607–612. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08508.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poolman B., Nijssen R. M., Konings W. N. Dependence of Streptococcus lactis phosphate transport on internal phosphate concentration and internal pH. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5373–5378. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5373-5378.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poolman B., Smid E. J., Konings W. N. Kinetic properties of a phosphate-bond-driven glutamate-glutamine transport system in Streptococcus lactis and Streptococcus cremoris. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2755–2761. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2755-2761.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rao N. N., Torriani A. Molecular aspects of phosphate transport in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Jul;4(7):1083–1090. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00682.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads D. B., Epstein W. Cation transport in Escherichia coli. IX. Regulation of K transport. J Gen Physiol. 1978 Sep;72(3):283–295. doi: 10.1085/jgp.72.3.283. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richarme G., Kepes A. Study of binding protein-ligand interaction by ammonium sulfate-assisted adsorption on cellulose esters filters. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Jan 12;742(1):16–24. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(83)90353-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg H., Gerdes R. G., Chegwidden K. Two systems for the uptake of phosphate in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1977 Aug;131(2):505–511. doi: 10.1128/jb.131.2.505-511.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg H., Medveczky N., La Nauze J. M. Phosphate transport in Bacillus cereus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1969 Oct 14;193(1):159–167. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(69)90069-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinbo T., Kamo N., Kurihara K., Kobatake Y. A PVC-based electrode sensitive to DDA+ as a device for monitoring the membrane potential in biological systems. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1978 Apr 30;187(2):414–422. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(78)90052-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TORRIANI A. Influence of inorganic phosphate in the formation of phosphatases by Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1960 Mar 11;38:460–469. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(60)91281-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tommassen J., Lugtenberg B. PHO-regulon of Escherichia coli K12: a minireview. Ann Microbiol (Paris) 1982 Mar-Apr;133(2):243–249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willsky G. R., Malamy M. H. Characterization of two genetically separable inorganic phosphate transport systems in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 Oct;144(1):356–365. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.1.356-365.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Groenestijn J. W., Bentvelsen M. M., Deinema M. H., Zehnder A. J. Polyphosphate-degrading enzymes in Acinetobacter spp. and activated sludge. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Jan;55(1):219–223. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.1.219-223.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Groenestijn J. W., Zuidema M., van de Worp J. J., Deinema M. H., Zehnder A. J. Influence of environmental parameters on polyphosphate accumulation in Acinetobacter sp. Antonie Van Leeuwenhoek. 1989;55(1):67–82. doi: 10.1007/BF02309620. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



