Abstract
Elongation factor Tu (EF-Tu).GTP has the primary function of promoting the efficient and correct interaction of aminoacyl-tRNA with the ribosome. Very little is known about the elements in EF-Tu involved in this interaction. We describe a mutant form of EF-Tu, isolated in Salmonella typhimurium, that causes a severe defect in the interaction of the ternary complex with the ribosome. The mutation causes the substitution of Val for Gly-280 in domain II of EF-Tu. The in vivo growth and translation phenotypes of strains harboring this mutation are indistinguishable from those of strains in which the same tuf gene is insertionally inactivated. Viable cells are not obtained when the other tuf gene is inactivated, showing that the mutant EF-Tu alone cannot support cell growth. We have confirmed, by partial protein sequencing, that the mutant EF-Tu is present in the cells. In vitro analysis of the natural mixture of wild-type and mutant EF-Tu allows us to identify the major defect of this mutant. Our data shows that the EF-Tu is homogeneous and competent with respect to guanine nucleotide binding and exchange, stimulation of nucleotide exchange by EF-Ts, and ternary complex formation with aminoacyl-tRNA. However various measures of translational efficiency show a significant reduction, which is associated with a defective interaction between the ribosome and the mutant EF-Tu.GTP.aminoacyl-tRNA complex. In addition, the antibiotic kirromycin, which blocks translation by binding EF-Tu on the ribosome, fails to do so with this mutant EF-Tu, although it does form a complex with EF-Tu. Our results suggest that this region of domain II in EF-Tu has an important function and influences the binding of the ternary complex to the codon-programmed ribosome during protein synthesis. Models involving either a direct or an indirect effect of the mutation are discussed.
Full text
PDF



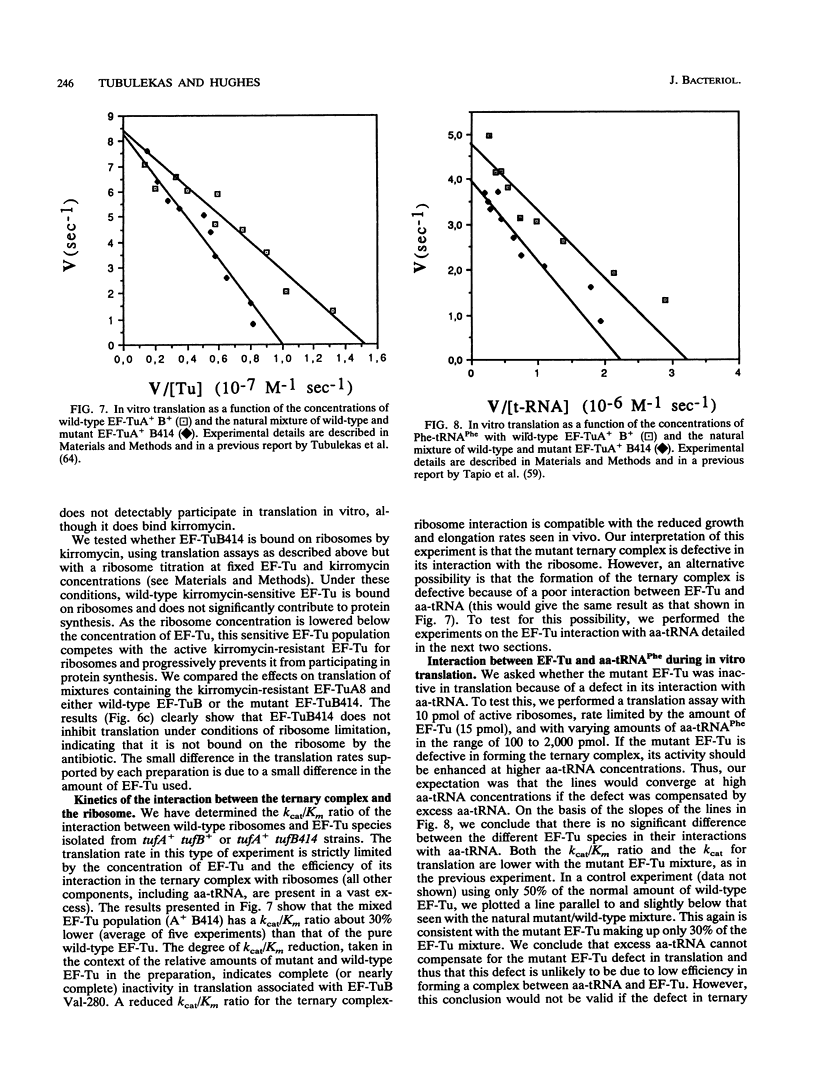
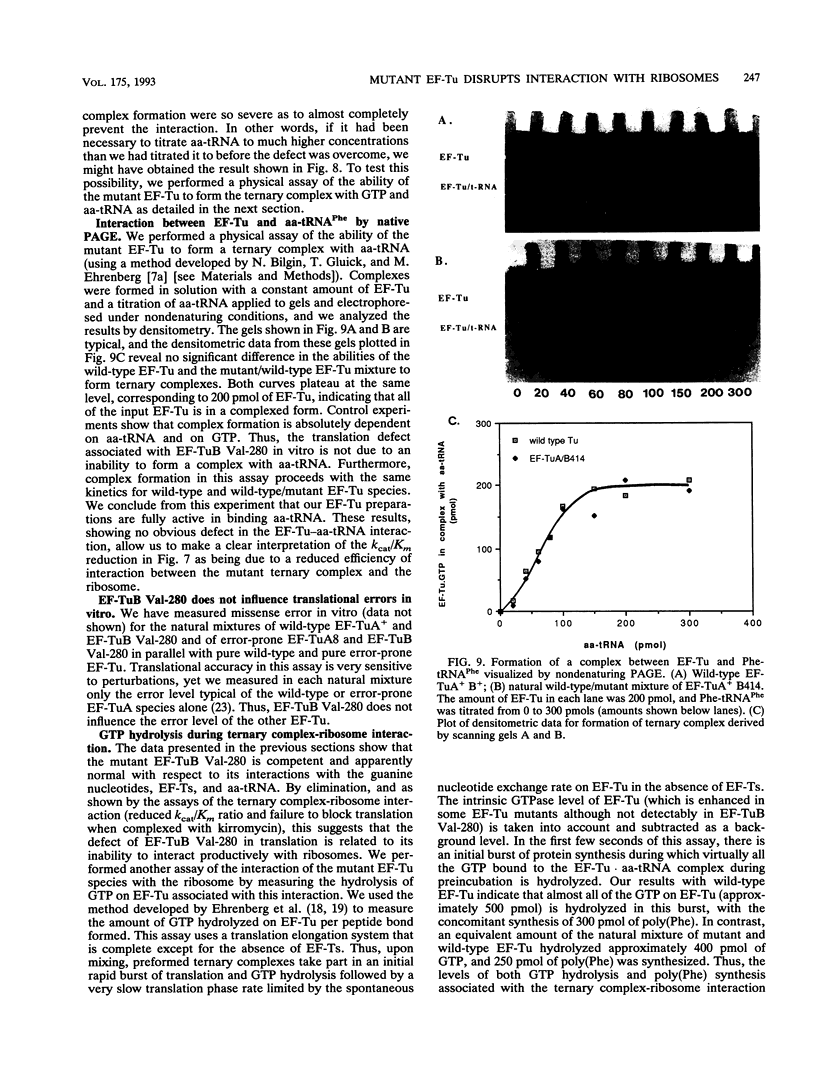



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abdulkarim F., Tuohy T. M., Buckingham R. H., Hughes D. Missense substitutions lethal to essential functions of EF-Tu. Biochimie. 1991 Dec;73(12):1457–1464. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(91)90178-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anborgh P. H., Cool R. H., Gümüsel F., Harmark K., Jacquet E., Weijland A., Mistou M. Y., Parmeggiani A. Structure-function relationships of elongation factor Tu as studied by mutagenesis. Biochimie. 1991 Jul-Aug;73(7-8):1051–1059. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(91)90147-s. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anborgh P. H., Swart G. W., Parmeggiani A. Kirromycin-induced modifications facilitate the separation of EF-Tu species and reveal intermolecular interactions. FEBS Lett. 1991 Nov 4;292(1-2):232–236. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80874-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andersson D. I., Bohman K., Isaksson L. A., Kurland C. G. Translation rates and misreading characteristics of rpsD mutants in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;187(3):467–472. doi: 10.1007/BF00332630. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antonsson B., Leberman R. Modification of amino groups in EF-Tu.GTP and the ternary complex EF-Tu.GTP.valyl-tRNAVal. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Jun 15;141(3):483–487. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08218.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron C., Böck A. The length of the aminoacyl-acceptor stem of the selenocysteine-specific tRNA(Sec) of Escherichia coli is the determinant for binding to elongation factors SELB or Tu. J Biol Chem. 1991 Oct 25;266(30):20375–20379. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bilgin N., Claesens F., Pahverk H., Ehrenberg M. Kinetic properties of Escherichia coli ribosomes with altered forms of S12. J Mol Biol. 1992 Apr 20;224(4):1011–1027. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90466-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumenthal T., Douglass J., Smith D. Conformational alteration of protein synthesis elongation factor EF-Tu by EF-Ts and by kirromycin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Aug;74(8):3264–3267. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.8.3264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bohman K., Ruusala T., Jelenc P. C., Kurland C. G. Kinetic impairment of restrictive streptomycin-resistant ribosomes. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;198(2):90–99. doi: 10.1007/BF00328706. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourne H. R., Sanders D. A., McCormick F. The GTPase superfamily: conserved structure and molecular mechanism. Nature. 1991 Jan 10;349(6305):117–127. doi: 10.1038/349117a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boutorin A. S., Clark B. F., Ebel J. P., Kruse T. A., Petersen H. U., Remy P., Vassilenko S. A study of the interaction of Escherichia coli elongation factor-Tu with aminoacyl-tRNAs by partial digestion with cobra venom ribonuclease. J Mol Biol. 1981 Nov 5;152(3):593–608. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90271-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark B. F., Kjeldgaard M., la Cour T. F., Thirup S., Nyborg J. Structural determination of the functional sites of E. coli elongation factor Tu. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Aug 27;1050(1-3):203–208. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90167-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creti R., Citarella F., Tiboni O., Sanangelantoni A., Palm P., Cammarano P. Nucleotide sequence of a DNA region comprising the gene for elongation factor 1 alpha (EF-1 alpha) from the ultrathermophilic archaeote Pyrococcus woesei: phylogenetic implications. J Mol Evol. 1991 Oct;33(4):332–342. doi: 10.1007/BF02102864. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dever T. E., Glynias M. J., Merrick W. C. GTP-binding domain: three consensus sequence elements with distinct spacing. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1814–1818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duffy L. K., Gerber L., Johnson A. E., Miller D. L. Identification of a histidine residue near the aminoacyl transfer ribonucleic acid binding site of elongation factor Tu. Biochemistry. 1981 Aug 4;20(16):4663–4666. doi: 10.1021/bi00519a022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duisterwinkel F. J., Kraal B., De Graaf J. M., Talens A., Bosch L., Swart G. W., Parmeggiani A., La Cour T. F., Nyborg J., Clark B. F. Specific alterations of the EF-Tu polypeptide chain considered in the light of its three-dimensional structure. EMBO J. 1984 Jan;3(1):113–120. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01770.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrenberg M., Rojas A. M., Weiser J., Kurland C. G. How many EF-Tu molecules participate in aminoacyl-tRNA binding and peptide bond formation in Escherichia coli translation? J Mol Biol. 1990 Feb 20;211(4):739–749. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(90)90074-V. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausner T. P., Atmadja J., Nierhaus K. H. Evidence that the G2661 region of 23S rRNA is located at the ribosomal binding sites of both elongation factors. Biochimie. 1987 Sep;69(9):911–923. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(87)90225-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopfield J. J. Kinetic proofreading: a new mechanism for reducing errors in biosynthetic processes requiring high specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Oct;71(10):4135–4139. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.10.4135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes D., Atkins J. F., Thompson S. Mutants of elongation factor Tu promote ribosomal frameshifting and nonsense readthrough. EMBO J. 1987 Dec 20;6(13):4235–4239. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1987.tb02772.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes D. Both genes for EF-Tu in Salmonella typhimurium are individually dispensable for growth. J Mol Biol. 1990 Sep 5;215(1):41–51. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80093-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes D. Mutant forms of tufA and tufB independently suppress nonsense mutations. J Mol Biol. 1987 Oct 20;197(4):611–615. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(87)90467-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang Y. W., McCabe P. G., Innis M. A., Miller D. L. Site-directed mutagenesis of the GDP binding domain of bacterial elongation factor Tu. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Nov 1;274(2):394–403. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90452-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang Y. W., Miller D. L. A mutation that alters the nucleotide specificity of elongation factor Tu, a GTP regulatory protein. J Biol Chem. 1987 Sep 25;262(27):13081–13085. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hwang Y. W., Sanchez A., Miller D. L. Mutagenesis of bacterial elongation factor Tu at lysine 136. A conserved amino acid in GTP regulatory proteins. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):8304–8309. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones M. D., Petersen T. E., Nielsen K. M., Magnusson S., Sottrup-Jensen L., Gausing K., Clark B. F. The complete amino-acid sequence of elongation factor Tu from Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1980 Jul;108(2):507–526. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1980.tb04748.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jonák J., Petersen T. E., Meloun B., Rychlík I. Histidine residues in elongation factor EF-tu from Escherichia coli protected by aminoacyl-tRNA against photo-oxidation. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Oct 15;144(2):295–303. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08463.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaziro Y. The role of guanosine 5'-triphosphate in polypeptide chain elongation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Sep 21;505(1):95–127. doi: 10.1016/0304-4173(78)90009-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinzy T. G., Freeman J. P., Johnson A. E., Merrick W. C. A model for the aminoacyl-tRNA binding site of eukaryotic elongation factor 1 alpha. J Biol Chem. 1992 Jan 25;267(3):1623–1632. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kinzy T. G., Merrick W. C. Characterization of a limited trypsin digestion form of eukaryotic elongation factor 1 alpha. J Biol Chem. 1991 Mar 5;266(7):4099–4105. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kjeldgaard M., Nyborg J. Refined structure of elongation factor EF-Tu from Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1992 Feb 5;223(3):721–742. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90986-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Knowlton R. G., Yarus M. Discrimination between aminoacyl groups on su+ 7 tRNA by elongation factor Tu. J Mol Biol. 1980 Jun 5;139(4):721–732. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90057-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leberman R., Antonsson B., Giovanelli R., Guariguata R., Schumann R., Wittinghofer A. A simplified procedure for the isolation of bacterial polypeptide elongation factor EF-Tu. Anal Biochem. 1980 May 1;104(1):29–36. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90272-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liljas A. Structural studies of ribosomes. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1982;40(3):161–228. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(82)90013-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ludwig W., Weizenegger M., Betzl D., Leidel E., Lenz T., Ludvigsen A., Möllenhoff D., Wenzig P., Schleifer K. H. Complete nucleotide sequences of seven eubacterial genes coding for the elongation factor Tu: functional, structural and phylogenetic evaluations. Arch Microbiol. 1990;153(3):241–247. doi: 10.1007/BF00249075. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsudaira P. Sequence from picomole quantities of proteins electroblotted onto polyvinylidene difluoride membranes. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10035–10038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz-Boutigue M. H., Reinbolt J., Ebel J. P., Ehresmann C., Ehresmann B. Crosslinking of elongation factor Tu to tRNA(Phe) by trans-diamminedichloroplatinum (II). Characterization of two crosslinking sites on EF-Tu. FEBS Lett. 1989 Mar 13;245(1-2):194–200. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(89)80220-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Noller H. F. Intermediate states in the movement of transfer RNA in the ribosome. Nature. 1989 Nov 9;342(6246):142–148. doi: 10.1038/342142a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moazed D., Robertson J. M., Noller H. F. Interaction of elongation factors EF-G and EF-Tu with a conserved loop in 23S RNA. Nature. 1988 Jul 28;334(6180):362–364. doi: 10.1038/334362a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson L., Nygård O. Structural and functional studies of the interaction of the eukaryotic elongation factor EF-2 with GTP and ribosomes. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Jan 15;171(1-2):293–299. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb13789.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninio J. Kinetic amplification of enzyme discrimination. Biochimie. 1975;57(5):587–595. doi: 10.1016/s0300-9084(75)80139-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parmeggiani A., Swart G. W., Mortensen K. K., Jensen M., Clark B. F., Dente L., Cortese R. Properties of a genetically engineered G domain of elongation factor Tu. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 May;84(10):3141–3145. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.10.3141. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peter M. E., Reiser C. O., Schirmer N. K., Kiefhaber T., Ott G., Grillenbeck N. W., Sprinzl M. Interaction of the isolated domain II/III of Thermus thermophilus elongation factor Tu with the nucleotide exchange factor EF-Ts. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Dec 11;18(23):6889–6893. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.23.6889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peter M. E., Schirmer N. K., Reiser C. O., Sprinzl M. Mapping the effector region in Thermus thermophilus elongation factor Tu. Biochemistry. 1990 Mar 20;29(11):2876–2884. doi: 10.1021/bi00463a033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruusala T., Ehrenberg M., Kurland C. G. Catalytic effects of elongation factor Ts on polypeptide synthesis. EMBO J. 1982;1(1):75–78. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01127.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruusala T., Ehrenberg M., Kurland C. G. Is there proofreading during polypeptide synthesis? EMBO J. 1982;1(6):741–745. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1982.tb01240.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ryazanov A. G., Shestakova E. A., Natapov P. G. Phosphorylation of elongation factor 2 by EF-2 kinase affects rate of translation. Nature. 1988 Jul 14;334(6178):170–173. doi: 10.1038/334170a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. E., Roth J. R. Linkage map of Salmonella typhimurium, Edition VI. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Sep;47(3):410–453. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.3.410-453.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schirmer N. K., Reiser C. O., Sprinzl M. Effect of Thermus thermophilus elongation factor Ts on the conformation of elongation factor Tu. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Sep 1;200(2):295–300. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16185.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seong B. L., Lee C. P., RajBhandary U. L. Suppression of amber codons in vivo as evidence that mutants derived from Escherichia coli initiator tRNA can act at the step of elongation in protein synthesis. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 15;264(11):6504–6508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swart G. W., Parmeggiani A., Kraal B., Bosch L. Effects of the mutation glycine-222----aspartic acid on the functions of elongation factor Tu. Biochemistry. 1987 Apr 7;26(7):2047–2054. doi: 10.1021/bi00381a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapio S., Bilgin N., Ehrenberg M. Impaired in vitro kinetics of EF-Tu mutant Aa. Eur J Biochem. 1990 Mar 10;188(2):347–354. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1990.tb15410.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapio S., Isaksson L. A. Antagonistic effects of mutant elongation factor Tu and ribosomal protein S12 on control of translational accuracy, suppression and cellular growth. Biochimie. 1988 Feb;70(2):273–281. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(88)90071-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapio S., Kurland C. G. Mutant EF-Tu increases missense error in vitro. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Oct;205(1):186–188. doi: 10.1007/BF02428051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapprich W. E., Dahlberg A. E. A single base mutation at position 2661 in E. coli 23S ribosomal RNA affects the binding of ternary complex to the ribosome. EMBO J. 1990 Aug;9(8):2649–2655. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07447.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson R. C., Stone P. J. Proofreading of the codon-anticodon interaction on ribosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Jan;74(1):198–202. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.1.198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tubulekas I., Buckingham R. H., Hughes D. Mutant ribosomes can generate dominant kirromycin resistance. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(12):3635–3643. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.12.3635-3643.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuohy T. M., Thompson S., Gesteland R. F., Hughes D., Atkins J. F. The role of EF-Tu and other translation components in determining translocation step size. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Aug 27;1050(1-3):274–278. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90180-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Noort J. M., Kraal B., Bosch L., La Cour T. F., Nyborg J., Clark B. F. Cross-linking of tRNA at two different sites of the elongation factor Tu. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):3969–3972. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.3969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vijgenboom E., Bosch L. Transfer of plasmid-borne tuf mutations to the chromosome as a genetic tool for studying the functioning of EF-TuA and EF-TuB in the E. coli cell. Biochimie. 1987 Oct;69(10):1021–1030. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(87)90002-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolf H., Chinali G., Parmeggiani A. Mechanism of the inhibition of protein synthesis by kirromycin. Role of elongation factor Tu and ribosomes. Eur J Biochem. 1977 May 2;75(1):67–75. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1977.tb11504.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- la Cour T. F., Nyborg J., Thirup S., Clark B. F. Structural details of the binding of guanosine diphosphate to elongation factor Tu from E. coli as studied by X-ray crystallography. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2385–2388. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03943.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van de Klundert J. A., den Turk E., Borman A. H., van der Meide P. H., Bosch L. Isolation and characterization of a mocimycin resistant mutant of Escherichia coli with an altered elongation factor EF-Tu. FEBS Lett. 1977 Sep 15;81(2):303–307. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(77)80540-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Meide P. H., Vijgenboom E., Talens A., Bosch L. The role of EF-Tu in the expression of tufA and tufB genes. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Feb 1;130(2):397–407. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07166.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]