Abstract
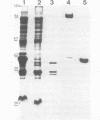
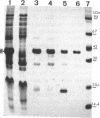
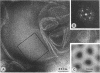
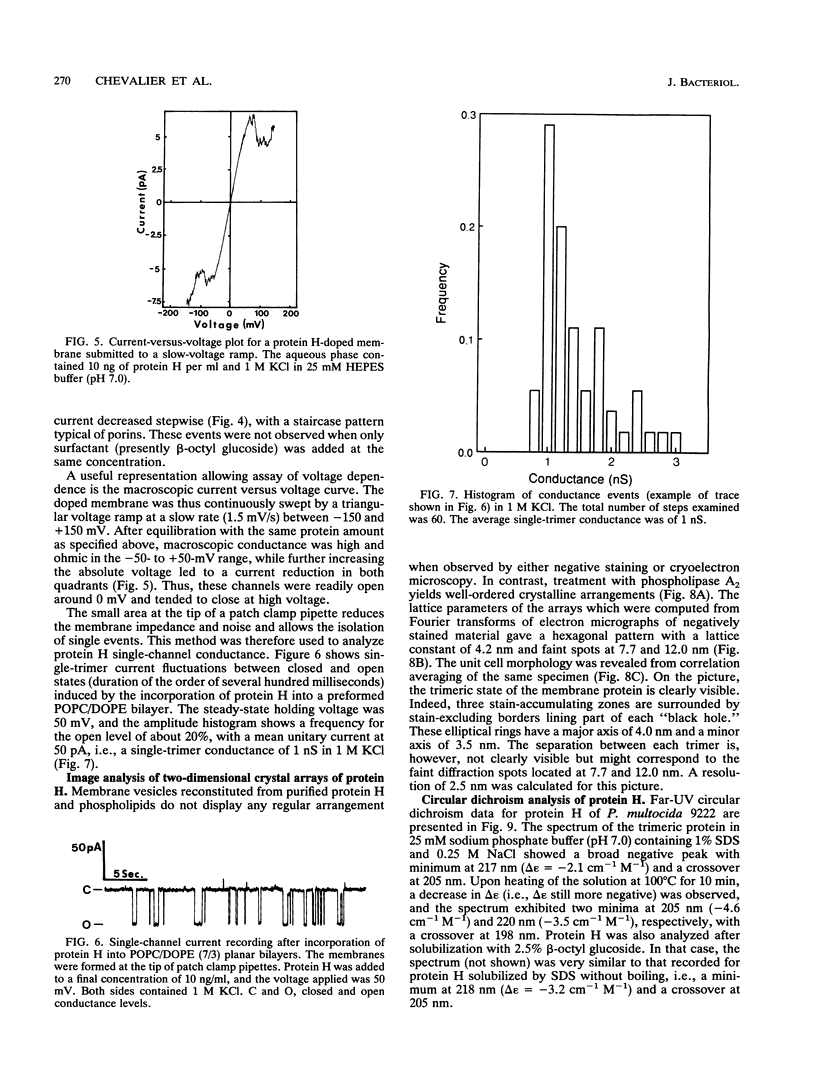
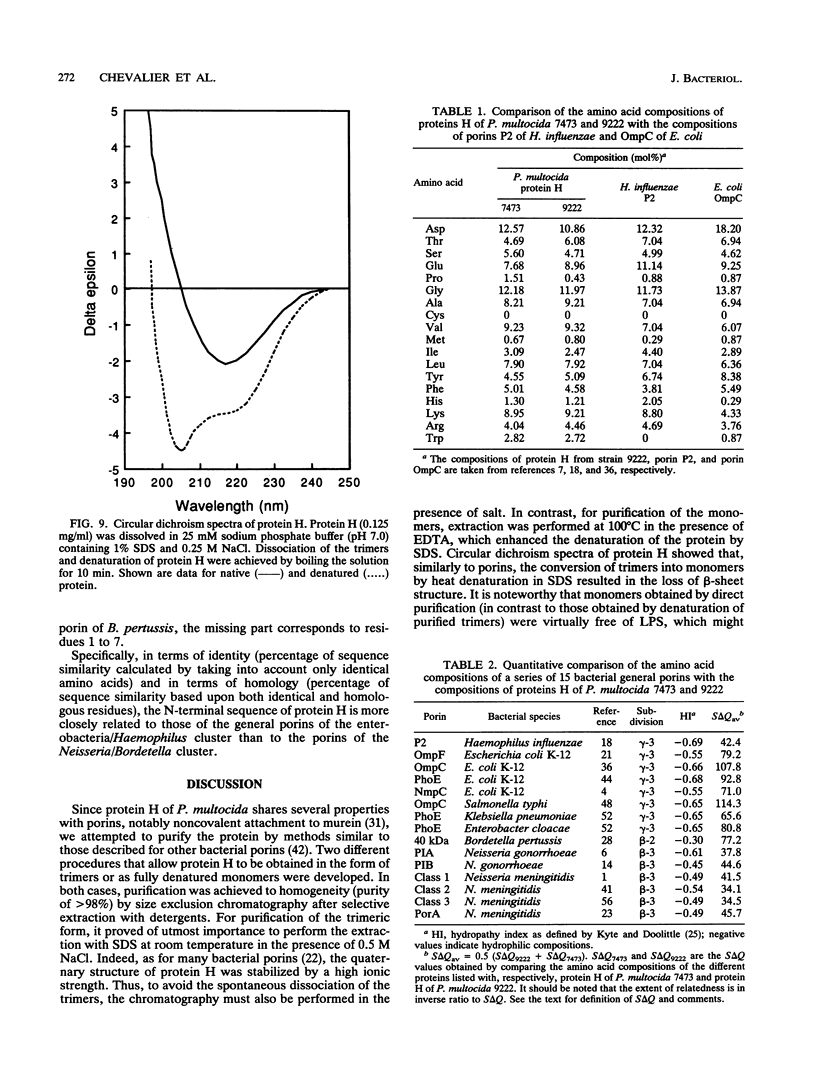
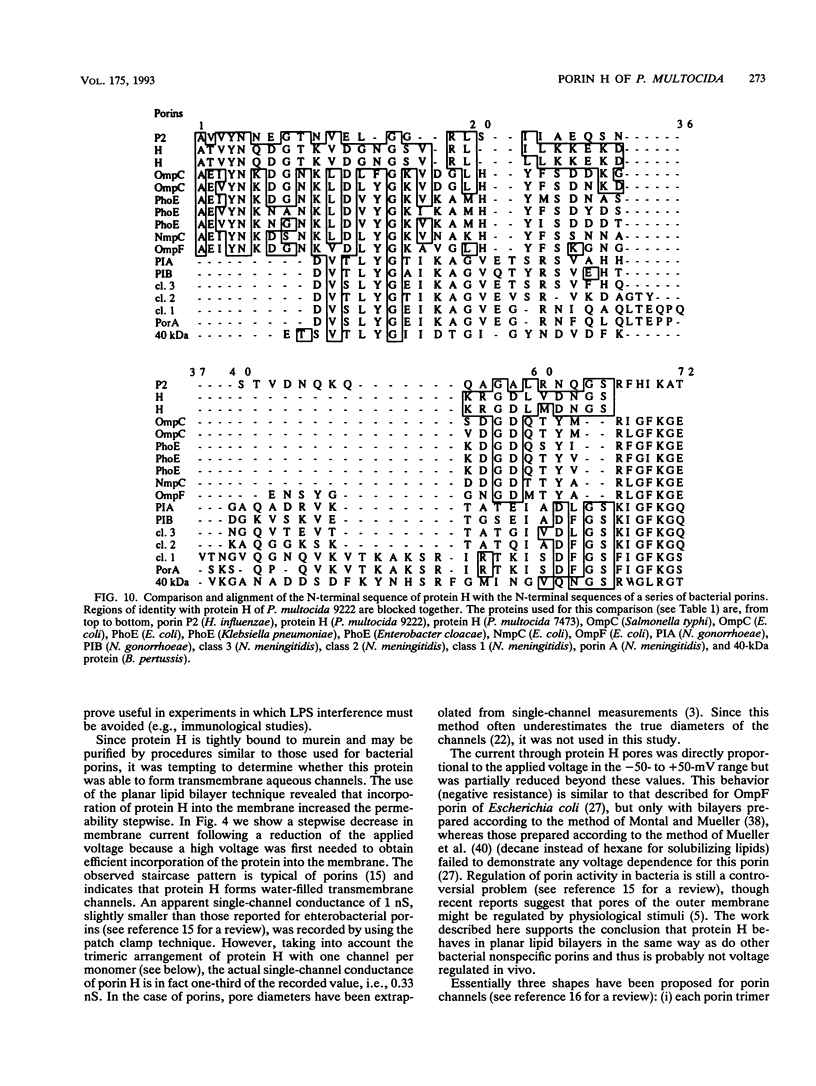
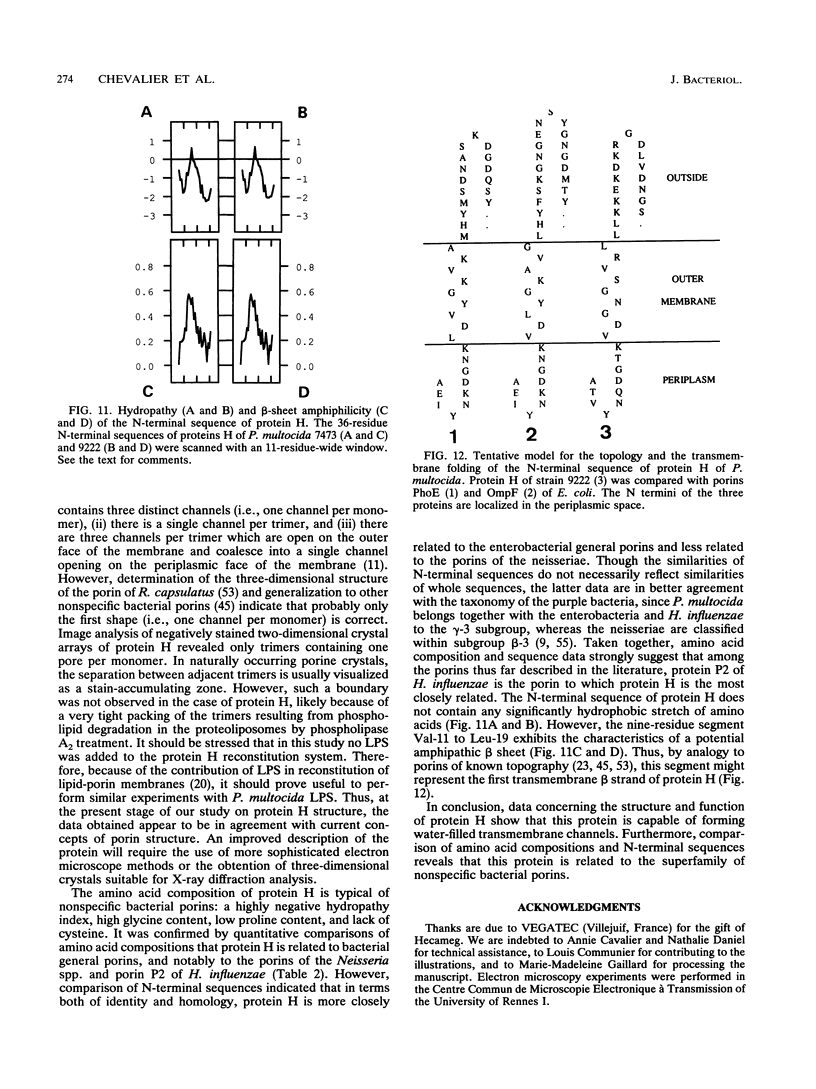
Protein H (B. Lugtenberg, R. van Boxtel, D. Evenberg, M. de Jong, P. Storm, and J. Frik, Infect. Immun. 52:175-182, 1986) is the major polypeptide of the outer membrane of Pasteurella multocida, a bacterium pathogenic for humans and animals. We have purified this protein to homogeneity by size exclusion chromatography after selective extraction with surfactants and demonstrated its pore-forming ability after reincorporation into planar lipid bilayers. In these experiments, the current through the pores was a linear function of the applied voltage in the range of -50 to +50 mV. Voltages beyond +/- 50 mV tended to partially close the channels, giving rise to apparent negative resistances. These observations suggest that protein H channels are probably not voltage regulated in vivo. With the patch clamp technique, single-channel conductance fluctuations of 0.33 nS were recorded in 1 M KCl. Electrophoretic and circular dichroism analyses showed that protein H forms homotrimers stable in sodium dodecyl sulfate at room temperature, with a high content of beta-sheet secondary structure. Upon boiling, the trimers were fully dissociated into monomers with an increase of alpha helix and irregular structure, at the expense of beta sheets. The apparent molecular mass of fully denatured monomers ranged between 37 and 41.8 kDa, depending on the electrophoretic system used for analysis. The trimeric arrangement of protein H was confirmed by image analysis of negatively stained, two-dimensional crystal arrays. This morphological study revealed, in agreement with electrophoretical data, a trimeric structure with an overall diameter of 7.7 nm. Each monomer appeared to contain a pore with an average diameter of 1 nm. Quantitative comparisons revealed that the amino acid composition (hydropathy index of -0.40) and the N-terminal sequence (determined over 36 residues) of protein H are similar to those of bacterial general porins, notably porin P2 of Haemophilus influenzae. We conclude from this set of structural and functional data that protein H of P. multocida is a pore-forming protein related to the superfamily of the nonspecific bacterial porins.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barlow A. K., Heckels J. E., Clarke I. N. The class 1 outer membrane protein of Neisseria meningitidis: gene sequence and structural and immunological similarities to gonococcal porins. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Feb;3(2):131–139. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb01802.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz R., Bauer K. Permeation of hydrophilic molecules through the outer membrane of gram-negative bacteria. Review on bacterial porins. Eur J Biochem. 1988 Sep 1;176(1):1–19. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1988.tb14245.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benz R., Janko K., Boos W., Läuger P. Formation of large, ion-permeable membrane channels by the matrix protein (porin) of Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Aug 17;511(3):305–319. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(78)90269-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blasband A. J., Marcotte W. R., Jr, Schnaitman C. A. Structure of the lc and nmpC outer membrane porin protein genes of lambdoid bacteriophage. J Biol Chem. 1986 Sep 25;261(27):12723–12732. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buechner M., Delcour A. H., Martinac B., Adler J., Kung C. Ion channel activities in the Escherichia coli outer membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 May 9;1024(1):111–121. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(90)90214-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carbonetti N. H., Sparling P. F. Molecular cloning and characterization of the structural gene for protein I, the major outer membrane protein of Neisseria gonorrhoeae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Dec;84(24):9084–9088. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.24.9084. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chevalier G., Le Henaff M., Wroblewski H. Purification, composition en aminoacides et séquence N-terminale de la protéine majoritaire (protéine H) de la membrane externe de Pasteurella multocida. C R Acad Sci III. 1992;314(6):253–258. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cornish-Bowden A. Critical values for testing the significance of amino acid composition indexes. Anal Biochem. 1980 Jul 1;105(2):233–238. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(80)90450-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewhirst F. E., Paster B. J., Olsen I., Fraser G. J. Phylogeny of 54 representative strains of species in the family Pasteurellaceae as determined by comparison of 16S rRNA sequences. J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(6):2002–2013. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.6.2002-2013.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engel A., Massalski A., Schindler H., Dorset D. L., Rosenbusch J. P. Porin channel triplets merge into single outlets in Escherichia coli outer membranes. Nature. 1985 Oct 17;317(6038):643–645. doi: 10.1038/317643a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frank J., Verschoor A., Boublik M. Computer averaging of electron micrographs of 40S ribosomal subunits. Science. 1981 Dec 18;214(4527):1353–1355. doi: 10.1126/science.7313694. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gotschlich E. C., Seiff M. E., Blake M. S., Koomey M. Porin protein of Neisseria gonorrhoeae: cloning and gene structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(22):8135–8139. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.22.8135. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E. Role of porins in outer membrane permeability. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):929–933. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.929-933.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansen E. J., Hasemann C., Clausell A., Capra J. D., Orth K., Moomaw C. R., Slaughter C. A., Latimer J. L., Miller E. E. Primary structure of the porin protein of Haemophilus influenzae type b determined by nucleotide sequence analysis. Infect Immun. 1989 Apr;57(4):1100–1107. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.4.1100-1107.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helenius A., Sarvas M., Simons K. Asymmetric and symmetric membrane reconstitution by detergent elimination. Studies with Semliki-Forest-virus spike glycoprotein and penicillinase from the membrane of Bacillus licheniformis. Eur J Biochem. 1981 May;116(1):27–35. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1981.tb05296.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inokuchi K., Mutoh N., Matsuyama S., Mizushima S. Primary structure of the ompF gene that codes for a major outer membrane protein of Escherichia coli K-12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 11;10(21):6957–6968. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.21.6957. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jap B. K., Walian P. J. Biophysics of the structure and function of porins. Q Rev Biophys. 1990 Nov;23(4):367–403. doi: 10.1017/s003358350000559x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeanteur D., Lakey J. H., Pattus F. The bacterial porin superfamily: sequence alignment and structure prediction. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Sep;5(9):2153–2164. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02145.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessel M., Brennan M. J., Trus B. L., Bisher M. E., Steven A. C. Naturally crystalline porin in the outer membrane of Bordetella pertussis. J Mol Biol. 1988 Sep 5;203(1):275–278. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(88)90108-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kyte J., Doolittle R. F. A simple method for displaying the hydropathic character of a protein. J Mol Biol. 1982 May 5;157(1):105–132. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90515-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakey J. H., Pattus F. The voltage-dependent activity of Escherichia coli porins in different planar bilayer reconstitutions. Eur J Biochem. 1989 Dec 8;186(1-2):303–308. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1989.tb15209.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li Z. M., Hannah J. H., Stibitz S., Nguyen N. Y., Manclark C. R., Brennan M. J. Cloning and sequencing of the structural gene for the porin protein of Bordetella pertussis. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jul;5(7):1649–1656. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01912.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., van Boxtel R., Evenberg D., de Jong M., Storm P., Frik J. Biochemical and immunological characterization of cell surface proteins of Pasteurella multocida strains causing atrophic rhinitis in swine. Infect Immun. 1986 Apr;52(1):175–182. doi: 10.1128/iai.52.1.175-182.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lugtenberg B., van Boxtel R., de Jong M. Atrophic rhinitis in swine: correlation of Pasteurella multocida pathogenicity with membrane protein and lipopolysaccharide patterns. Infect Immun. 1984 Oct;46(1):48–54. doi: 10.1128/iai.46.1.48-54.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MOORE S., STEIN W. H. Procedures for the chromatographic determination of amino acids on four per cent cross-linked sulfonated polystyrene resins. J Biol Chem. 1954 Dec;211(2):893–906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mannella C. A. Lateral segregation of sterol and channel proteins in the mitochondrial outer membrane induced by phospholipase A2: evidence from negative-stain electron microscopy using filipin. J Ultrastruct Mol Struct Res. 1988 Feb;98(2):212–216. doi: 10.1016/s0889-1605(88)80912-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marck C. 'DNA Strider': a 'C' program for the fast analysis of DNA and protein sequences on the Apple Macintosh family of computers. Nucleic Acids Res. 1988 Mar 11;16(5):1829–1836. doi: 10.1093/nar/16.5.1829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno T., Chou M. Y., Inouye M. A comparative study on the genes for three porins of the Escherichia coli outer membrane. DNA sequence of the osmoregulated ompC gene. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):6932–6940. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizuno T., Mizushima S. Isolation and characterization of deletion mutants of ompR and envZ, regulatory genes for expression of the outer membrane proteins OmpC and OmpF in Escherichia coli. J Biochem. 1987 Feb;101(2):387–396. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a121923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Montal M., Mueller P. Formation of bimolecular membranes from lipid monolayers and a study of their electrical properties. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Dec;69(12):3561–3566. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.12.3561. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murakami K., Gotschlich E. C., Seiff M. E. Cloning and characterization of the structural gene for the class 2 protein of Neisseria meningitidis. Infect Immun. 1989 Aug;57(8):2318–2323. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.8.2318-2323.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- OSBORN M. J. STUDIES ON THE GRAM-NEGATIVE CELL WALL. I. EVIDENCE FOR THE ROLE OF 2-KETO- 3-DEOXYOCTONATE IN THE LIPOPOLYSACCHARIDE OF SALMONELLA TYPHIMURIUM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Sep;50:499–506. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.3.499. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overbeeke N., Bergmans H., van Mansfeld F., Lugtenberg B. Complete nucleotide sequence of phoE, the structural gene for the phosphate limitation inducible outer membrane pore protein of Escherichia coli K12. J Mol Biol. 1983 Feb 5;163(4):513–532. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90110-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauptit R. A., Schirmer T., Jansonius J. N., Rosenbusch J. P., Parker M. W., Tucker A. D., Tsernoglou D., Weiss M. S., Schultz G. E. A common channel-forming motif in evolutionarily distant porins. J Struct Biol. 1991 Oct;107(2):136–145. doi: 10.1016/1047-8477(91)90017-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pedersen K. B., Barfod K. The aetiological significance of Bordetella bronchiseptica and Pasteurella multocida in atrophic rhinitis of swine. Nord Vet Med. 1981 Dec;33(12):513–522. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plusquellec D., Chevalier G., Talibart R., Wróblewski H. Synthesis and characterization of 6-O-(N-heptylcarbamoyl)-methyl-alpha-D-glucopyranoside, a new surfactant for membrane studies. Anal Biochem. 1989 May 15;179(1):145–153. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(89)90215-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Puente J. L., Alvarez-Scherer V., Gosset G., Calva E. Comparative analysis of the Salmonella typhi and Escherichia coli ompC genes. Gene. 1989 Nov 30;83(2):197–206. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90105-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxton W. O., Baumeister W. The correlation averaging of a regularly arranged bacterial cell envelope protein. J Microsc. 1982 Aug;127(Pt 2):127–138. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1982.tb00405.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiltz E., Kreusch A., Nestel U., Schulz G. E. Primary structure of porin from Rhodobacter capsulatus. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Aug 1;199(3):587–594. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16158.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tunón P., Johansson K. E. Yet another improved silver staining method for the detection of proteins in polyacrylamide gels. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1984 May;9(2):171–179. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(84)90008-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van der Ley P., Bekkers A., Van Meersbergen J., Tommassen J. A comparative study on the phoE genes of three enterobacterial species. Implications for structure-function relationships in a pore-forming protein of the outer membrane. Eur J Biochem. 1987 Apr 15;164(2):469–475. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1987.tb11080.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M. S., Abele U., Weckesser J., Welte W., Schiltz E., Schulz G. E. Molecular architecture and electrostatic properties of a bacterial porin. Science. 1991 Dec 13;254(5038):1627–1630. doi: 10.1126/science.1721242. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M. S., Kreusch A., Schiltz E., Nestel U., Welte W., Weckesser J., Schulz G. E. The structure of porin from Rhodobacter capsulatus at 1.8 A resolution. FEBS Lett. 1991 Mar 25;280(2):379–382. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80336-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff K., Stern A. The class 3 outer membrane protein (PorB) of Neisseria meningitidis: gene sequence and homology to the gonococcal porin PIA. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Oct 1;67(2):179–185. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90351-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wróblewski H., Johansson K. E., Hjérten S. Purification and characterization of spiralin, the main protein of the Spiroplasma citri membrane. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Mar 1;465(2):275–289. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(77)90079-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang J. T., Wu C. S., Martinez H. M. Calculation of protein conformation from circular dichroism. Methods Enzymol. 1986;130:208–269. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)30013-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]