Abstract
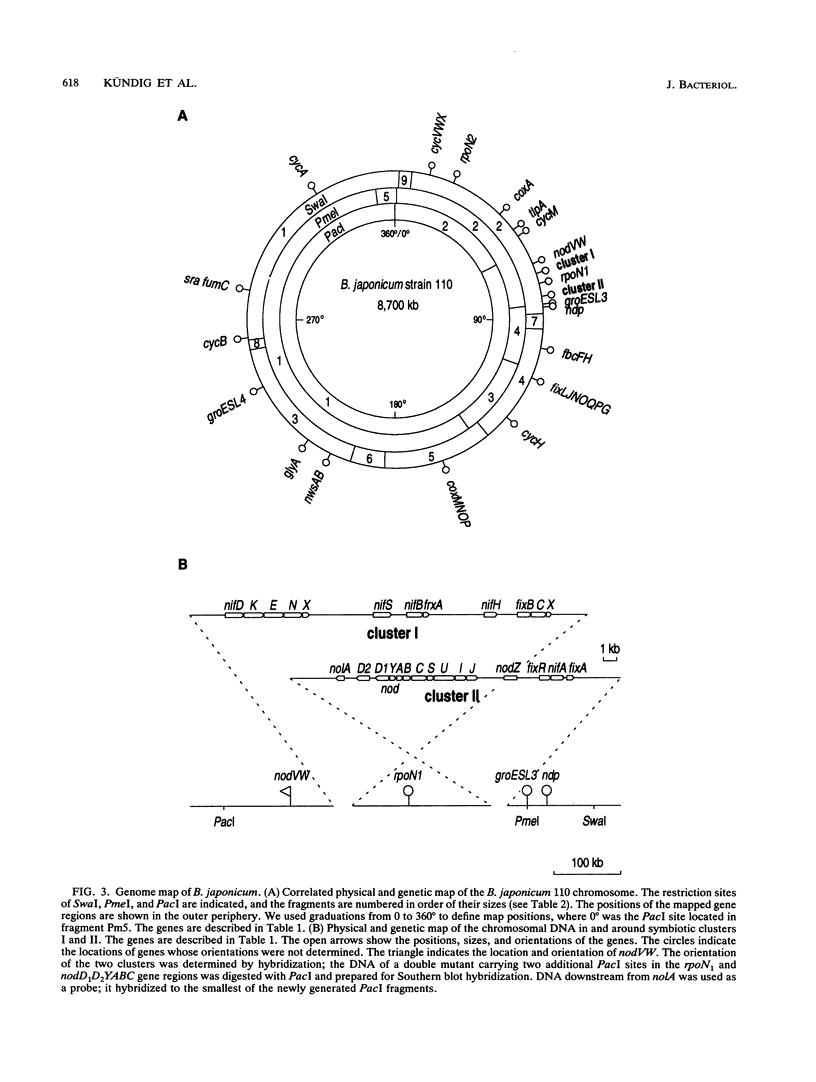
We describe a compilation of 79 known genes of Bradyrhizobium japonicum 110, 63 of which were placed on a correlated physical and genetic map of the chromosome. Genomic DNA was restricted with enzymes PacI, PmeI, and SwaI, which yielded two, five, and nine fragments, respectively. Linkage of some of the fragments was established by performing Southern blot hybridization experiments. For probes we used isolated, labelled fragments that were produced either by PmeI or by SwaI. Genes were mapped on individual restriction fragments by performing gene-directed mutagenesis. The principle of this method was to introduce recognition sites for all three restriction enzymes mentioned above into or very near the desired gene loci. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of restricted mutant DNA then resulted in an altered fragment pattern compared with wild-type DNA. This allowed us to identify overlapping fragments and to determine the exact position of any selected gene locus. The technique was limited only by the accuracy of the fragment size estimates. After linkage of all of the restriction fragments we concluded that the B. japonicum genome consists of a single, circular chromosome that is approximately 8,700 kb long. Genes directly concerned with nodulation and symbiotic nitrogen fixation are clustered in a chromosomal section that is about 380 kb long.
Full text
PDF








Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Acuña G., Ebeling S., Hennecke H. Cloning, sequencing, and mutational analysis of the Bradyrhizobium japonicum fumC-like gene: evidence for the existence of two different fumarases. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Apr;137(4):991–1000. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-4-991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aguilar O. M., Taormino J., Thöny B., Ramseier T., Hennecke H., Szalay A. A. The nifEN genes participating in FeMo cofactor biosynthesis and genes encoding dinitrogenase are part of the same operon in Bradyrhizobium species. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Dec;224(3):413–420. doi: 10.1007/BF00262436. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anand R., Villasante A., Tyler-Smith C. Construction of yeast artificial chromosome libraries with large inserts using fractionation by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3425–3433. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3425. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anthamatten D., Hennecke H. The regulatory status of the fixL- and fixJ-like genes in Bradyrhizobium japonicum may be different from that in Rhizobium meliloti. Mol Gen Genet. 1991 Jan;225(1):38–48. doi: 10.1007/BF00282640. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anthamatten D., Scherb B., Hennecke H. Characterization of a fixLJ-regulated Bradyrhizobium japonicum gene sharing similarity with the Escherichia coli fnr and Rhizobium meliloti fixK genes. J Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;174(7):2111–2120. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.7.2111-2120.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bachmann B. J. Linkage map of Escherichia coli K-12, edition 8. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Jun;54(2):130–197. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.2.130-197.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banfalvi Z., Nieuwkoop A., Schell M., Besl L., Stacey G. Regulation of nod gene expression in Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Nov;214(3):420–424. doi: 10.1007/BF00330475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bott M., Bolliger M., Hennecke H. Genetic analysis of the cytochrome c-aa3 branch of the Bradyrhizobium japonicum respiratory chain. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Dec;4(12):2147–2157. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00576.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bott M., Preisig O., Hennecke H. Genes for a second terminal oxidase in Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Arch Microbiol. 1992;158(5):335–343. doi: 10.1007/BF00245362. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bott M., Ritz D., Hennecke H. The Bradyrhizobium japonicum cycM gene encodes a membrane-anchored homolog of mitochondrial cytochrome c. J Bacteriol. 1991 Nov;173(21):6766–6772. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.21.6766-6772.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantor C. R., Smith C. L., Mathew M. K. Pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of very large DNA molecules. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1988;17:287–304. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.17.060188.001443. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson T. A., Guerinot M. L., Chelm B. K. Characterization of the gene encoding glutamine synthetase I (glnA) from Bradyrhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1985 May;162(2):698–703. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.2.698-703.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang A. C., Cohen S. N. Construction and characterization of amplifiable multicopy DNA cloning vehicles derived from the P15A cryptic miniplasmid. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jun;134(3):1141–1156. doi: 10.1128/jb.134.3.1141-1156.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen H., Keseler I. M., Shimkets L. J. Genome size of Myxococcus xanthus determined by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4206–4213. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4206-4213.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doctor F., Modi V. V. Genetic mapping of leucine and isoleucine-valine loci in Rhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1976 May;126(2):997–998. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.2.997-998.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebeling S., Kündig C., Hennecke H. Discovery of a rhizobial RNA that is essential for symbiotic root nodule development. J Bacteriol. 1991 Oct;173(20):6373–6382. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.20.6373-6382.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebeling S., Noti J. D., Hennecke H. Identification of a new Bradyrhizobium japonicum gene (frxA) encoding a ferredoxinlike protein. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1999–2001. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1999-2001.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fan J. B., Chikashige Y., Smith C. L., Niwa O., Yanagida M., Cantor C. R. Construction of a Not I restriction map of the fission yeast Schizosaccharomyces pombe genome. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 11;17(7):2801–2818. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.7.2801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. "A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity". Addendum. Anal Biochem. 1984 Feb;137(1):266–267. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90381-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frustaci J. M., O'Brian M. R. Characterization of a Bradyrhizobium japonicum ferrochelatase mutant and isolation of the hemH gene. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jul;174(13):4223–4229. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.13.4223-4229.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuhrmann M., Hennecke H. Rhizobium japonicum nitrogenase Fe protein gene (nifH). J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):1005–1011. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.1005-1011.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gabel C., Maier R. J. Nucleotide sequence of the coxA gene encoding subunit I of cytochrome aa3 of Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 25;18(20):6143–6143. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.20.6143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girard M. L., Flores M., Brom S., Romero D., Palacios R., Dávila G. Structural complexity of the symbiotic plasmid of Rhizobium leguminosarum bv. phaseoli. J Bacteriol. 1991 Apr;173(8):2411–2419. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.8.2411-2419.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gubler M., Zürcher T., Hennecke H. The Bradyrhizobium japonicum fixBCX operon: identification of fixX and of a 5' mRNA region affecting the level of the fixBCX transcript. Mol Microbiol. 1989 Feb;3(2):141–148. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1989.tb01803.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerinot M. L., Chelm B. K. Isolation and expression of the Bradyrhizobium japonicum adenylate cyclase gene (cya) in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1984 Sep;159(3):1068–1071. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.3.1068-1071.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göttfert M., Grob P., Hennecke H. Proposed regulatory pathway encoded by the nodV and nodW genes, determinants of host specificity in Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2680–2684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göttfert M., Hitz S., Hennecke H. Identification of nodS and nodU, two inducible genes inserted between the Bradyrhizobium japonicum nodYABC and nodIJ genes. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1990 Sep-Oct;3(5):308–316. doi: 10.1094/mpmi-3-308. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Göttfert M., Holzhäuser D., Bäni D., Hennecke H. Structural and functional analysis of two different nodD genes in Bradyrhizobium japonicum USDA110. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1992 May-Jun;5(3):257–265. doi: 10.1094/mpmi-5-257. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn M., Hennecke H. Mapping of a Bradyrhizobium japonicum DNA Region Carrying Genes for Symbiosis and an Asymmetric Accumulation of Reiterated Sequences. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1987 Sep;53(9):2247–2252. doi: 10.1128/aem.53.9.2247-2252.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn Matthias, Hennecke Hauke. Cloning and Mapping of a Novel Nodulation Region from Bradyrhizobium japonicum by Genetic Complementation of a Deletion Mutant. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1988 Jan;54(1):55–61. doi: 10.1128/aem.54.1.55-61.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanahan D. Studies on transformation of Escherichia coli with plasmids. J Mol Biol. 1983 Jun 5;166(4):557–580. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80284-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heath J. D., Perkins J. D., Sharma B., Weinstock G. M. NotI genomic cleavage map of Escherichia coli K-12 strain MG1655. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;174(2):558–567. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.2.558-567.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennecke H., Günther I., Binder F. A novel cloning vector for the direct selection of recombinant DNA in E. coli. Gene. 1982 Sep;19(2):231–234. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90011-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennecke H. Nitrogen fixation genes involved in the Bradyrhizobium japonicum-soybean symbiosis. FEBS Lett. 1990 Aug 1;268(2):422–426. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81297-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itaya M., Tanaka T. Complete physical map of the Bacillus subtilis 168 chromosome constructed by a gene-directed mutagenesis method. J Mol Biol. 1991 Aug 5;220(3):631–648. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90106-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein S., Lohman K., Clover R., Walker G. C., Signer E. R. A directional, high-frequency chromosomal mobilization system for genetic mapping of Rhizobium meliloti. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;174(1):324–326. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.1.324-326.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohara Y., Akiyama K., Isono K. The physical map of the whole E. coli chromosome: application of a new strategy for rapid analysis and sorting of a large genomic library. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):495–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90503-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kullik I., Fritsche S., Knobel H., Sanjuan J., Hennecke H., Fischer H. M. Bradyrhizobium japonicum has two differentially regulated, functional homologs of the sigma 54 gene (rpoN). J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(3):1125–1138. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.3.1125-1138.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai E., Birren B. W., Clark S. M., Simon M. I., Hood L. Pulsed field gel electrophoresis. Biotechniques. 1989 Jan;7(1):34–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Latreille J., Barlogie B., Dosik G., Johnston D. A., Drewinko B., Alexanian R. Cellular DNA content as a marker of human multiple myeloma. Blood. 1980 Mar;55(3):403–408. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Link A. J., Olson M. V. Physical map of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae genome at 110-kilobase resolution. Genetics. 1991 Apr;127(4):681–698. doi: 10.1093/genetics/127.4.681. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Long S. R. Rhizobium genetics. Annu Rev Genet. 1989;23:483–506. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.23.120189.002411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. B., Chapman K. A., Chelm B. K. Role of the Bradyrhizobium japonicum ntrC gene product in differential regulation of the glutamine synthetase II gene (glnII). J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5452–5459. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5452-5459.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin G. B., Thomashow M. F., Chelm B. K. Bradyrhizobium japonicum glnB, a putative nitrogen-regulatory gene, is regulated by NtrC at tandem promoters. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5638–5645. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5638-5645.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masterson R. V., Prakash R. K., Atherly A. G. Conservation of symbiotic nitrogen fixation gene sequences in Rhizobium japonicum and Bradyrhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):21–26. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.21-26.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathew M. K., Smith C. L., Cantor C. R. High-resolution separation and accurate size determination in pulsed-field gel electrophoresis of DNA. 1. DNA size standards and the effect of agarose and temperature. Biochemistry. 1988 Dec 27;27(26):9204–9210. doi: 10.1021/bi00426a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClelland M., Jones R., Patel Y., Nelson M. Restriction endonucleases for pulsed field mapping of bacterial genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Aug 11;15(15):5985–6005. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.15.5985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClung C. R., Somerville J. E., Guerinot M. L., Chelm B. K. Structure of the Bradyrhizobium japonicum gene hemA encoding 5-aminolevulinic acid synthase. Gene. 1987;54(1):133–139. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90355-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meade H. M., Signer E. R. Genetic mapping of Rhizobium meliloti. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 May;74(5):2076–2078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.5.2076. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Megias M., Caviedes M. A., Palomares A. J., Perezsilva J. Use of plasmid R68.45 for constructing a circular linkage map of the Rhizobium trifolii chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jan;149(1):59–64. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.1.59-64.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noti J. D., Folkerts O., Turken A. N., Szalay A. A. Organization and characterization of genes essential for symbiotic nitrogen fixation from Bradyrhizobium japonicum I110. J Bacteriol. 1986 Sep;167(3):774–783. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.3.774-783.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada N., Sasakawa C., Tobe T., Talukder K. A., Komatsu K., Yoshikawa M. Construction of a physical map of the chromosome of Shigella flexneri 2a and the direct assignment of nine virulence-associated loci identified by Tn5 insertions. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Sep;5(9):2171–2180. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02147.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perret X., Broughton W. J., Brenner S. Canonical ordered cosmid library of the symbiotic plasmid of Rhizobium species NGR234. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Mar 1;88(5):1923–1927. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.5.1923. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramseier T. M., Göttfert M. Codon usage and G + C content in Bradyrhizobium japonicum genes are not uniform. Arch Microbiol. 1991;156(4):270–276. doi: 10.1007/BF00262997. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramseier T. M., Winteler H. V., Hennecke H. Discovery and sequence analysis of bacterial genes involved in the biogenesis of c-type cytochromes. J Biol Chem. 1991 Apr 25;266(12):7793–7803. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Regensburger B., Hennecke H. RNA polymerase from Rhizobium japonicum. Arch Microbiol. 1983 Aug;135(2):103–109. doi: 10.1007/BF00408017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossbach S., Hennecke H. Identification of glyA as a symbiotically essential gene in Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jan;5(1):39–47. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01824.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rossbach S., Loferer H., Acuña G., Appleby C. A., Hennecke H. Cloning, sequencing and mutational analysis of the cytochrome c552 gene (cycB) from Bradyrhizobium japonicum strain 110. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Oct 1;67(2):145–152. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90345-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell P., Schell M. G., Nelson K. K., Halverson L. J., Sirotkin K. M., Stacey G. Isolation and characterization of the DNA region encoding nodulation functions in Bradyrhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1985 Dec;164(3):1301–1308. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.3.1301-1308.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadowsky M. J., Cregan P. B., Gottfert M., Sharma A., Gerhold D., Rodriguez-Quinones F., Keyser H. H., Hennecke H., Stacey G. The Bradyrhizobium japonicum nolA gene and its involvement in the genotype-specific nodulation of soybeans. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 15;88(2):637–641. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.2.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sayavedra-Soto L. A., Powell G. K., Evans H. J., Morris R. O. Nucleotide sequence of the genetic loci encoding subunits of Bradyrhizobium japonicum uptake hydrogenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Nov;85(22):8395–8399. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.22.8395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekine M., Watanabe K., Syono K. Nucleotide sequence of a gene for indole-3-acetamide hydrolase from Bradyrhizobium japonicum. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Aug 11;17(15):6400–6400. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.15.6400. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. L., Condemine G., Chang S. Y., McGary E., Chang S. Insertion of rare cutting sites nearby genes allows their rapid physical mapping: localization of the E. coli map locus. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Jan 25;17(2):817–817. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.2.817. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. L., Condemine G. New approaches for physical mapping of small genomes. J Bacteriol. 1990 Mar;172(3):1167–1172. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.3.1167-1172.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobral B. W., Atherly A. G. A rapid and cost-effective method for preparing genomic DNA from gram-negative bacteria in agarose plugs for pulsed-field gel electrophoresis. Biotechniques. 1989 Oct;7(9):938–938. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobral B. W., Honeycutt R. J., Atherly A. G., McClelland M. Electrophoretic separation of the three Rhizobium meliloti replicons. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(16):5173–5180. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.16.5173-5180.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobral B. W., Honeycutt R. J., Atherly A. G. The genomes of the family Rhizobiaceae: size, stability, and rarely cutting restriction endonucleases. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(2):704–709. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.2.704-709.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sobral B. W., Sadowsky M. J., Atherly A. G. Genome analysis of Bradyrhizobium japonicum serocluster 123 field isolates by using field inversion gel electrophoresis. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jun;56(6):1949–1953. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.6.1949-1953.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thöny-Meyer L., Stax D., Hennecke H. An unusual gene cluster for the cytochrome bc1 complex in Bradyrhizobium japonicum and its requirement for effective root nodule symbiosis. Cell. 1989 May 19;57(4):683–697. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90137-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thöny B., Fischer H. M., Anthamatten D., Bruderer T., Hennecke H. The symbiotic nitrogen fixation regulatory operon (fixRnifA) of Bradyrhizobium japonicum is expressed aerobically and is subject to a novel, nifA-independent type of activation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1987 Oct 26;15(20):8479–8499. doi: 10.1093/nar/15.20.8479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tully R. E., Sadowsky M. J., Keister D. L. Characterization of cytochromes c550 and c555 from Bradyrhizobium japonicum: cloning, mutagenesis, and sequencing of the c555 gene (cycC). J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(24):7887–7895. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.24.7887-7895.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ventra L., Weiss A. S. Transposon-mediated restriction mapping of the Bacillus subtilis chromosome. Gene. 1989 May 15;78(1):29–36. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90311-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wells S. E., Kuykendall L. D. Tryptophan auxotrophs of Rhizobium japonicum. J Bacteriol. 1983 Dec;156(3):1356–1358. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.3.1356-1358.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. K., McClelland M. Dissection of the Salmonella typhimurium genome by use of a Tn5 derivative carrying rare restriction sites. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(11):3807–3811. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.11.3807-3811.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young J. P., Downer H. L., Eardly B. D. Phylogeny of the phototrophic rhizobium strain BTAi1 by polymerase chain reaction-based sequencing of a 16S rRNA gene segment. J Bacteriol. 1991 Apr;173(7):2271–2277. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.7.2271-2277.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Berkum P. Evidence for a Third Uptake Hydrogenase Phenotype among the Soybean Bradyrhizobia. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Dec;56(12):3835–3841. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.12.3835-3841.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





