Abstract
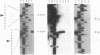
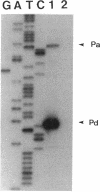
Transcription of the major Bacillus subtilis autolysin gene (cwlB) was investigated. Deletion of the region upstream of the gene cluster lppX-cwbA-cwlB led to a loss of promoter activity. Primer extension analysis suggested that the cwlB operon is transcribed by E sigma D and E sigma A, the former transcripts being predominants at the exponential growth phase. Expression of the lppX-lacZ fusion gene was reduced by about 90% in a sigD-null mutant. A sin (flaD1) mutation caused a severe defect in transcription of the lppX-cwbA-cwlB operon. The sin (flaD1) mutation also reduced expression of a sigD-lacZ fusion gene constructed in the B. subtilis chromosome. Since the sigD-null mutant exhibits motility and autolysin deficiencies and filamentation, similar phenotypes in the sin (flaD1) mutant may be caused by reduction in expression of the sigma D protein.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akamatsu T., Sekiguchi J. Genetic mapping by means of protoplast fusion in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Jun;208(1-2):254–262. doi: 10.1007/BF00330451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anagnostopoulos C., Spizizen J. REQUIREMENTS FOR TRANSFORMATION IN BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Bacteriol. 1961 May;81(5):741–746. doi: 10.1128/jb.81.5.741-746.1961. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnosti D. N., Chamberlin M. J. Secondary sigma factor controls transcription of flagellar and chemotaxis genes in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(3):830–834. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.3.830. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ayusawa D., Yoneda Y., Yamane K., Maruo B. Pleiotropic phenomena in autolytic enzyme(s) content, flagellation, and simultaneous hyperproduction of extracellular alpha-amylase and protease in a Bacillus subtilis mutant. J Bacteriol. 1975 Oct;124(1):459–469. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.1.459-469.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle R. J., Koch A. L. The functions of autolysins in the growth and division of Bacillus subtilis. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1987;15(2):169–222. doi: 10.3109/10408418709104457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubnau D. Genetic competence in Bacillus subtilis. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Sep;55(3):395–424. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.3.395-424.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fein J. E., Rogers H. J. Autolytic enzyme-deficient mutants of Bacillus subtilis 168. J Bacteriol. 1976 Sep;127(3):1427–1442. doi: 10.1128/jb.127.3.1427-1442.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster S. J. Cloning, expression, sequence analysis and biochemical characterization of an autolytic amidase of Bacillus subtilis 168 trpC2. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Aug;137(8):1987–1998. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-8-1987. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaur N. K., Dubnau E., Smith I. Characterization of a cloned Bacillus subtilis gene that inhibits sporulation in multiple copies. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):860–869. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.860-869.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaur N. K., Oppenheim J., Smith I. The Bacillus subtilis sin gene, a regulator of alternate developmental processes, codes for a DNA-binding protein. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(2):678–686. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.2.678-686.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guinand M., Michel G., Balassa G. Lytic enzymes in sporulating Bacillus subtilis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1976 Feb 23;68(4):1287–1293. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(76)90336-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmann J. D. Alternative sigma factors and the regulation of flagellar gene expression. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Dec;5(12):2875–2882. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01847.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Helmann J. D., Márquez L. M., Chamberlin M. J. Cloning, sequencing, and disruption of the Bacillus subtilis sigma 28 gene. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1568–1574. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1568-1574.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbold D. R., Glaser L. Bacillus subtilis N-acetylmuramic acid L-alanine amidase. J Biol Chem. 1975 Mar 10;250(5):1676–1682. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbold D. R., Glaser L. Interaction of N-acetylmuramic acid L-alanine amidase with cell wall polymers. J Biol Chem. 1975 Sep 25;250(18):7231–7238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höltje J. V., Tuomanen E. I. The murein hydrolases of Escherichia coli: properties, functions and impact on the course of infections in vivo. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Mar;137(3):441–454. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-3-441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inoue T., Cech T. R. Secondary structure of the circular form of the Tetrahymena rRNA intervening sequence: a technique for RNA structure analysis using chemical probes and reverse transcriptase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):648–652. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.648. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallio P. T., Fagelson J. E., Hoch J. A., Strauch M. A. The transition state regulator Hpr of Bacillus subtilis is a DNA-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1991 Jul 15;266(20):13411–13417. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamei K., Hara S., Ikenaka T., Murao S. Amino acid sequence of a lysozyme (B-enzyme) from Bacillus subtilis YT-25. J Biochem. 1988 Nov;104(5):832–836. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122558. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroda A., Imazeki M., Sekiguchi J. Purification and characterization of a cell wall hydrolase encoded by the cwlA gene of Bacillus subtilis. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1991 Jun 1;65(1):9–13. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(91)90462-j. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroda A., Rashid M. H., Sekiguchi J. Molecular cloning and sequencing of the upstream region of the major Bacillus subtilis autolysin gene: a modifier protein exhibiting sequence homology to the major autolysin and the spoIID product. J Gen Microbiol. 1992 Jun;138(6):1067–1076. doi: 10.1099/00221287-138-6-1067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroda A., Sekiguchi J. Cloning, sequencing and genetic mapping of a Bacillus subtilis cell wall hydrolase gene. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Nov;136(11):2209–2216. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-11-2209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuroda A., Sekiguchi J. Molecular cloning and sequencing of a major Bacillus subtilis autolysin gene. J Bacteriol. 1991 Nov;173(22):7304–7312. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.22.7304-7312.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Louie P., Lee A., Stansmore K., Grant R., Ginther C., Leighton T. Roles of rpoD, spoIIF, spoIIJ, spoIIN, and sin in regulation of Bacillus subtilis stage II sporulation-specific transcription. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(11):3570–3576. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.11.3570-3576.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandic-Mulec I., Gaur N., Bai U., Smith I. Sin, a stage-specific repressor of cellular differentiation. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(11):3561–3569. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.11.3561-3569.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Msadek T., Kunst F., Henner D., Klier A., Rapoport G., Dedonder R. Signal transduction pathway controlling synthesis of a class of degradative enzymes in Bacillus subtilis: expression of the regulatory genes and analysis of mutations in degS and degU. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):824–834. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.824-834.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Márquez L. M., Helmann J. D., Ferrari E., Parker H. M., Ordal G. W., Chamberlin M. J. Studies of sigma D-dependent functions in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):3435–3443. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.3435-3443.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Priest F. G. Extracellular enzyme synthesis in the genus Bacillus. Bacteriol Rev. 1977 Sep;41(3):711–753. doi: 10.1128/br.41.3.711-753.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qi F. X., Doi R. H. Localization of a second SigH promoter in the Bacillus subtilis sigA operon and regulation of dnaE expression by the promoter. J Bacteriol. 1990 Oct;172(10):5631–5636. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.10.5631-5636.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers H. J., Taylor C., Rayter S., Ward J. B. Purification and properties of autolytic endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase and the N-acetylmuramyl-L-alanine amidase from Bacillus subtilis strain 168. J Gen Microbiol. 1984 Sep;130(9):2395–2402. doi: 10.1099/00221287-130-9-2395. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadaie Y., Kada T. Bacillus subtilis gene involved in cell division, sporulation, and exoenzyme secretion. J Bacteriol. 1985 Aug;163(2):648–653. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.2.648-653.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadaie Y., Takamatsu H., Nakamura K., Yamane K. Sequencing reveals similarity of the wild-type div+ gene of Bacillus subtilis to the Escherichia coli secA gene. Gene. 1991 Feb 1;98(1):101–105. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90110-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer P., Millet J., Aubert J. P. Catabolic repression of bacterial sporulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Sep;54(3):704–711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.3.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekiguchi J., Ezaki B., Kodama K., Akamatsu T. Molecular cloning of a gene affecting the autolysin level and flagellation in Bacillus subtilis. J Gen Microbiol. 1988 Jun;134(6):1611–1621. doi: 10.1099/00221287-134-6-1611. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekiguchi J., Ohsu H., Kuroda A., Moriyama H., Akamatsu T. Nucleotide sequences of the Bacillus subtilis flaD locus and a B. licheniformis homologue affecting the autolysin level and flagellation. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Jul;136(7):1223–1230. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-7-1223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sekiguchi J., Takada N., Okada H. Genes affecting the productivity of alpha-amylase in Bacillus subtilis Marburg. J Bacteriol. 1975 Feb;121(2):688–694. doi: 10.1128/jb.121.2.688-694.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimotsu H., Henner D. J. Modulation of Bacillus subtilis levansucrase gene expression by sucrose and regulation of the steady-state mRNA level by sacU and sacQ genes. J Bacteriol. 1986 Oct;168(1):380–388. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.1.380-388.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinmetz M., Kunst F., Dedonder R. Mapping of mutations affecting synthesis of exocellular enzymes in Bacillus subtilis. Identity of the sacUh, amyB and pap mutations. Mol Gen Genet. 1976 Nov 17;148(3):281–285. doi: 10.1007/BF00332902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]