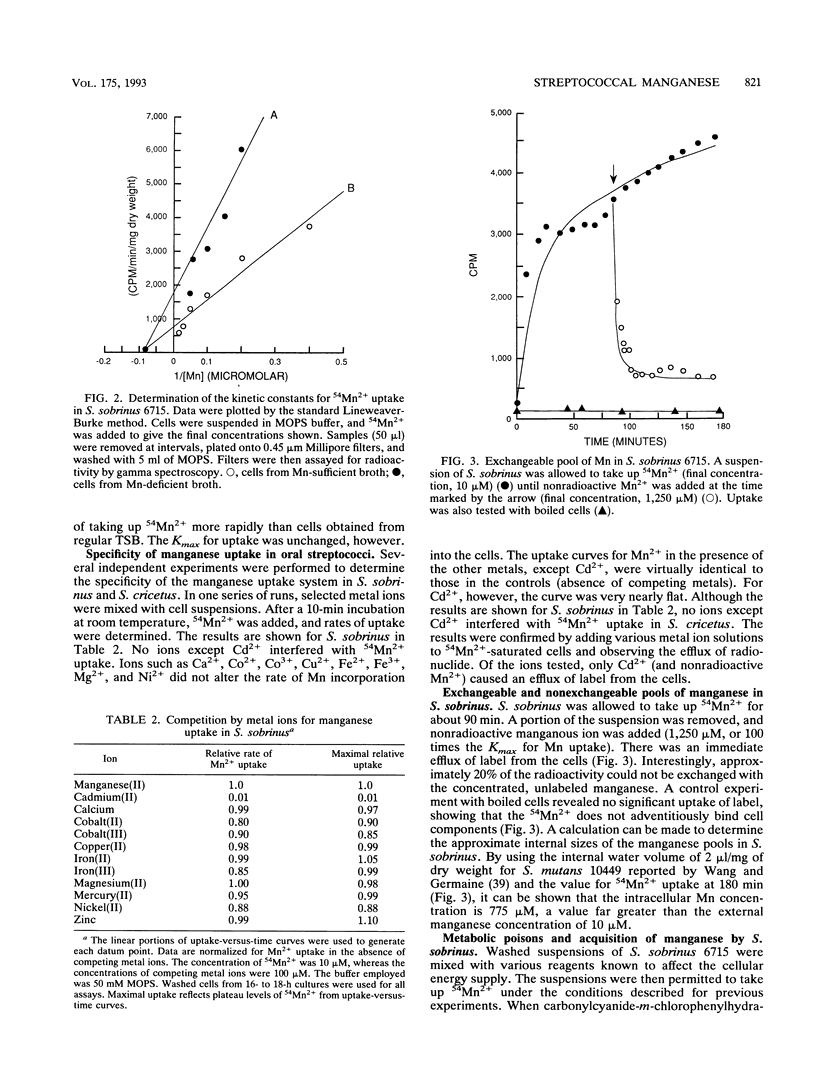
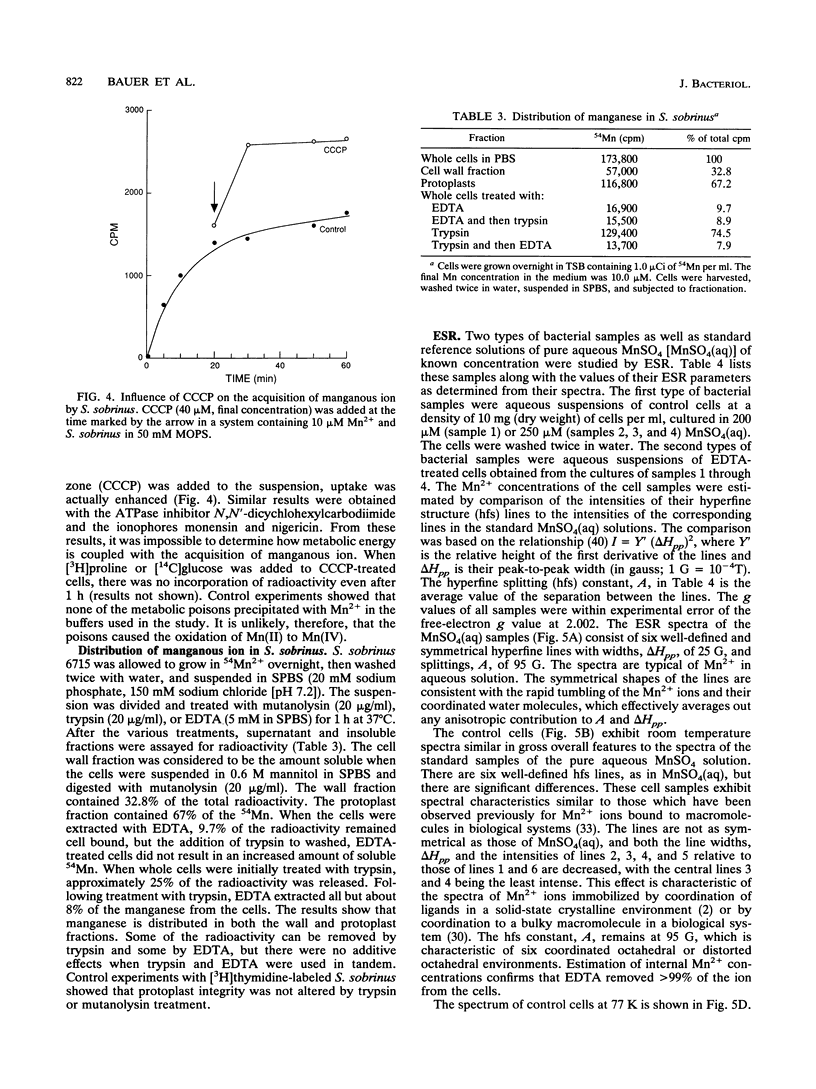
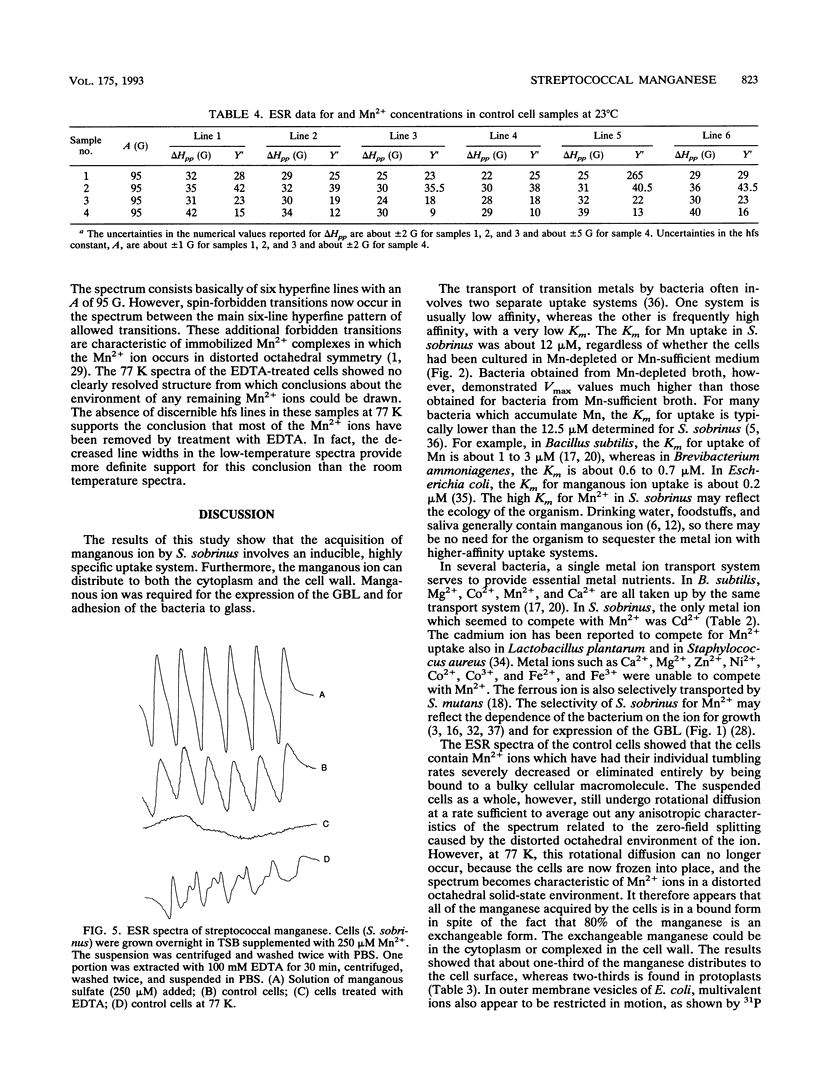
Abstract
The cariogenic bacteria Streptococcus sobrinus and S. cricetus were shown to have an absolute requirement for manganous ion in order to bind glucans or to adhere to glass in the presence of sucrose. The bacteria possessed a reasonably high affinity transport system for 54Mn2+, yielding a Km of about 12 microM. The Vmax for uptake of 54Mn2+ in S. sobrinus was increased when the bacteria were grown in Mn-depleted medium, but the Km remained the same. There was no evidence for two Mn2+ uptake systems, commonly observed for many bacteria. Ions such as Ca2+, Co2+, Co3+, Cu2+, Fe2+, Fe3+, Hg2+, Mg2+, Ni2+, and Zn2+ did not inhibit the uptake of 54Mn2+ by the bacteria, although Cd2+ was a potent inhibitor. Fractionation experiments showed that manganese was distributed in protoplasts (67%) and in the cell wall (33%). Approximately 80% of the 54Mn2+ in S. sobrinus was rapidly exchangeable with nonradioactive Mn2+. Electron spin resonance experiments showed that all of the manganese was bound or restricted in mobility. Proton motive force-dissipating agents increased the acquisition of 54Mn2+ by the streptococci, probably because the wall became more negatively charged when the cell could no longer produce protons.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aranha H., Strachan R. C., Arceneaux J. E., Byers B. R. Effect of trace metals on growth of Streptococcus mutans in a teflon chemostat. Infect Immun. 1982 Feb;35(2):456–460. doi: 10.1128/iai.35.2.456-460.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archibald F. S., Duong M. N. Manganese acquisition by Lactobacillus plantarum. J Bacteriol. 1984 Apr;158(1):1–8. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.1.1-8.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Archibald F. Manganese: its acquisition by and function in the lactic acid bacteria. Crit Rev Microbiol. 1986;13(1):63–109. doi: 10.3109/10408418609108735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beighton D. The influence of manganese on carbohydrate metabolism and caries induction by Streptococcus mutans strain Ingbritt. Caries Res. 1982;16(2):189–192. doi: 10.1159/000260596. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beveridge T. J. Role of cellular design in bacterial metal accumulation and mineralization. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1989;43:147–171. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.43.100189.001051. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bowen W. H. The trace element requirements of cariogenic and non-cariogenic streptococci. Arch Oral Biol. 1968 Jun;13(6):713–714. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(68)90151-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chludzinski A. M., Germaine G. R., Schachtele C. F. Streptoccus mutans dextransucrase: purification, properties, and requirement for primer dextran. J Dent Res. 1976 Apr;55(Spec No):C75–C86. doi: 10.1177/002203457605500329011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curtiss R., 3rd Genetic analysis of Streptococcus mutans virulence. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1985;118:253–277. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-70586-1_14. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curzon M. E., Crocker D. C. Relationships of trace elements in human tooth enamel to dental caries. Arch Oral Biol. 1978;23(8):647–653. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(78)90189-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Doyle R. J., Matthews T. H., Streips U. N. Chemical basis for selectivity of metal ions by the Bacillus subtilis cell wall. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jul;143(1):471–480. doi: 10.1128/jb.143.1.471-480.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake D., Taylor K. G., Bleiweis A. S., Doyle R. J. Specificity of the glucan-binding lectin of Streptococcus cricetus. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1864–1872. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1864-1872.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake D., Taylor K. G., Doyle R. J. Expression of the glucan-binding lectin of Streptococcus cricetus requires manganous ion. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):2205–2207. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.2205-2207.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenstadt E., Fisher S., Der C. L., Silver S. Manganese transport in Bacillus subtilis W23 during growth and sporulation. J Bacteriol. 1973 Mar;113(3):1363–1372. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.3.1363-1372.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans S. L., Arceneaux J. E., Byers B. R., Martin M. E., Aranha H. Ferrous iron transport in Streptococcus mutans. J Bacteriol. 1986 Dec;168(3):1096–1099. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.3.1096-1099.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fisher S., Buxbaum L., Toth K., Eisenstadt E., Silver S. Regulation of manganese accumulation and exchange in Bacillus subtilis W23. J Bacteriol. 1973 Mar;113(3):1373–1380. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.3.1373-1380.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Fitzgerald R. J. Dextran-induced agglutination of Streptococcus mutans, and its potential role in the formation of microbial dental plaques. J Bacteriol. 1969 May;98(2):341–346. doi: 10.1128/jb.98.2.341-346.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gibbons R. J., Nygaard M. Synthesis of insoluble dextran and its significance in the formation of gelatinous deposits by plaque-forming streptococci. Arch Oral Biol. 1968 Oct;13(10):1249–1262. doi: 10.1016/0003-9969(68)90081-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landale E. C., McCabe M. M. Characterization by affinity electrophoresis of an alpha-1,6-glucan-binding protein from Streptococcus sobrinus. Infect Immun. 1987 Dec;55(12):3011–3016. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.12.3011-3016.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesche W. J. Role of Streptococcus mutans in human dental decay. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Dec;50(4):353–380. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.4.353-380.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lü-Lü, Singh J. S., Galperin M. Y., Drake D., Taylor K. G., Doyle R. J. Chelating agents inhibit activity and prevent expression of streptococcal glucan-binding lectins. Infect Immun. 1992 Sep;60(9):3807–3813. doi: 10.1128/iai.60.9.3807-3813.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin M. E., Strachan R. C., Aranha H., Evans S. L., Salin M. L., Welch B., Arceneaux J. E., Byers B. R. Oxygen toxicity in Streptococcus mutans: manganese, iron, and superoxide dismutase. J Bacteriol. 1984 Aug;159(2):745–749. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.2.745-749.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry R. D., Silver S. Cadmium and manganese transport in Staphylococcus aureus membrane vesicles. J Bacteriol. 1982 May;150(2):973–976. doi: 10.1128/jb.150.2.973-976.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver S., Johnseine P., King K. Manganese Active Transport in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1970 Dec;104(3):1299–1306. doi: 10.1128/jb.104.3.1299-1306.1970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strachan R. C., Aranha H., Lodge J. S., Arceneaux J. E., Byers B. R. Teflon chemostat for studies of trace metal metabolism in Streptococcus mutans and other bacteria. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Jan;43(1):257–260. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.1.257-260.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urrutia Mera M., Kemper M., Doyle R., Beveridge T. J. The membrane-induced proton motive force influences the metal binding ability of Bacillus subtilis cell walls. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Dec;58(12):3837–3844. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.12.3837-3844.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang Y. B., Germaine G. R. Effect of lysozyme on glucose fermentation, cytoplasmic pH, and intracellular potassium concentrations in Streptococcus mutans 10449. Infect Immun. 1991 Feb;59(2):638–644. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.2.638-644.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



