Abstract
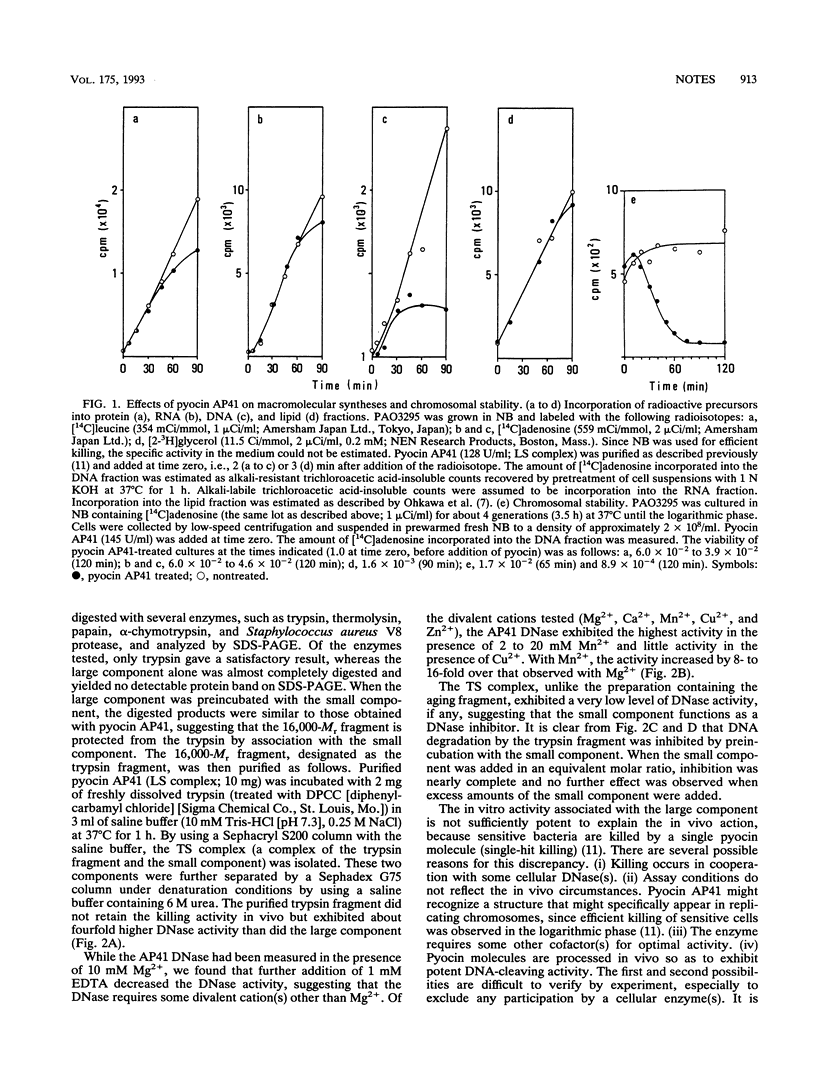
Pyocin AP41 degrades the chromosomal DNA in sensitive strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa but has little effect on RNA, protein, and lipid syntheses. In vitro experiments showed that the carboxyl-terminal part of the large subunit of pyocin AP41 carries an inherent DNase that is responsible for its killing action.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cole S. T., Saint-Joanis B., Pugsley A. P. Molecular characterisation of the colicin E2 operon and identification of its products. Mol Gen Genet. 1985;198(3):465–472. doi: 10.1007/BF00332940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway B. W., Rossiter H., Burgess D., Dodge J. Aeruginocin tolerant mutants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Genet Res. 1973 Dec;22(3):239–253. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300013069. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau P. C., Rowsome R. W., Zuker M., Visentin L. P. Comparative nucleotide sequences encoding the immunity proteins and the carboxyl-terminal peptides of colicins E2 and E3. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Nov 26;12(22):8733–8745. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.22.8733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Obinata M., Mizuno D. Mechanism of colicin E2-induced DNA degradation in Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Feb 18;199(2):330–339. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90076-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okawa I., Maruo B., Kageyama M. Preferential inhibition of lipid synthesis by the bacteriocin pyocin S2. J Biochem. 1975 Jul;78(1):213–223. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugsley A. P. Autoinduced synthesis of colicin E2. Mol Gen Genet. 1983;190(3):379–383. doi: 10.1007/BF00331062. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ringrose P. Sedimentation analysis of DNA degradation products resulting from the action of colicin E2 on Escherichia coli. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 Aug 8;213(2):320–334. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(70)90040-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano Y., Kageyama M. Genetic determinant of pyocin AP41 as an insert in the Pseudomonas aeruginosa chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1984 May;158(2):562–570. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.2.562-570.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano Y., Kageyama M. Purification and properties of an S-type pyocin, pyocin AP41. J Bacteriol. 1981 May;146(2):733–739. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.2.733-739.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaller K., Nomura M. Colicin E2 is DNA endonuclease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Nov;73(11):3989–3993. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.11.3989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto H., Nishida K. I., Beppu T., Arima K. Tryptic digestion of colicin E2 and its active fragment. J Biochem. 1978 Mar;83(3):827–834. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]