Abstract
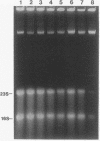
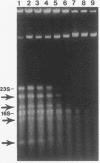
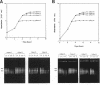
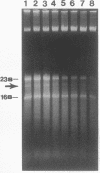
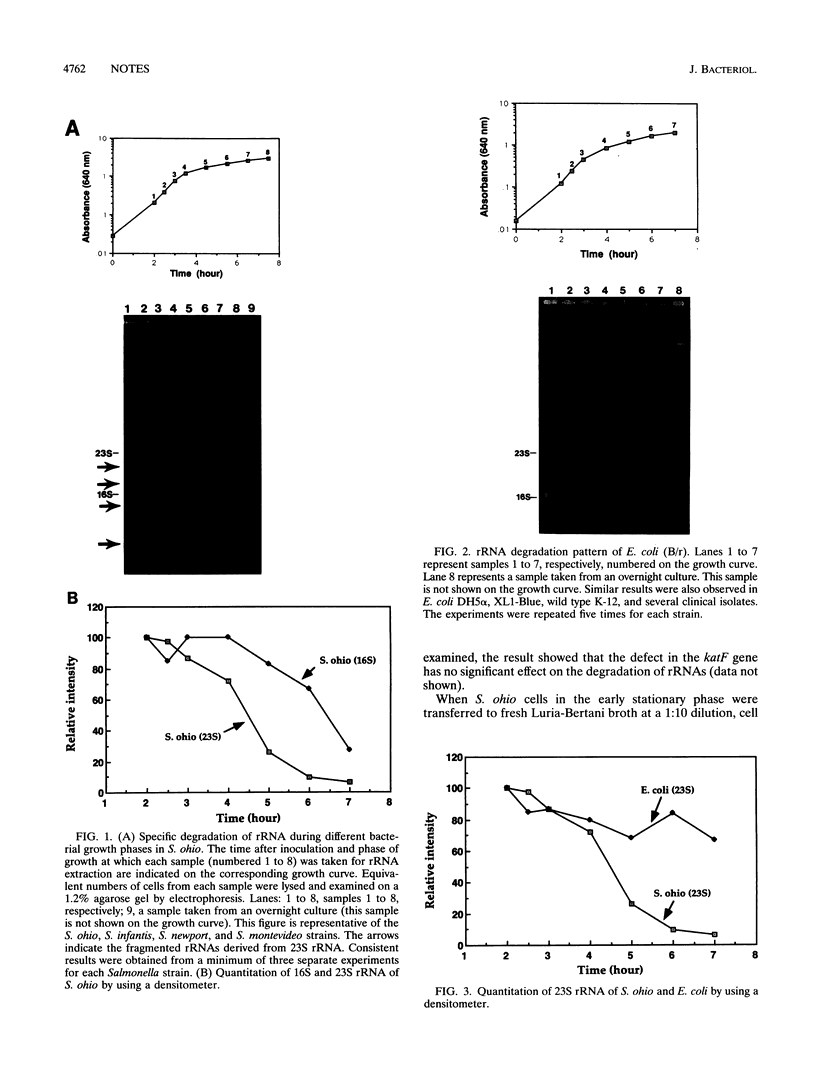
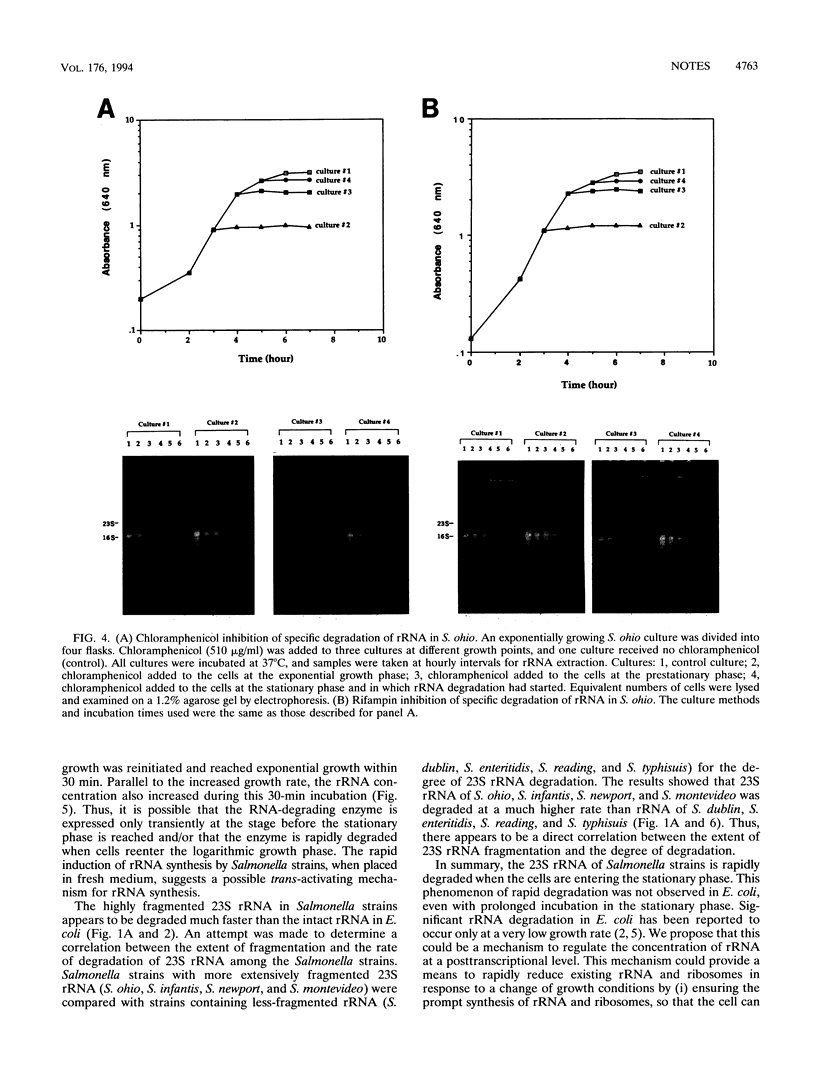
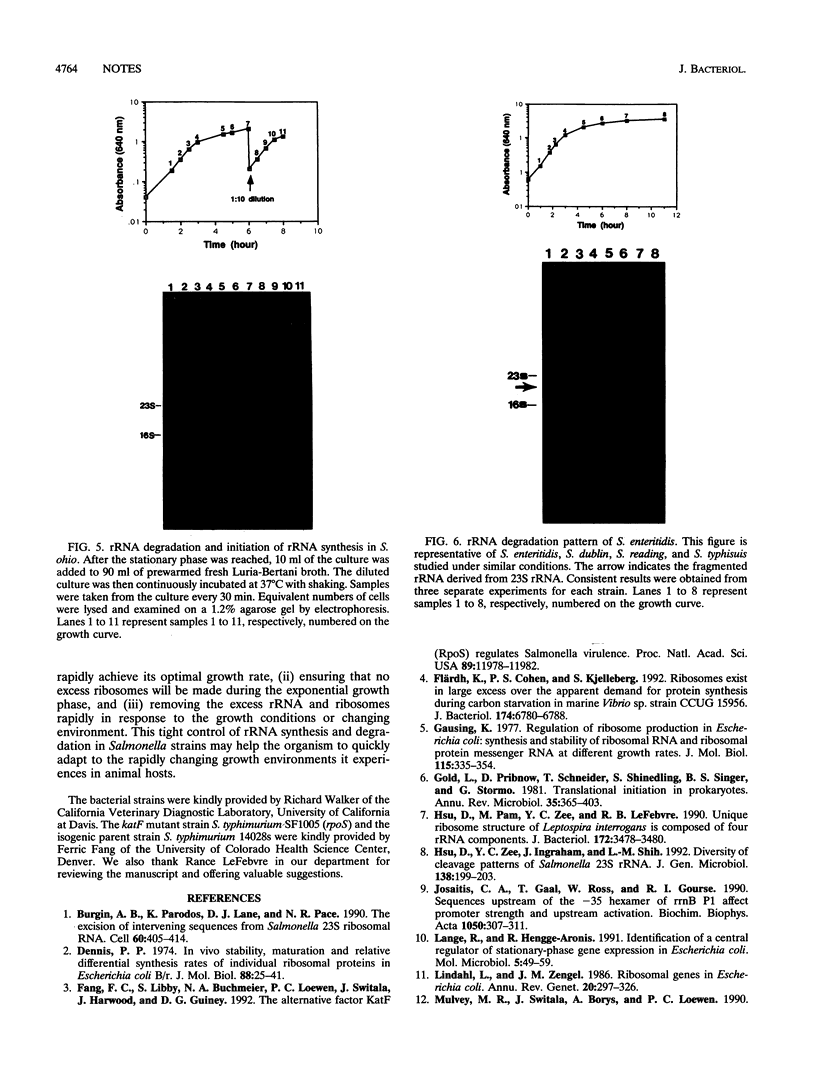
We have previously shown that the 23S rRNA of Salmonella strains is highly fragmented by specific enzyme cleavages. In this article, we report that 23S rRNA of Salmonella strains is rapidly degraded as the cells enter the stationary phase. More than 90% of the 23S rRNA is degraded when the cells reach the stationary phase. The rate of degradation of 23S rRNA correlated with its degree of fragmentation. This degradation is probably mediated by newly synthesized protein factor(s), since treatment with chloramphenicol or rifampin inhibits the rRNA degradation. We propose that degradation of 23S rRNA is a novel mechanism in the regulation of the bacterial 23S rRNA and ribosome concentration and that this additional regulatory mechanism provides some selective advantage to cells.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Burgin A. B., Parodos K., Lane D. J., Pace N. R. The excision of intervening sequences from Salmonella 23S ribosomal RNA. Cell. 1990 Feb 9;60(3):405–414. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90592-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dennis P. P. In vivo stability, maturation and relative differential synthesis rates of individual ribosomal proteins in Escherichia coli B/r. J Mol Biol. 1974 Sep 5;88(1):25–41. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(74)90293-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Flärdh K., Cohen P. S., Kjelleberg S. Ribosomes exist in large excess over the apparent demand for protein synthesis during carbon starvation in marine Vibrio sp. strain CCUG 15956. J Bacteriol. 1992 Nov;174(21):6780–6788. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.21.6780-6788.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gausing K. Regulation of ribosome production in Escherichia coli: synthesis and stability of ribosomal RNA and of ribosomal protein messenger RNA at different growth rates. J Mol Biol. 1977 Sep 25;115(3):335–354. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90158-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold L., Pribnow D., Schneider T., Shinedling S., Singer B. S., Stormo G. Translational initiation in prokaryotes. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1981;35:365–403. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.35.100181.002053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu D., Pan M. J., Zee Y. C., LeFebvre R. B. Unique ribosome structure of Leptospira interrogans is composed of four rRNA components. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jun;172(6):3478–3480. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.6.3478-3480.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu D., Zee Y. C., Ingraham J., Shih L. M. Diversity of cleavage patterns of Salmonella 23S rRNA. J Gen Microbiol. 1992 Jan;138(1):199–203. doi: 10.1099/00221287-138-1-199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Josaitis C. A., Gaal T., Ross W., Gourse R. L. Sequences upstream of the-35 hexamer of rrnB P1 affect promoter strength and upstream activation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Aug 27;1050(1-3):307–311. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90186-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lange R., Hengge-Aronis R. Identification of a central regulator of stationary-phase gene expression in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jan;5(1):49–59. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01825.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindahl L., Zengel J. M. Ribosomal genes in Escherichia coli. Annu Rev Genet. 1986;20:297–326. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.20.120186.001501. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura M., Gourse R., Baughman G. Regulation of the synthesis of ribosomes and ribosomal components. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:75–117. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.000451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. The 3'-terminal sequence of Escherichia coli 16S ribosomal RNA: complementarity to nonsense triplets and ribosome binding sites. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Apr;71(4):1342–1346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.4.1342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verbeek H., Nilsson L., Baliko G., Bosch L. Potential binding sites of the trans-activator FIS are present upstream of all rRNA operons and of many but not all tRNA operons. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Aug 27;1050(1-3):302–306. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90185-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vicente M., Kushner S. R., Garrido T., Aldea M. The role of the 'gearbox' in the transcription of essential genes. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Sep;5(9):2085–2091. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb02137.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada A., Yamazaki Y., Fujita N., Ishihama A. Structure and probable genetic location of a "ribosome modulation factor" associated with 100S ribosomes in stationary-phase Escherichia coli cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(7):2657–2661. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.7.2657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wittmann H. G. Components of bacterial ribosomes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1982;51:155–183. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.51.070182.001103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zacharias M., Theissen G., Bradaczek C., Wagner R. Analysis of sequence elements important for the synthesis and control of ribosomal RNA in E coli. Biochimie. 1991 Jun;73(6):699–712. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(91)90050-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]