Abstract
Two extracellular autolysins have been detected in the spent culture supernatants of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 by using renaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The two autolysins were isolated from the culture supernatant by trichloroacetic acid precipitation and were shown to have apparent molecular masses of 26 and 29 kDa. The 26-kDa autolysin first appears during the early exponential phase of growth and then declines sharply, while the 29-kDa autolysin first appears in the late exponential phase of growth and continues well into the stationary phase. Fractionation of whole cells indicated that the 26-kDa enzyme was also localized within the periplasm, with a lesser amount of activity associated with the cytoplasmic membrane. The 29-kDa autolytic activity was distributed within the cell equally between the periplasm and the cytoplasmic membrane. The pH optima of the isolated 26- and 29-kDa autolysins are 6.0 and 5.0, respectively. Further evidence from both protease susceptibility and inhibition studies confirms that these two extracellular autolysins isolated from P. aeruginosa PAO1 are separate and distinct.
Full text
PDF


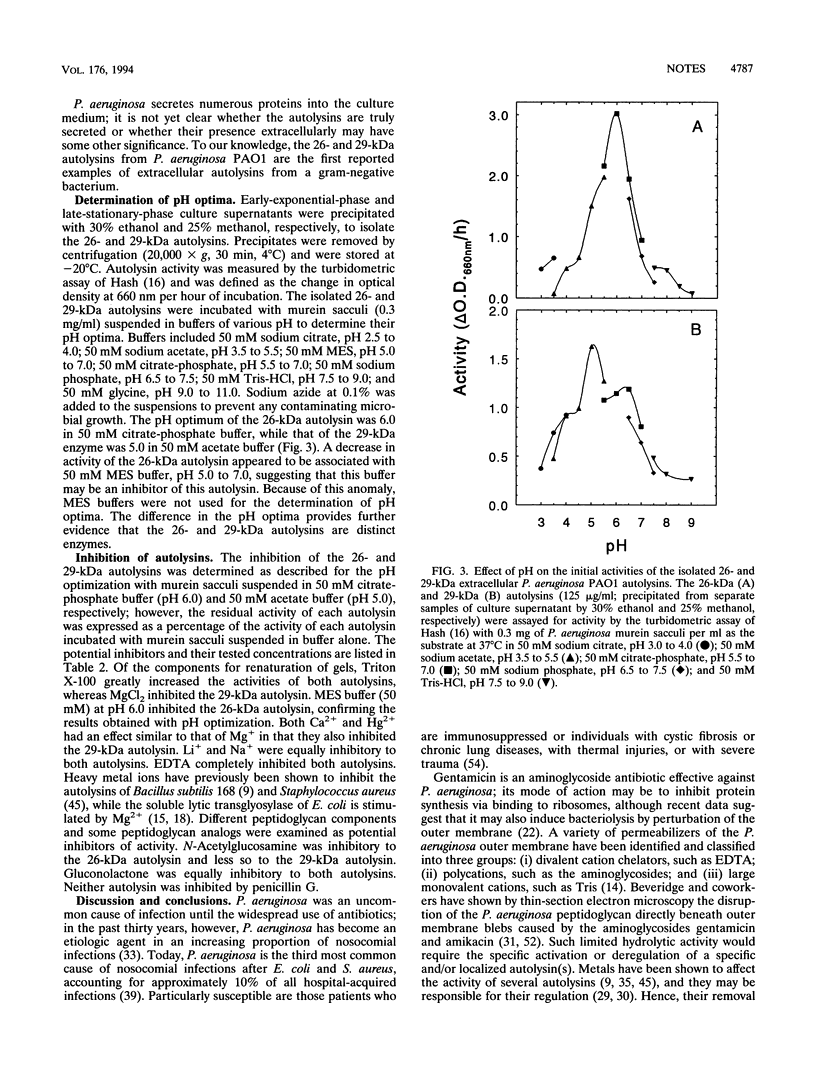


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brito N., Falcón M. A., Carnicero A., Gutiérrez-Navarro A. M., Mansito T. B. Purification and peptidase activity of a bacteriolytic extracellular enzyme from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Res Microbiol. 1989 Feb;140(2):125–137. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(89)90046-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burman L. G., Park J. T. Changes in the composition of Escherichia coli murein as it ages during exponential growth. J Bacteriol. 1983 Aug;155(2):447–453. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.2.447-453.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke A. J. Extent of peptidoglycan O acetylation in the tribe Proteeae. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jul;175(14):4550–4553. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.14.4550-4553.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Driehuis F., Wouters J. T. Effect of growth rate and cell shape on the peptidoglycan composition in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jan;169(1):97–101. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.1.97-101.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fontana R., Satta G., Romanzi C. A. Penicillins activate autolysins extracted from both Escherichia coli and Klebsiella pneumoniae envelopes. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1977 Dec;12(6):745–747. doi: 10.1128/aac.12.6.745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Foster S. J. Analysis of the autolysins of Bacillus subtilis 168 during vegetative growth and differentiation by using renaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jan;174(2):464–470. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.2.464-470.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glauner B., Höltje J. V. Growth pattern of the murein sacculus of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1990 Nov 5;265(31):18988–18996. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodell E. W., Schwarz U. Release of cell wall peptides into culture medium by exponentially growing Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):391–397. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.391-397.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenway D. L., Perkins H. R. Turnover of the cell wall peptidoglycan during growth of Neisseria gonorrhoeae and Escherichia coli. Relative stability of newly synthesized material. J Gen Microbiol. 1985 Feb;131(2):253–263. doi: 10.1099/00221287-131-2-253. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock R. E., Wong P. G. Compounds which increase the permeability of the Pseudomonas aeruginosa outer membrane. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1984 Jul;26(1):48–52. doi: 10.1128/aac.26.1.48. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartmann R., Höltje J. V., Schwarz U. Targets of penicillin action in Escherichia coli. Nature. 1972 Feb 25;235(5339):426–429. doi: 10.1038/235426a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hash J. H. Measurement of bacteriolytic enzymes. J Bacteriol. 1967 Mar;93(3):1201–1202. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.3.1201-1202.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins M. L., Shockman G. D. Procaryotic cell division with respect to wall and membranes. CRC Crit Rev Microbiol. 1971 May;1(1):29–72. doi: 10.3109/10408417109104477. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höltje J. V., Mirelman D., Sharon N., Schwarz U. Novel type of murein transglycosylase in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1975 Dec;124(3):1067–1076. doi: 10.1128/jb.124.3.1067-1076.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Höltje J. V., Tuomanen E. I. The murein hydrolases of Escherichia coli: properties, functions and impact on the course of infections in vivo. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Mar;137(3):441–454. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-3-441. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jayaswal R. K., Lee Y. I., Wilkinson B. J. Cloning and expression of a Staphylococcus aureus gene encoding a peptidoglycan hydrolase activity. J Bacteriol. 1990 Oct;172(10):5783–5788. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.10.5783-5788.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kadurugamuwa J. L., Clarke A. J., Beveridge T. J. Surface action of gentamicin on Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1993 Sep;175(18):5798–5805. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.18.5798-5805.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keck W., Wientjes F. B., Schwarz U. Comparison of two hydrolytic murein transglycosylases of Escherichia coli. Eur J Biochem. 1985 May 2;148(3):493–497. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb08866.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch A. L. Additional arguments for the key role of "smart" autolysins in the enlargement of the wall of gram-negative bacteria. Res Microbiol. 1990 Jun;141(5):529–541. doi: 10.1016/0923-2508(90)90017-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusser W., Ishiguro E. E. Involvement of the relA gene in the autolysis of Escherichia coli induced by inhibitors of peptidoglycan biosynthesis. J Bacteriol. 1985 Nov;164(2):861–865. doi: 10.1128/jb.164.2.861-865.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leclerc D., Asselin A. Detection of bacterial cell wall hydrolases after denaturing polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. Can J Microbiol. 1989 Aug;35(8):749–753. doi: 10.1139/m89-125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leduc M., Kasra R., van Heijenoort J. Induction and control of the autolytic system of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1982 Oct;152(1):26–34. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.1.26-34.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leduc M., van Heijenoort J. Autolysis of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 Apr;142(1):52–59. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.1.52-59.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Martin N. L., Beveridge T. J. Gentamicin interaction with Pseudomonas aeruginosa cell envelope. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1986 Jun;29(6):1079–1087. doi: 10.1128/aac.29.6.1079. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mett H., Keck W., Funk A., Schwarz U. Two different species of murein transglycosylase in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1980 Oct;144(1):45–52. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.1.45-52.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison A. J., Jr, Wenzel R. P. Epidemiology of infections due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Sep-Oct;6 (Suppl 3):S627–S642. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.supplement_3.s627. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olijhoek A. J., Klencke S., Pas E., Nanninga N., Schwarz U. Volume growth, murein synthesis, and murein cross-linkage during the division cycle of Escherichia coli PA3092. J Bacteriol. 1982 Dec;152(3):1248–1254. doi: 10.1128/jb.152.3.1248-1254.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peetz R. H., Kenny G. E. Prevention of autolysis in suspensions of Neisseria gonorrhoeae by mercuric ions. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jul;135(1):283–285. doi: 10.1128/jb.135.1.283-285.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pisabarro A. G., de Pedro M. A., Vázquez D. Structural modifications in the peptidoglycan of Escherichia coli associated with changes in the state of growth of the culture. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):238–242. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.238-242.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potvin C., Leclerc D., Tremblay G., Asselin A., Bellemare G. Cloning, sequencing and expression of a Bacillus bacteriolytic enzyme in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Oct;214(2):241–248. doi: 10.1007/BF00337717. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Presslitz J. E., Ray V. A. DD-carboxypeptidase and peptidoglycan transpeptidase from Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1975 May;7(5):578–581. doi: 10.1128/aac.7.5.578. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers H. J., Forsberg C. W. Role of autolysins in the killing of bacteria by some bactericidal antibiotics. J Bacteriol. 1971 Dec;108(3):1235–1243. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.3.1235-1243.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHOCKMAN G. D., KOLB J. J., TOENNIES G. Relations between bacterial cell wall synthesis, growth phase, and autolysis. J Biol Chem. 1958 Feb;230(2):961–977. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwarz U., Asmus A., Frank H. Autolytic enzymes and cell division of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1969 May 14;41(3):419–429. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90285-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shockman G. D. Symposium on the fine structure and replication of bacteria and their parts. IV. Unbalanced cell-wall synthesis: autolysis and cell-wall thickening. Bacteriol Rev. 1965 Sep;29(3):345–358. doi: 10.1128/br.29.3.345-358.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugai M., Akiyama T., Komatsuzawa H., Miyake Y., Suginaka H. Characterization of sodium dodecyl sulfate-stable Staphylococcus aureus bacteriolytic enzymes by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Nov;172(11):6494–6498. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.11.6494-6498.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A., Albino A., Zanati E. Multiple antibiotic resistance in a bacterium with suppressed autolytic system. Nature. 1970 Jul 11;227(5254):138–140. doi: 10.1038/227138a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomasz A. The mechanism of the irreversible antimicrobial effects of penicillins: how the beta-lactam antibiotics kill and lyse bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1979;33:113–137. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.33.100179.000553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuomanen E., Markiewicz Z., Tomasz A. Autolysis-resistant peptidoglycan of anomalous composition in amino-acid-starved Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1373–1376. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1373-1376.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderwinkel E., De Vlieghere M. Modulation of Escherichia coli N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase activity by phosphatidylglycerol. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Jan 28;838(1):54–59. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(85)90249-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderwinkel E., de Vlieghere M., Charles P., Baptist V. Nature of the interactions involved in the lipid-protein complexes of the Escherichia coli N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1987 Jun 17;913(2):238–244. doi: 10.1016/0167-4838(87)90335-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderwinkel E., de Vlieghere M., de Tanhoffer de Volcsey L. Activity of N-acetylmuramoyl-L-alanine amidase in phospholipidic environments. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Jan 26;663(1):46–57. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(81)90193-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- WEIDEL W., PELZER H. BAGSHAPED MACROMOLECULES--A NEW OUTLOOK ON BACTERIAL CELL WALLS. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1964;26:193–232. doi: 10.1002/9780470122716.ch5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker S. G., Beveridge T. J. Amikacin disrupts the cell envelope of Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 9027. Can J Microbiol. 1988 Jan;34(1):12–18. doi: 10.1139/m88-003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young L. S. The clinical challenge of infections due to Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Rev Infect Dis. 1984 Sep-Oct;6 (Suppl 3):S603–S607. doi: 10.1093/clinids/6.supplement_3.s603. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Pedro M. A., Schwarz U. Heterogeneity of newly inserted and preexisting murein in the sacculus of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Sep;78(9):5856–5860. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.9.5856. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]