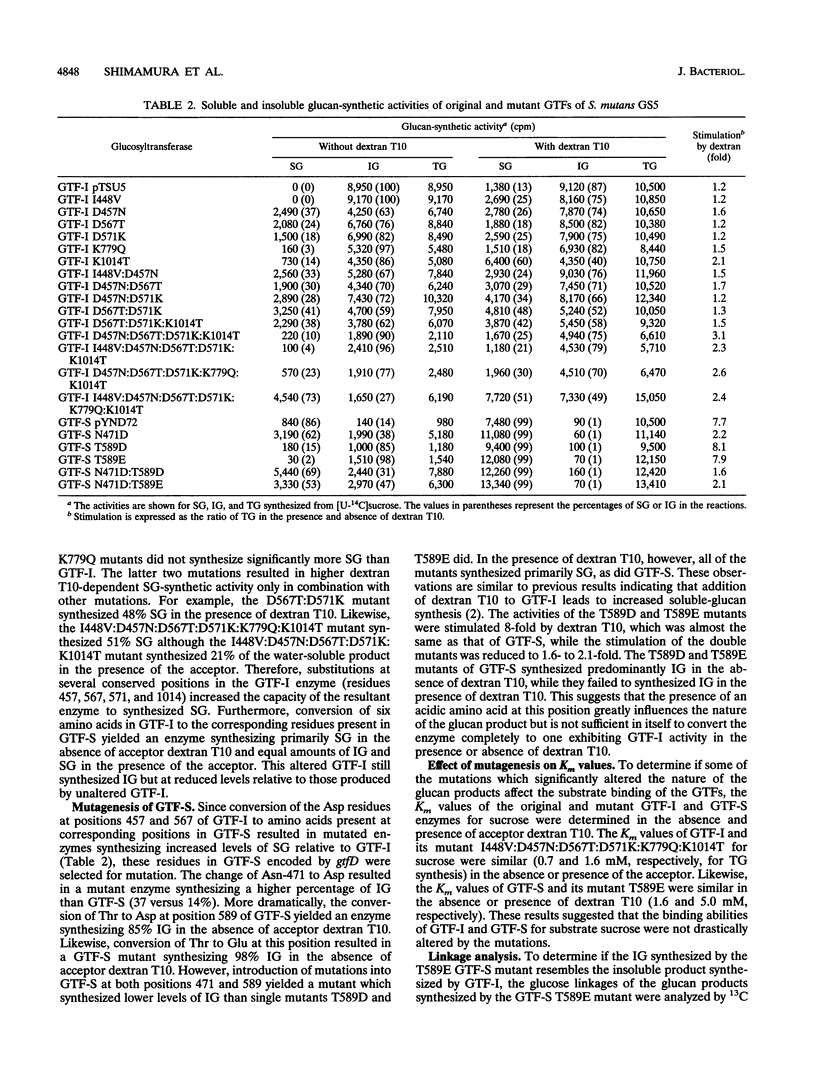
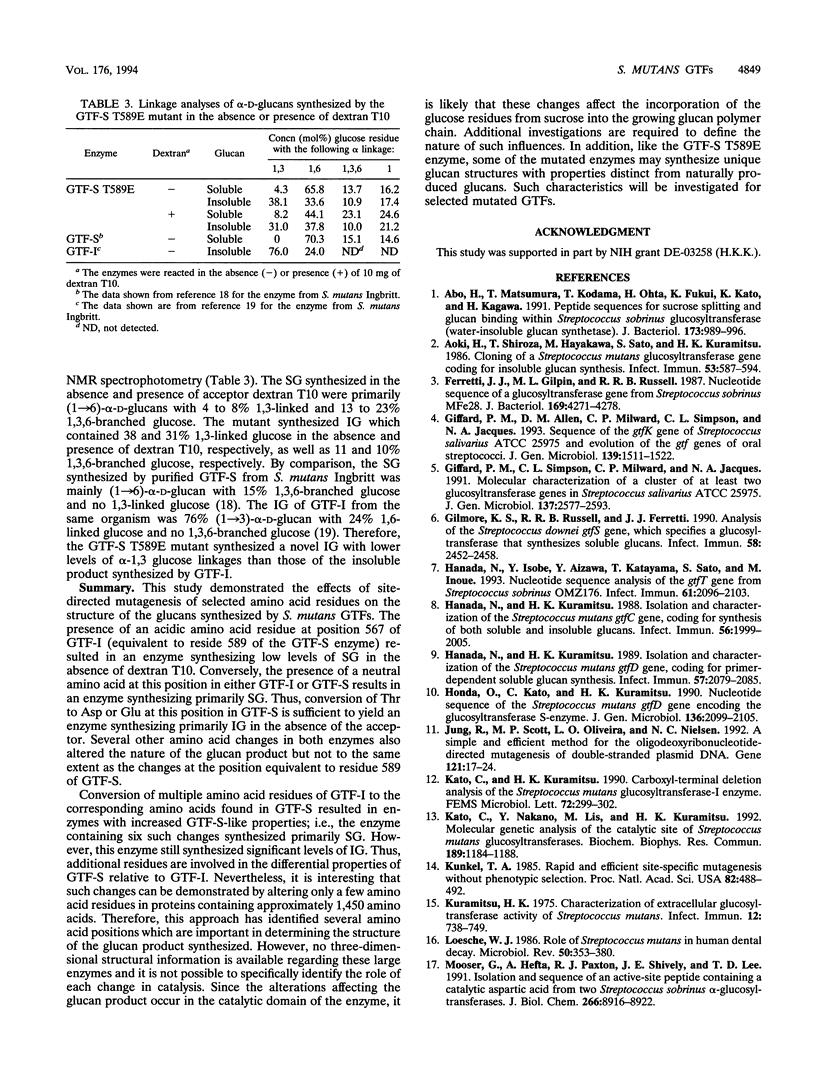
Abstract
The glucosyltransferases (GTFs) of mutans streptococci are important virulence factors in the sucrose-dependent colonization of tooth surfaces by these organisms. To investigate the structure-function relationship of the GTFs, an approach was initiated to identify amino acid residues of the GTFs which affect the incorporation of glucose residues into the glucan polymer. Conserved amino acid residues were identified in the GTF-S and GTF-I enzymes of the mutans streptococci and were selected for site-directed mutagenesis in the corresponding enzymes from Streptococcus mutans GS5. Conversion of six amino acid residues of the GTF-I enzyme to those present at the corresponding positions in GTF-S, either singly or in multiple combinations, resulted in enzymes synthesizing increased levels of soluble glucans. The enzyme containing six alterations synthesized 73% water-soluble glucan in the absence of acceptor dextran T10, while parental enzyme GTF-I synthesized no such glucan product. Conversely, when residue 589 of the GTF-S enzyme was converted from Thr to either Asp or Glu, the resulting enzyme synthesized primarily water-insoluble glucan in the absence of the acceptor. Therefore, this approach has identified several amino acid positions which influence the nature of the glucan product synthesized by GTFs.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abo H., Matsumura T., Kodama T., Ohta H., Fukui K., Kato K., Kagawa H. Peptide sequences for sucrose splitting and glucan binding within Streptococcus sobrinus glucosyltransferase (water-insoluble glucan synthetase). J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(3):989–996. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.3.989-996.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aoki H., Shiroza T., Hayakawa M., Sato S., Kuramitsu H. K. Cloning of a Streptococcus mutans glucosyltransferase gene coding for insoluble glucan synthesis. Infect Immun. 1986 Sep;53(3):587–594. doi: 10.1128/iai.53.3.587-594.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferretti J. J., Gilpin M. L., Russell R. R. Nucleotide sequence of a glucosyltransferase gene from Streptococcus sobrinus MFe28. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):4271–4278. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.4271-4278.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giffard P. M., Allen D. M., Milward C. P., Simpson C. L., Jacques N. A. Sequence of the gtfK gene of Streptococcus salivarius ATCC 25975 and evolution of the gtf genes of oral streptococci. J Gen Microbiol. 1993 Jul;139(7):1511–1522. doi: 10.1099/00221287-139-7-1511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giffard P. M., Simpson C. L., Milward C. P., Jacques N. A. Molecular characterization of a cluster of at least two glucosyltransferase genes in Streptococcus salivarius ATCC 25975. J Gen Microbiol. 1991 Nov;137(11):2577–2593. doi: 10.1099/00221287-137-11-2577. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilmore K. S., Russell R. R., Ferretti J. J. Analysis of the Streptococcus downei gtfS gene, which specifies a glucosyltransferase that synthesizes soluble glucans. Infect Immun. 1990 Aug;58(8):2452–2458. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.8.2452-2458.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanada N., Isobe Y., Aizawa Y., Katayama T., Sato S., Inoue M. Nucleotide sequence analysis of the gtfT gene from Streptococcus sobrinus OMZ176. Infect Immun. 1993 May;61(5):2096–2103. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.5.2096-2103.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanada N., Kuramitsu H. K. Isolation and characterization of the Streptococcus mutans gtfC gene, coding for synthesis of both soluble and insoluble glucans. Infect Immun. 1988 Aug;56(8):1999–2005. doi: 10.1128/iai.56.8.1999-2005.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hanada N., Kuramitsu H. K. Isolation and characterization of the Streptococcus mutans gtfD gene, coding for primer-dependent soluble glucan synthesis. Infect Immun. 1989 Jul;57(7):2079–2085. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.7.2079-2085.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Honda O., Kato C., Kuramitsu H. K. Nucleotide sequence of the Streptococcus mutans gtfD gene encoding the glucosyltransferase-S enzyme. J Gen Microbiol. 1990 Oct;136(10):2099–2105. doi: 10.1099/00221287-136-10-2099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jung R., Scott M. P., Oliveira L. O., Nielsen N. C. A simple and efficient method for the oligodeoxyribonucleotide-directed mutagenesis of double-stranded plasmid DNA. Gene. 1992 Nov 2;121(1):17–24. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(92)90157-k. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato C., Kuramitsu H. K. Carboxyl-terminal deletion analysis of the Streptococcus mutans glucosyltransferase-I enzyme. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1990 Nov;60(3):299–302. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(90)90321-g. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kato C., Nakano Y., Lis M., Kuramitsu H. K. Molecular genetic analysis of the catalytic site of Streptococcus mutans glucosyltransferases. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1992 Dec 15;189(2):1184–1188. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(92)92329-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):488–492. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.488. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuramitsu H. K. Characterization of extracellular glucosyltransferase activity of Steptococcus mutans. Infect Immun. 1975 Oct;12(4):738–749. doi: 10.1128/iai.12.4.738-749.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Loesche W. J. Role of Streptococcus mutans in human dental decay. Microbiol Rev. 1986 Dec;50(4):353–380. doi: 10.1128/mr.50.4.353-380.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mooser G., Hefta S. A., Paxton R. J., Shively J. E., Lee T. D. Isolation and sequence of an active-site peptide containing a catalytic aspartic acid from two Streptococcus sobrinus alpha-glucosyltransferases. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 15;266(14):8916–8922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukasa H., Shimamura A., Tsumori H. Purification and characterization of basic glucosyltransferase from Streptococcus mutans serotype c. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1982 Oct 28;719(1):81–89. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(82)90310-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mukasa H., Shimamura A., Tsumori H. Purification and characterization of cell-associated glucosyltransferase synthesizing insoluble glucan from Streptococcus mutans serotype c. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Jul;135(7):2055–2063. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-7-2055. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano Y. J., Kuramitsu H. K. Mechanism of Streptococcus mutans glucosyltransferases: hybrid-enzyme analysis. J Bacteriol. 1992 Sep;174(17):5639–5646. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.17.5639-5646.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimamura A. Use of 13C-n.m.r. spectroscopy for the quantitative estimation of 3-O- and 3,6-di-O-substituted D-glucopyranosyl residues in alpha-D-glucans formed by the D-glucosyltransferases of Streptococcus sobrinus. Carbohydr Res. 1989 Feb 1;185(2):239–248. doi: 10.1016/0008-6215(89)80039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shiroza T., Ueda S., Kuramitsu H. K. Sequence analysis of the gtfB gene from Streptococcus mutans. J Bacteriol. 1987 Sep;169(9):4263–4270. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.9.4263-4270.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueda S., Shiroza T., Kuramitsu H. K. Sequence analysis of the gtfC gene from Streptococcus mutans GS-5. Gene. 1988 Sep 15;69(1):101–109. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90382-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita Y., Bowen W. H., Burne R. A., Kuramitsu H. K. Role of the Streptococcus mutans gtf genes in caries induction in the specific-pathogen-free rat model. Infect Immun. 1993 Sep;61(9):3811–3817. doi: 10.1128/iai.61.9.3811-3817.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



