Abstract
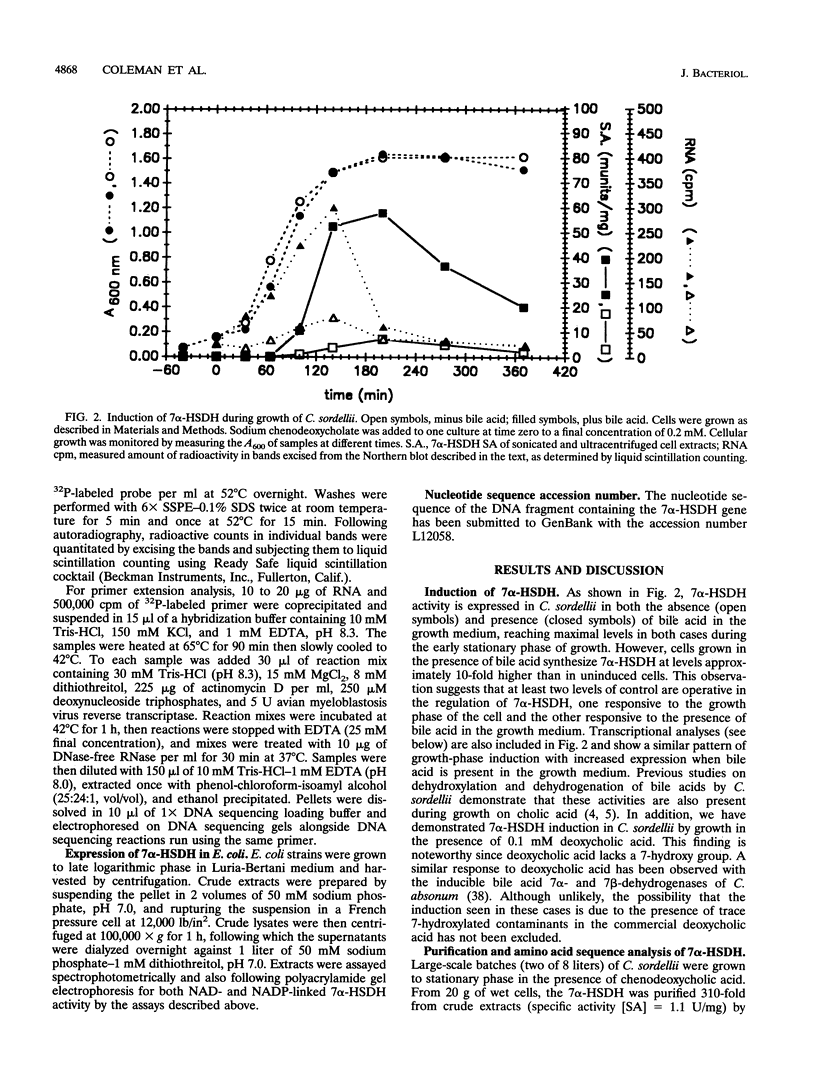
A bile acid-inducible NADP-linked 7 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase (7 alpha-HSDH) from Clostridium sordellii ATCC 9714 was purified 310-fold by ion-exchange, gel filtration, and dye-ligand affinity chromatography. Sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis analysis of the purified enzyme showed one predominant peptide band (30,000 Da). The N-terminal sequence was determined, and the corresponding oligonucleotides were synthesized and used to screen EcoRI and HindIII genomic digests of C. sordellii. Two separate fragments (4,500 bp, EcoRI; 3,200 bp, HindIII) were subsequently cloned by ligation to pUC19 and transformation into Escherichia coli DH5 alpha-MCR. The EcoRI fragment was shown to contain a truncated 7 alpha-HSDH gene, while the HindIII fragment contained the entire coding region. E. coli clones containing the HindIII insert expressed high levels of an NADP-linked 7 alpha-HSDH. Nucleotide sequence analyses suggest that the 7 alpha-HSDH is encoded by a monocistronic transcriptional unit, with DNA sequence elements resembling rho-independent terminators located in both the upstream and downstream flanking regions. The transcriptional start site was located by primer extension analysis. Northern (RNA) blot analysis indicated that induction is mediated at the transcriptional level in response to the presence of bile acid in the growth medium. In addition, growth-phase-dependent expression is observed in uninduced cultures. Analysis of the predicted protein sequence indicates that the enzyme can be classified in the short-chain dehydrogenase group.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Akao T., Akao T., Hattori M., Namba T., Kobashi K. 3 beta-Hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase of Ruminococcus sp. from human intestinal bacteria. J Biochem. 1986 May;99(5):1425–1431. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a135612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Akao T., Akao T., Kobashi K. Purification and characterization of 7 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase from Ruminococcus sp. of human intestine. J Biochem. 1987 Sep;102(3):613–619. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a122095. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aries V., Hill M. J. Degradation of steroids by intestinal bacteria. II. Enzymes catalysing the oxidoreduction of the 3 alpha-, 7 alpha- and 12 alpha-hydroxyl groups in cholic acid, and the dehydroxylation of the 7-hydroxyl group. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1970 May 5;202(3):535–543. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(70)90124-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baron S. F., Franklund C. V., Hylemon P. B. Cloning, sequencing, and expression of the gene coding for bile acid 7 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase from Eubacterium sp. strain VPI 12708. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(15):4558–4569. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.15.4558-4569.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Braun M., Lünsdorf H., Bückmann A. F. 12 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase from Clostridium group P, strain C 48-50. Production, purification and characterization. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Mar 14;196(2):439–450. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15835.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen Z., Lee W. R., Chang S. H. Role of aspartic acid 38 in the cofactor specificity of Drosophila alcohol dehydrogenase. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Dec 5;202(2):263–267. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16371.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman J. P., White W. B., Lijewski M., Hylemon P. B. Nucleotide sequence and regulation of a gene involved in bile acid 7-dehydroxylation by Eubacterium sp. strain VPI 12708. J Bacteriol. 1988 May;170(5):2070–2077. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.5.2070-2077.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edenharder R. Dehydroxylation of cholic acid at C12 and epimerization at C5 and C7 by Bacteroides species. J Steroid Biochem. 1984 Oct;21(4):413–420. doi: 10.1016/0022-4731(84)90304-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edenharder R., Pfützner A. Characterization of NADP-dependent 12 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase from Clostridium paraputrificum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1988 Oct 14;962(3):362–370. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(88)90266-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edenharder R., Pfützner A., Hammann R. Characterization of NAD-dependent 3 alpha- and 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase and of NADP-dependent 7 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase from Peptostreptococcus productus. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Aug 8;1004(2):230–238. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(89)90272-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edenharder R., Pfützner M., Hammann R. NADP-dependent 3 beta-, 7 alpha- and 7 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase activities from a lecithinase-lipase-negative Clostridium species 25.11.c. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1989 Mar 14;1002(1):37–44. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(89)90061-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferrari A., Pacini N., Canzi E. A note on bile acids transformations by strains of Bifidobacterium. J Appl Bacteriol. 1980 Oct;49(2):193–197. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2672.1980.tb05117.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franklund C. V., de Prada P., Hylemon P. B. Purification and characterization of a microbial, NADP-dependent bile acid 7 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. J Biol Chem. 1990 Jun 15;265(17):9842–9849. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freier S. M., Kierzek R., Jaeger J. A., Sugimoto N., Caruthers M. H., Neilson T., Turner D. H. Improved free-energy parameters for predictions of RNA duplex stability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9373–9377. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garnier T., Canard B., Cole S. T. Cloning, mapping, and molecular characterization of the rRNA operons of Clostridium perfringens. J Bacteriol. 1991 Sep;173(17):5431–5438. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.17.5431-5438.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh D., Weeks C. M., Grochulski P., Duax W. L., Erman M., Rimsay R. L., Orr J. C. Three-dimensional structure of holo 3 alpha,20 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase: a member of a short-chain dehydrogenase family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Nov 15;88(22):10064–10068. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.22.10064. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopal-Srivastava R., Mallonee D. H., White W. B., Hylemon P. B. Multiple copies of a bile acid-inducible gene in Eubacterium sp. strain VPI 12708. J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4420–4426. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4420-4426.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graves M. C., Rabinowitz J. C. In vivo and in vitro transcription of the Clostridium pasteurianum ferredoxin gene. Evidence for "extended" promoter elements in gram-positive organisms. J Biol Chem. 1986 Aug 25;261(24):11409–11415. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grell E. H., Jacobson K. B., Murphy J. B. Alcohol Dehydrogenase in Drosophila melanogaster: Isozymes and Genetic Variants. Science. 1965 Jul 2;149(3679):80–82. doi: 10.1126/science.149.3679.80. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayakawa S., Hattori T. 7alpha-dehydroxylation of cholic acid by Clostridium bifermentans strain ATCC 9714 and Clostridium sordellii strain NCIB 6929. FEBS Lett. 1970 Jan 26;6(2):131–133. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(70)80020-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano S., Masuda N. Characterization of NADP-dependent 7 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases from Peptostreptococcus productus and Eubacterium aerofaciens. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 May;43(5):1057–1063. doi: 10.1128/aem.43.5.1057-1063.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano S., Masuda N. Transformation of bile acids by Eubacterium lentum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Nov;42(5):912–915. doi: 10.1128/aem.42.5.912-915.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirano S., Nakama R., Tamaki M., Masuda N., Oda H. Isolation and characterization of thirteen intestinal microorganisms capable of 7 alpha-dehydroxylating bile acids. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1981 Mar;41(3):737–745. doi: 10.1128/aem.41.3.737-745.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hylemon P. B., Sherrod J. A. Multiple forms of 7-alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase in selected strains of Bacteroides fragilis. J Bacteriol. 1975 May;122(2):418–424. doi: 10.1128/jb.122.2.418-424.1975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim A. Y., Blaschek H. P. Construction of an Escherichia coli-Clostridium perfringens shuttle vector and plasmid transformation of Clostridium perfringens. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1989 Feb;55(2):360–365. doi: 10.1128/aem.55.2.360-365.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krafft A. E., Hylemon P. B. Purification and characterization of a novel form of 20 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase from Clostridium scindens. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):2925–2932. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.2925-2932.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LINDNER F., JUNK R., NESEMANN G., SCHMIDT-THOME J. Gewinnung von 20 bata-Hydroxysteroiden aus 17 alpha. 21-Dihydroxy-20-ketosteroiden durch mikrobiologische Hydrierung mit Streptomyces hydrogenans. Hoppe Seylers Z Physiol Chem. 1958;313:117–123. doi: 10.1515/bchm2.1958.313.1.117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MARCUS P. I., TALALAY P. Induction and purification of alpha- and beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases. J Biol Chem. 1956 Feb;218(2):661–674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald I. A., Jellett J. F., Mahony D. E., Holdeman L. V. Bile salt 3 alpha- and 12 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases from Eubacterium lentum and related organisms. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1979 May;37(5):992–1000. doi: 10.1128/aem.37.5.992-1000.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald I. A., Roach P. D. Bile induction of 7 alpha- and 7 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases in Clostridium absonum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Aug 24;665(2):262–269. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(81)90011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald I. A., Sutherland J. D. Further studies on the bile salt induction of 7 alpha- and 7 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases in Clostridium absonum. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1983 Feb 7;750(2):397–403. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(83)90045-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald I. A., Williams C. N., Mahony D. E. 7Alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase from Escherichia coli B: preliminary studies. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1973 Jun 6;309(2):243–253. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(73)90022-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald I. A., Williams C. N., Mahony D. E., Christie W. M. NAD- and NADP-dependent 7alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases from bacteroides fragilis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Mar 28;384(1):12–24. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90091-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marekov L., Krook M., Jörnvall H. Prokaryotic 20 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase is an enzyme of the 'short-chain, non-metalloenzyme' alcohol dehydrogenase type. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jun 18;266(1-2):51–54. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81504-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midtvedt T., Norman A. Bile acid transformations by microbial strains belonging to genera found in intestinal contents. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1967;71(4):629–638. doi: 10.1111/j.1699-0463.1967.tb05183.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran C. P., Jr, Lang N., LeGrice S. F., Lee G., Stephens M., Sonenshein A. L., Pero J., Losick R. Nucleotide sequences that signal the initiation of transcription and translation in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(3):339–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00729452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payne D. W., Talalay P. Isolation of novel microbial 3 alpha-, 3 beta-, and 17 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases. Purification, characterization, and analytical applications of a 17 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase from an Alcaligenes sp. J Biol Chem. 1985 Nov 5;260(25):13648–13655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson B., Krook M., Jörnvall H. Characteristics of short-chain alcohol dehydrogenases and related enzymes. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Sep 1;200(2):537–543. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16215.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rawlings M., Cronan J. E., Jr The gene encoding Escherichia coli acyl carrier protein lies within a cluster of fatty acid biosynthetic genes. J Biol Chem. 1992 Mar 25;267(9):5751–5754. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SQIRE P. G., DELIN S., PORATH J. PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL CHARACTERIZATION OF HYDROXYSTEROID DEHYDROGENASES FROM PSEUDOMONAS TESTOSTERONI. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1964 Sep 18;89:409–421. doi: 10.1016/0926-6569(64)90067-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherman D. H., Malpartida F., Bibb M. J., Kieser H. M., Bibb M. J., Hopwood D. A. Structure and deduced function of the granaticin-producing polyketide synthase gene cluster of Streptomyces violaceoruber Tü22. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2717–2725. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08413.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sherrod J. A., Hylemon P. B. Partial purification and characterization of NAD-dependent 7alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase from Bacteroides thetaiotaomicron. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 Feb 23;486(2):351–358. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(77)90031-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skålhegg B. A., Fausa O. Enzymatic Determination of bile acids. the NADP-specific 7alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase from P. testosteroni (ATCC 11996). Scand J Gastroenterol. 1977;12(4):433–439. doi: 10.3109/00365527709181684. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland J. D., Williams C. N. Bile acid induction of 7 alpha- and 7 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenases in Clostridium limosum. J Lipid Res. 1985 Mar;26(3):344–350. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White W. B., Coleman J. P., Hylemon P. B. Molecular cloning of a gene encoding a 45,000-dalton polypeptide associated with bile acid 7-dehydroxylation in Eubacterium sp. strain VPI 12708. J Bacteriol. 1988 Feb;170(2):611–616. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.2.611-616.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin S. J., Vagelopoulos N., Lundquist G., Jörnvall H. Pseudomonas 3 beta-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase. Primary structure and relationships to other steroid dehydrogenases. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Apr 23;197(2):359–365. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb15919.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshimoto T., Higashi H., Kanatani A., Lin X. S., Nagai H., Oyama H., Kurazono K., Tsuru D. Cloning and sequencing of the 7 alpha-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase gene from Escherichia coli HB101 and characterization of the expressed enzyme. J Bacteriol. 1991 Apr;173(7):2173–2179. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.7.2173-2179.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




