Abstract
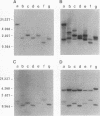
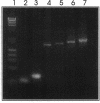
Numerous field isolates of Moraxella bovis have previously been classified by serological techniques into seven serogroups, each defined by homologous cross-reaction with antisera prepared against purified pili of a single prototype strain. The gene encoding pilin from each of the prototype strains has been characterized by nucleotide sequence determination. The coding sequences show extensive homology (70 to 80%) while the proximal downstream sequences show a dichotomy into nonhomologous sets. The pilin genes of three more strains were also characterized. The presence of an additional, partial pilin gene in each prototype strain was confirmed by Southern blot analysis, and the partial pilin genes from two strains of one serogroup were characterized by sequence determination. Features of the pilin gene sequences are considered in relation to pilin gene inversion and the serological variants of strains which may arise from gene inversion events.
Full text
PDF







Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ehrlich M., Wilson G. G., Kuo K. C., Gehrke C. W. N4-methylcytosine as a minor base in bacterial DNA. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):939–943. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.939-943.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elleman T. C., Hoyne P. A., Lepper A. W. Characterization of the pilin gene of Moraxella bovis Dalton 2d and expression of pili from M. bovis in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Infect Immun. 1990 Jun;58(6):1678–1684. doi: 10.1128/iai.58.6.1678-1684.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elleman T. C. Pilins of Bacteroides nodosus: molecular basis of serotypic variation and relationships to other bacterial pilins. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Jun;52(2):233–247. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.2.233-247.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fulks K. A., Marrs C. F., Stevens S. P., Green M. R. Sequence analysis of the inversion region containing the pilin genes of Moraxella bovis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jan;172(1):310–316. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.1.310-316.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gouy M., Gautier C. Codon usage in bacteria: correlation with gene expressivity. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Nov 25;10(22):7055–7074. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.22.7055. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosjean H., Fiers W. Preferential codon usage in prokaryotic genes: the optimal codon-anticodon interaction energy and the selective codon usage in efficiently expressed genes. Gene. 1982 Jun;18(3):199–209. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90157-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hattori M., Sakaki Y. Dideoxy sequencing method using denatured plasmid templates. Anal Biochem. 1986 Feb 1;152(2):232–238. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90403-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins D. G., Sharp P. M. CLUSTAL: a package for performing multiple sequence alignment on a microcomputer. Gene. 1988 Dec 15;73(1):237–244. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90330-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T. Correlation between the abundance of Escherichia coli transfer RNAs and the occurrence of the respective codons in its protein genes. J Mol Biol. 1981 Feb 15;146(1):1–21. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90363-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T. Correlation between the abundance of Escherichia coli transfer RNAs and the occurrence of the respective codons in its protein genes: a proposal for a synonymous codon choice that is optimal for the E. coli translational system. J Mol Biol. 1981 Sep 25;151(3):389–409. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90003-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikemura T. Correlation between the abundance of yeast transfer RNAs and the occurrence of the respective codons in protein genes. Differences in synonymous codon choice patterns of yeast and Escherichia coli with reference to the abundance of isoaccepting transfer RNAs. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jul 15;158(4):573–597. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90250-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson K., Parker M. L., Lory S. Nucleotide sequence and transcriptional initiation site of two Pseudomonas aeruginosa pilin genes. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 25;261(33):15703–15708. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepper A. W., Elleman T. C., Hoyne P. A., Lehrbach P. R., Atwell J. L., Schwartzkoff C. L., Egerton J. R., Tennent J. M. A Moraxella bovis pili vaccine produced by recombinant DNA technology for the prevention of infectious bovine keratoconjunctivitis. Vet Microbiol. 1993 Jul;36(1-2):175–183. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(93)90138-w. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lepper A. W., Power B. E. Infectivity and virulence of Australian strains of Moraxella bovis for the murine and bovine eye in relation to pilus serogroup sub-unit size and degree of piliation. Aust Vet J. 1988 Oct;65(10):305–309. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-0813.1988.tb14512.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrs C. F., Rozsa F. W., Hackel M., Stevens S. P., Glasgow A. C. Identification, cloning, and sequencing of piv, a new gene involved in inverting the pilin genes of Moraxella lacunata. J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4370–4377. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4370-4377.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrs C. F., Ruehl W. W., Schoolnik G. K., Falkow S. Pilin-gene phase variation of Moraxella bovis is caused by an inversion of the pilin genes. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):3032–3039. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.3032-3039.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrs C. F., Schoolnik G., Koomey J. M., Hardy J., Rothbard J., Falkow S. Cloning and sequencing of a Moraxella bovis pilin gene. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):132–139. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.132-139.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J. New M13 vectors for cloning. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:20–78. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01005-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore L. J., Lepper A. W. A unified serotyping scheme for Moraxella bovis. Vet Microbiol. 1991 Sep;29(1):75–83. doi: 10.1016/0378-1135(91)90111-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore L. J., Rutter J. M. Antigenic analysis of fimbrial proteins from Moraxella bovis. J Clin Microbiol. 1987 Nov;25(11):2063–2070. doi: 10.1128/jcm.25.11.2063-2070.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ottow J. C. Ecology, physiology, and genetics of fimbriae and pili. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1975;29:79–108. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.29.100175.000455. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed K. C., Mann D. A. Rapid transfer of DNA from agarose gels to nylon membranes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Oct 25;13(20):7207–7221. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.20.7207. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruehl W. W., Marrs C. F., Fernandez R., Falkow S., Schoolnik G. K. Purification, characterization, and pathogenicity of Moraxella bovis pili. J Exp Med. 1988 Sep 1;168(3):983–1002. doi: 10.1084/jem.168.3.983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. M., Li W. H. Codon usage in regulatory genes in Escherichia coli does not reflect selection for 'rare' codons. Nucleic Acids Res. 1986 Oct 10;14(19):7737–7749. doi: 10.1093/nar/14.19.7737. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]