Abstract
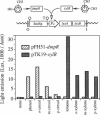
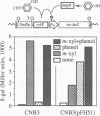
The Pu promoter of the toluene degradation plasmid pWW0 of Pseudomonas putida drives expression of an operon involved in the sequential oxidation of toluene and m- and p-xylenes to benzoate and toluates, respectively. Similarly, the Po promoter of plasmid pVI150 controls expression of an operon of Pseudomonas sp. strain CF600 which is required for the complete catabolism of phenol and cresols. These promoters, which both belong to the sigma 54-dependent class, are regulated by their cognate activators, XylR and DmpR, respectively. XylR and DmpR are homologous proteins, and both require aromatic compounds as effector molecules for activity. However, these two proteins respond to different profiles of aromatic compounds. The activity of each promoter in the presence of the heterologous regulator was monitored using lacZ and luxAB reporter systems. Genetic evidence is presented that the two activators can functionally substitute each other in the regulation of their corresponding promoters by binding the same upstream DNA segment. Furthermore, when coexpressed, the two proteins appear to act simultaneously on each of the promoters, expanding the responsiveness of these systems to the presence of effectors of both proteins. Potential mechanisms for the occurrence of evolutionary divergence between XylR and DmpR are discussed in view of the DNA sequence similarities among Pu, Po, and a third XylR-responsive promoter, Ps.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abril M. A., Michan C., Timmis K. N., Ramos J. L. Regulator and enzyme specificities of the TOL plasmid-encoded upper pathway for degradation of aromatic hydrocarbons and expansion of the substrate range of the pathway. J Bacteriol. 1989 Dec;171(12):6782–6790. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.12.6782-6790.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Assinder S. J., Williams P. A. The TOL plasmids: determinants of the catabolism of toluene and the xylenes. Adv Microb Physiol. 1990;31:1–69. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60119-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gomada M., Inouye S., Imaishi H., Nakazawa A., Nakazawa T. Analysis of an upstream regulatory sequence required for activation of the regulatory gene xylS in xylene metabolism directed by the TOL plasmid of Pseudomonas putida. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 Jun;233(3):419–426. doi: 10.1007/BF00265439. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harayama S., Kok M., Neidle E. L. Functional and evolutionary relationships among diverse oxygenases. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1992;46:565–601. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.46.100192.003025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harayama S., Rekik M., Bairoch A., Neidle E. L., Ornston L. N. Potential DNA slippage structures acquired during evolutionary divergence of Acinetobacter calcoaceticus chromosomal benABC and Pseudomonas putida TOL pWW0 plasmid xylXYZ, genes encoding benzoate dioxygenases. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(23):7540–7548. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.23.7540-7548.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harayama S., Rekik M., Wubbolts M., Rose K., Leppik R. A., Timmis K. N. Characterization of five genes in the upper-pathway operon of TOL plasmid pWW0 from Pseudomonas putida and identification of the gene products. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):5048–5055. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.5048-5055.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartnett C., Neidle E. L., Ngai K. L., Ornston L. N. DNA sequences of genes encoding Acinetobacter calcoaceticus protocatechuate 3,4-dioxygenase: evidence indicating shuffling of genes and of DNA sequences within genes during their evolutionary divergence. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):956–966. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.956-966.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrero M., de Lorenzo V., Timmis K. N. Transposon vectors containing non-antibiotic resistance selection markers for cloning and stable chromosomal insertion of foreign genes in gram-negative bacteria. J Bacteriol. 1990 Nov;172(11):6557–6567. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.11.6557-6567.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofer B., Eltis L. D., Dowling D. N., Timmis K. N. Genetic analysis of a Pseudomonas locus encoding a pathway for biphenyl/polychlorinated biphenyl degradation. Gene. 1993 Aug 16;130(1):47–55. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90345-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holtel A., Timmis K. N., Ramos J. L. Upstream binding sequences of the XylR activator protein and integration host factor in the xylS gene promoter region of the Pseudomonas TOL plasmid. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Apr 11;20(7):1755–1762. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.7.1755. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huala E., Ausubel F. M. The central domain of Rhizobium meliloti NifA is sufficient to activate transcription from the R. meliloti nifH promoter. J Bacteriol. 1989 Jun;171(6):3354–3365. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.6.3354-3365.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Gomada M., Sangodkar U. M., Nakazawa A., Nakazawa T. Upstream regulatory sequence for transcriptional activator XylR in the first operon of xylene metabolism on the TOL plasmid. J Mol Biol. 1990 Nov 20;216(2):251–260. doi: 10.1016/S0022-2836(05)80317-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Nakazawa A., Nakazawa T. Expression of the regulatory gene xylS on the TOL plasmid is positively controlled by the xylR gene product. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Aug;84(15):5182–5186. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.15.5182. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Nakazawa A., Nakazawa T. Nucleotide sequence of the regulatory gene xylR of the TOL plasmid from Pseudomonas putida. Gene. 1988 Jun 30;66(2):301–306. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90366-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kessler B., de Lorenzo V., Timmis K. N. A general system to integrate lacZ fusions into the chromosomes of gram-negative eubacteria: regulation of the Pm promoter of the TOL plasmid studied with all controlling elements in monocopy. Mol Gen Genet. 1992 May;233(1-2):293–301. doi: 10.1007/BF00587591. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunkel T. A., Roberts J. D., Zakour R. A. Rapid and efficient site-specific mutagenesis without phenotypic selection. Methods Enzymol. 1987;154:367–382. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)54085-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler T., Harayama S., Ramos J. L., Timmis K. N. Involvement of Pseudomonas putida RpoN sigma factor in regulation of various metabolic functions. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4326–4333. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4326-4333.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marqués S., Ramos J. L. Transcriptional control of the Pseudomonas putida TOL plasmid catabolic pathways. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Sep;9(5):923–929. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01222.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morett E., Segovia L. The sigma 54 bacterial enhancer-binding protein family: mechanism of action and phylogenetic relationship of their functional domains. J Bacteriol. 1993 Oct;175(19):6067–6074. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.19.6067-6074.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Myers R. M., Lerman L. S., Maniatis T. A general method for saturation mutagenesis of cloned DNA fragments. Science. 1985 Jul 19;229(4710):242–247. doi: 10.1126/science.2990046. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- North A. K., Klose K. E., Stedman K. M., Kustu S. Prokaryotic enhancer-binding proteins reflect eukaryote-like modularity: the puzzle of nitrogen regulatory protein C. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jul;175(14):4267–4273. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.14.4267-4273.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson O., Koncz C., Szalay A. A. The use of the luxA gene of the bacterial luciferase operon as a reporter gene. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Dec;215(1):1–9. doi: 10.1007/BF00331295. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornston L. N., Yeh W. K. Origins of metabolic diversity: evolutionary divergence by sequence repetition. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3996–4000. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3996. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramos J. L., Stolz A., Reineke W., Timmis K. N. Altered effector specificities in regulators of gene expression: TOL plasmid xylS mutants and their use to engineer expansion of the range of aromatics degraded by bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Nov;83(22):8467–8471. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.22.8467. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shapiro J. A. Natural genetic engineering of the bacterial genome. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 1993 Dec;3(6):845–848. doi: 10.1016/0959-437x(93)90003-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shingler V., Bartilson M., Moore T. Cloning and nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding the positive regulator (DmpR) of the phenol catabolic pathway encoded by pVI150 and identification of DmpR as a member of the NtrC family of transcriptional activators. J Bacteriol. 1993 Mar;175(6):1596–1604. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.6.1596-1604.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shingler V., Franklin F. C., Tsuda M., Holroyd D., Bagdasarian M. Molecular analysis of a plasmid-encoded phenol hydroxylase from Pseudomonas CF600. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 May;135(5):1083–1092. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-5-1083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shingler V., Moore T. Sensing of aromatic compounds by the DmpR transcriptional activator of phenol-catabolizing Pseudomonas sp. strain CF600. J Bacteriol. 1994 Mar;176(6):1555–1560. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.6.1555-1560.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shingler V., Powlowski J., Marklund U. Nucleotide sequence and functional analysis of the complete phenol/3,4-dimethylphenol catabolic pathway of Pseudomonas sp. strain CF600. J Bacteriol. 1992 Feb;174(3):711–724. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.3.711-724.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh W. K., Ornston L. N. Origins of metabolic diversity: substitution of homologous sequences into genes for enzymes with different catalytic activities. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5365–5369. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5365. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lorenzo V., Fernández S., Herrero M., Jakubzik U., Timmis K. N. Engineering of alkyl- and haloaromatic-responsive gene expression with mini-transposons containing regulated promoters of biodegradative pathways of Pseudomonas. Gene. 1993 Aug 16;130(1):41–46. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90344-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lorenzo V., Herrero M., Jakubzik U., Timmis K. N. Mini-Tn5 transposon derivatives for insertion mutagenesis, promoter probing, and chromosomal insertion of cloned DNA in gram-negative eubacteria. J Bacteriol. 1990 Nov;172(11):6568–6572. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.11.6568-6572.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lorenzo V., Herrero M., Metzke M., Timmis K. N. An upstream XylR- and IHF-induced nucleoprotein complex regulates the sigma 54-dependent Pu promoter of TOL plasmid. EMBO J. 1991 May;10(5):1159–1167. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1991.tb08056.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Lorenzo V., Timmis K. N. Analysis and construction of stable phenotypes in gram-negative bacteria with Tn5- and Tn10-derived minitransposons. Methods Enzymol. 1994;235:386–405. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(94)35157-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]