Abstract
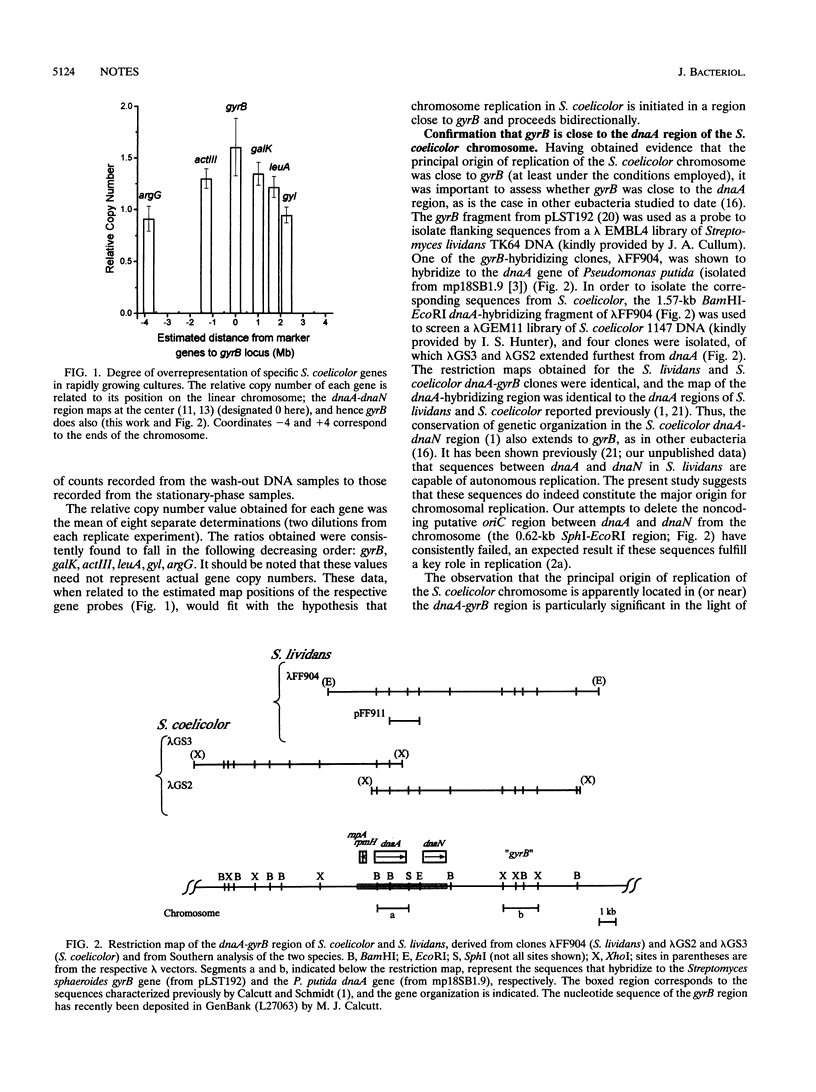
The degree of overrepresentation of selected chromosomal genes in rapidly growing cultures of Streptomyces coelicolor was assessed by quantitative DNA hybridization analysis. The results are consistent with the hypothesis that the principal origin of replication is close to the dnaA-gyrB region, in the center of the linear chromosome, and that replication proceeds bidirectionally.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Calcutt M. J., Schmidt F. J. Conserved gene arrangement in the origin region of the Streptomyces coelicolor chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1992 May;174(10):3220–3226. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.10.3220-3226.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casjens S., Huang W. M. Linear chromosomal physical and genetic map of Borrelia burgdorferi, the Lyme disease agent. Mol Microbiol. 1993 May;8(5):967–980. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01641.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fujita M. Q., Yoshikawa H., Ogasawara N. Structure of the dnaA region of Pseudomonas putida: conservation among three bacteria, Bacillus subtilis, Escherichia coli and P. putida. Mol Gen Genet. 1989 Feb;215(3):381–387. doi: 10.1007/BF00427033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hallam S. E., Malpartida F., Hopwood D. A. Nucleotide sequence, transcription and deduced function of a gene involved in polyketide antibiotic synthesis in Streptomyces coelicolor. Gene. 1988 Dec 30;74(2):305–320. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(88)90165-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hercomb J., Thierbach G., Baumberg S., Parish J. H. Cloning, characterization and expression in Escherichia coli of a leucine biosynthetic gene from Streptomyces rochei. J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Feb;133(2):317–322. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-2-317. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopwood D. A., Chater K. F., Dowding J. E., Vivian A. Advances in Streptomyces coelicolor genetics. Bacteriol Rev. 1973 Sep;37(3):371–405. doi: 10.1128/br.37.3.371-405.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishihara H., Nakano M. M., Ogawara H. Cloning of a gene from Streptomyces species complementing argG mutations. J Antibiot (Tokyo) 1985 Jun;38(6):787–794. doi: 10.7164/antibiotics.38.787. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendall K., Ali-Dunkrah U., Cullum J. Cloning of the galactokinase gene (galK) from Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J Gen Microbiol. 1987 Mar;133(3):721–725. doi: 10.1099/00221287-133-3-721. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kieser H. M., Kieser T., Hopwood D. A. A combined genetic and physical map of the Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1992 Sep;174(17):5496–5507. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.17.5496-5507.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leblond P., Redenbach M., Cullum J. Physical map of the Streptomyces lividans 66 genome and comparison with that of the related strain Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2). J Bacteriol. 1993 Jun;175(11):3422–3429. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.11.3422-3429.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin Y. S., Kieser H. M., Hopwood D. A., Chen C. W. The chromosomal DNA of Streptomyces lividans 66 is linear. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Dec;10(5):923–933. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb00964.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters M., Broda P. Evidence for the bidirectional replications of the Escherichia coli chromosome. Nat New Biol. 1971 Aug 4;232(31):137–140. doi: 10.1038/newbio232137a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogasawara N., Seiki M., Yoshikawa H. Effect of novobiocin on initiation of DNA replication in Bacillus subtilis. Nature. 1979 Oct 25;281(5733):702–704. doi: 10.1038/281702a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ogasawara N., Yoshikawa H. Genes and their organization in the replication origin region of the bacterial chromosome. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Mar;6(5):629–634. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01510.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohki M., Smith C. L. Tracking bacterial DNA replication forks in vivo by pulsed field gel electrophoresis. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 May 11;17(9):3479–3490. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.9.3479. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. P., Chater K. F. Cloning and transcription analysis of the entire glycerol utilization (gylABX) operon of Streptomyces coelicolor A3(2) and identification of a closely associated transcription unit. Mol Gen Genet. 1988 Jan;211(1):129–137. doi: 10.1007/BF00338403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiara A. S., Cundliffe E. Cloning and characterization of a DNA gyrase B gene from Streptomyces sphaeroides that confers resistance to novobiocin. EMBO J. 1988 Jul;7(7):2255–2259. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1988.tb03065.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakrzewska-Czerwińska J., Schrempf H. Characterization of an autonomously replicating region from the Streptomyces lividans chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1992 Apr;174(8):2688–2693. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.8.2688-2693.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



