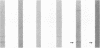Abstract
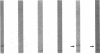
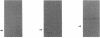
The ptl locus of Bordetella pertussis contains eight open reading frames which are predicted to encode proteins (PtlA to PtlH) that are essential for secretion of pertussis toxin from the bacterium and which are members of a family of transport proteins found in other types of bacteria. We have detected PtlE, PtlF, and PtlG in immunoblots of extracts of B. pertussis by using antibodies raised to fusion proteins consisting of maltose-binding protein and the individual Ptl proteins. These proteins have apparent molecular weights similar to those predicted by DNA sequence analysis. Cell fractionation studies indicated that all three Ptl proteins are associated with the membranes of B. pertussis, suggesting that the Ptl proteins form a gate or channel which facilitates transport of pertussis toxin. Cell extracts of other Bordetella spp. were probed with antibodies to Ptl proteins for the presence of these transport proteins. Neither Bordetella parapertussis nor Bordetella bronchiseptica contained detectable levels of PtlE or PtlF. This lack of detectable Ptl protein may provide an explanation for previous observations which indicated that introduction of the genes encoding pertussis toxin subunits from B. pertussis into other Bordetella spp. results in production of the toxin but not secretion of the toxin.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aricò B., Gross R., Smida J., Rappuoli R. Evolutionary relationships in the genus Bordetella. Mol Microbiol. 1987 Nov;1(3):301–308. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1987.tb01936.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aricò B., Rappuoli R. Bordetella parapertussis and Bordetella bronchiseptica contain transcriptionally silent pertussis toxin genes. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2847–2853. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2847-2853.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Armstrong S. K., Parker C. D. Heat-modifiable envelope proteins of Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1986 Oct;54(1):109–117. doi: 10.1128/iai.54.1.109-117.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs M. S., Gierasch L. M. Molecular mechanisms of protein secretion: the role of the signal sequence. Adv Protein Chem. 1986;38:109–180. doi: 10.1016/s0065-3233(08)60527-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Covacci A., Rappuoli R. Pertussis toxin export requires accessory genes located downstream from the pertussis toxin operon. Mol Microbiol. 1993 May;8(3):429–434. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01587.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ezzell J. W., Dobrogosz W. J., Kloos W. E., Manclark C. R. Phase-shift markers in Bordetella: alterations in envelope proteins. J Infect Dis. 1981 Apr;143(4):562–569. doi: 10.1093/infdis/143.4.562. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst T. R., Holmgren J. Transient entry of enterotoxin subunits into the periplasm occurs during their secretion from Vibrio cholerae. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1037–1045. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1037-1045.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holloway P. W. A simple procedure for removal of Triton X-100 from protein samples. Anal Biochem. 1973 May;53(1):304–308. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(73)90436-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Idigbe E. O., Parton R., Wardlaw A. C. Rapidity of antigenic modulation of Bordetella pertussis in modified Hornibrook medium. J Med Microbiol. 1981 Nov;14(4):409–418. doi: 10.1099/00222615-14-4-409. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaslow H. R., Burns D. L. Pertussis toxin and target eukaryotic cells: binding, entry, and activation. FASEB J. 1992 Jun;6(9):2684–2690. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.6.9.1612292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kenimer J. G., Kim K. J., Probst P. G., Manclark C. R., Burstyn D. G., Cowell J. L. Monoclonal antibodies to pertussis toxin: utilization as probes of toxin function. Hybridoma. 1989 Feb;8(1):37–51. doi: 10.1089/hyb.1989.8.37. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuldau G. A., De Vos G., Owen J., McCaffrey G., Zambryski P. The virB operon of Agrobacterium tumefaciens pTiC58 encodes 11 open reading frames. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Apr;221(2):256–266. doi: 10.1007/BF00261729. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LACEY B. W. Antigenic modulation of Bordetella pertussis. J Hyg (Lond) 1960 Mar;58:57–93. doi: 10.1017/s0022172400038134. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee C. K., Roberts A., Perrin S. Expression of pertussis toxin in Bordetella bronchiseptica and Bordetella parapertussis carrying recombinant plasmids. Infect Immun. 1989 May;57(5):1413–1418. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.5.1413-1418.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leininger E., Probst P. G., Brennan M. J., Kenimer J. G. Inhibition of Bordetella pertussis filamentous hemagglutinin-mediated cell adherence with monoclonal antibodies. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1993 Jan 1;106(1):31–38. doi: 10.1111/j.1574-6968.1993.tb05931.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Locht C., Keith J. M. Pertussis toxin gene: nucleotide sequence and genetic organization. Science. 1986 Jun 6;232(4755):1258–1264. doi: 10.1126/science.3704651. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchitto K. S., Munoz J. J., Keith J. M. Detection of subunits of pertussis toxin in Tn5-induced Bordetella mutants deficient in toxin biological activity. Infect Immun. 1987 May;55(5):1309–1313. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.5.1309-1313.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marchitto K. S., Smith S. G., Locht C., Keith J. M. Nucleotide sequence homology to pertussis toxin gene in Bordetella bronchiseptica and Bordetella parapertussis. Infect Immun. 1987 Mar;55(3):497–501. doi: 10.1128/iai.55.3.497-501.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicosia A., Perugini M., Franzini C., Casagli M. C., Borri M. G., Antoni G., Almoni M., Neri P., Ratti G., Rappuoli R. Cloning and sequencing of the pertussis toxin genes: operon structure and gene duplication. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Jul;83(13):4631–4635. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.13.4631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicosia A., Rappuoli R. Promoter of the pertussis toxin operon and production of pertussis toxin. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jun;169(6):2843–2846. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.6.2843-2846.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pizza M., Bugnoli M., Manetti R., Covacci A., Rappuoli R. The subunit S1 is important for pertussis toxin secretion. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17759–17763. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pugsley A. P., Poquet I., Kornacker M. G. Two distinct steps in pullulanase secretion by Escherichia coli K12. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Apr;5(4):865–873. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00760.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider D. R., Parker C. D. Effect of pyridines on phenotypic properties of Bordetella pertussis. Infect Immun. 1982 Nov;38(2):548–553. doi: 10.1128/iai.38.2.548-553.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamura M., Nogimori K., Murai S., Yajima M., Ito K., Katada T., Ui M., Ishii S. Subunit structure of islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin, in conformity with the A-B model. Biochemistry. 1982 Oct 26;21(22):5516–5522. doi: 10.1021/bi00265a021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorstenson Y. R., Kuldau G. A., Zambryski P. C. Subcellular localization of seven VirB proteins of Agrobacterium tumefaciens: implications for the formation of a T-DNA transport structure. J Bacteriol. 1993 Aug;175(16):5233–5241. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.16.5233-5241.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorstenson Y. R., Zambryski P. C. The essential virulence protein VirB8 localizes to the inner membrane of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol. 1994 Mar;176(6):1711–1717. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.6.1711-1717.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker M. J., Rohde M., Wehland J., Timmis K. N. Construction of minitransposons for constitutive and inducible expression of pertussis toxin in bvg-negative Bordetella bronchiseptica. Infect Immun. 1991 Nov;59(11):4238–4248. doi: 10.1128/iai.59.11.4238-4248.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. E., Akiyoshi D. E., Regier D., Datta A., Gordon M. P., Nester E. W. Characterization of the virB operon from an Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti plasmid. J Biol Chem. 1988 Apr 25;263(12):5804–5814. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. E., Akiyoshi D. E., Regier D., Datta A., Gordon M. P., Nester E. W. Correction: characterization of the virB operon from Agrobacterium tumefaciens Ti plasmid. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 15;265(8):4768–4768. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward J. E., Jr, Dale E. M., Nester E. W., Binns A. N. Identification of a virB10 protein aggregate in the inner membrane of Agrobacterium tumefaciens. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5200–5210. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5200-5210.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Falkow S. Transposon insertion and subsequent donor formation promoted by Tn501 in Bordetella pertussis. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jan;153(1):304–309. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.1.304-309.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Goodwin M. S. Lethal infection by Bordetella pertussis mutants in the infant mouse model. Infect Immun. 1989 Dec;57(12):3757–3764. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.12.3757-3764.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Hewlett E. L., Myers G. A., Falkow S. Pertussis toxin and extracytoplasmic adenylate cyclase as virulence factors of Bordetella pertussis. J Infect Dis. 1984 Aug;150(2):219–222. doi: 10.1093/infdis/150.2.219. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Johnson F. D., Burns D. L. Molecular characterization of an operon required for pertussis toxin secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Apr 1;90(7):2970–2974. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.7.2970. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss A. A., Melton A. R., Walker K. E., Andraos-Selim C., Meidl J. J. Use of the promoter fusion transposon Tn5 lac to identify mutations in Bordetella pertussis vir-regulated genes. Infect Immun. 1989 Sep;57(9):2674–2682. doi: 10.1128/iai.57.9.2674-2682.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wickner W., Driessen A. J., Hartl F. U. The enzymology of protein translocation across the Escherichia coli plasma membrane. Annu Rev Biochem. 1991;60:101–124. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.60.070191.000533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]