Abstract
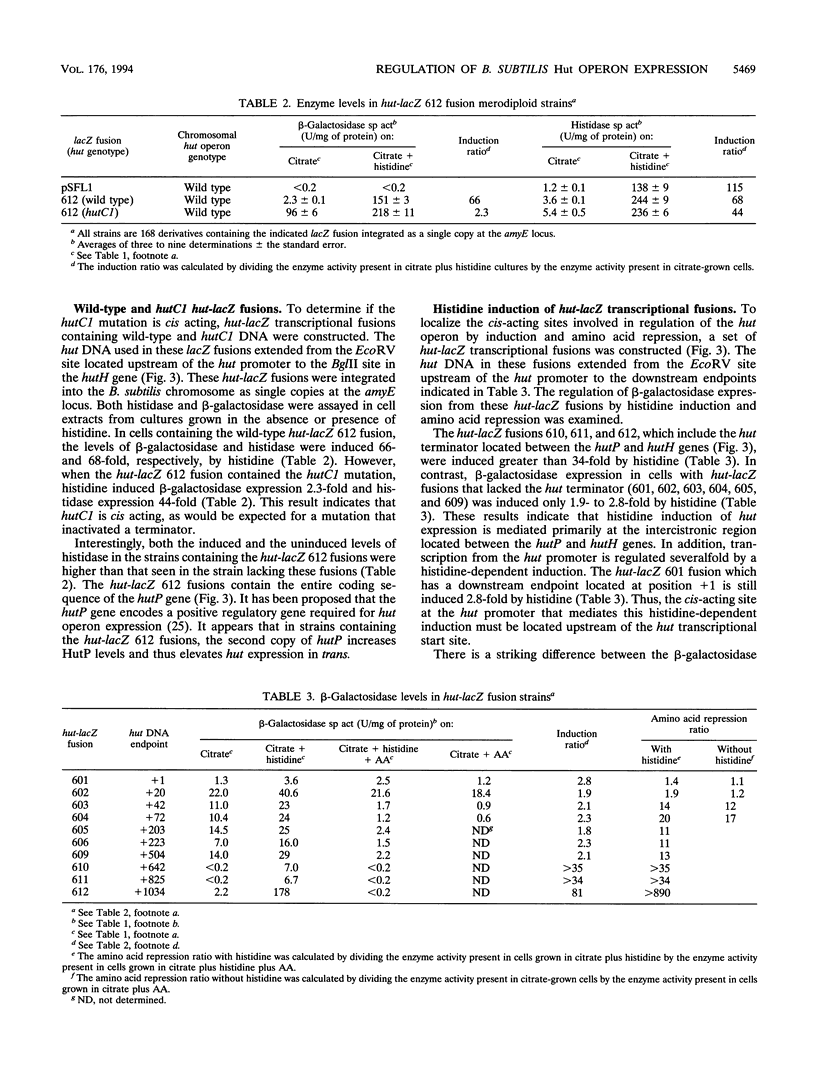
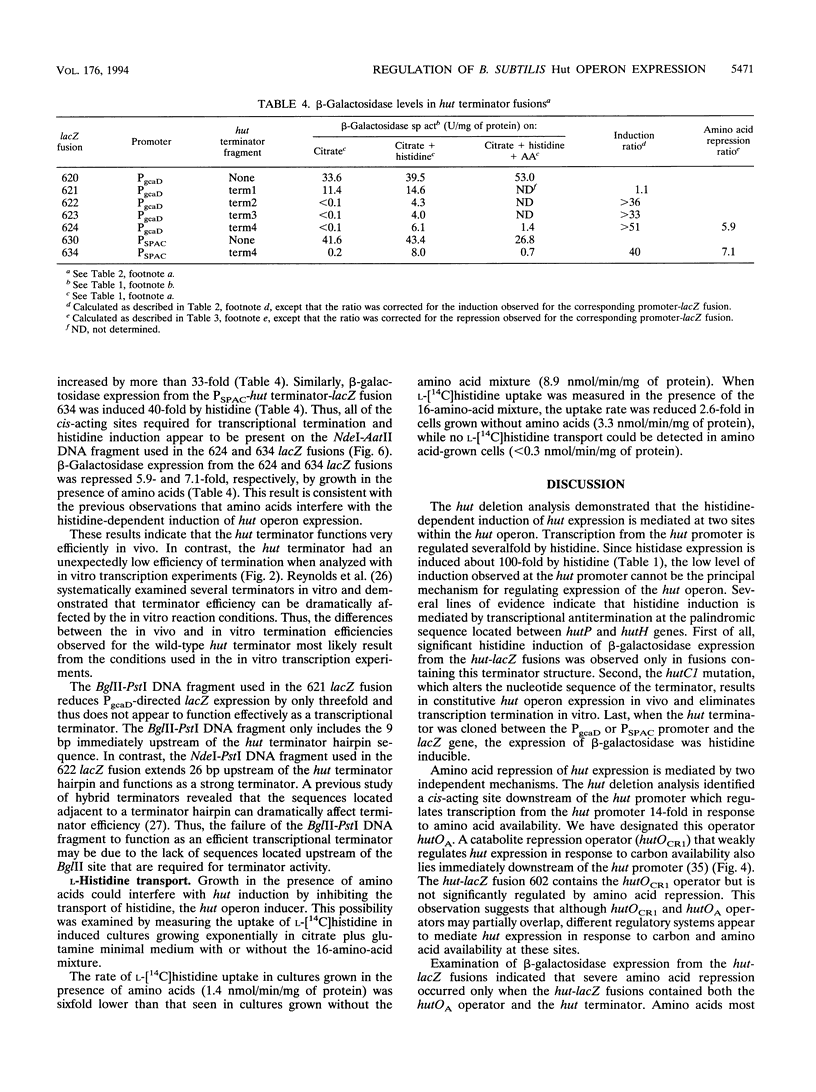
Expression of the Bacillus subtilis hut operon is induced by histidine and subject to regulation by carbon catabolite repression and amino acid repression. A set of hut-lacZ transcriptional fusions was constructed and used to identify the cis-acting sites required for histidine induction and amino acid repression. Histidine induction was found to be primarily mediated by transcriptional antitermination at a palindromic sequence located immediately downstream of the first structural gene in the hut operon, hutP. High levels of histidine induction were observed only in hut-lacZ fusions which contained this palindromic sequence. The hutC1 mutation, which results in constitutive expression of the hut operon, was sequenced and found to contain a GC to TA transversion located within the stem-loop structure. Transcription of hut DNA in vitro revealed that the palindromic structure functions as a transcriptional terminator with wild-type hut DNA but not with hutC1 DNA. Two sites were found to be involved in amino acid repression of hut expression: (i) an operator, hutOA, which lies downstream of the hut promoter, and (ii) the hut terminator. The rate of [14C]histidine uptake in amino acid-grown cells was sixfold lower than that seen in cells grown without amino acids. Thus, inhibition of histidine transport in amino acid-grown cells indirectly regulates hut expression by interfering with histidine induction at the hut terminator.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aksoy S., Squires C. L., Squires C. Translational coupling of the trpB and trpA genes in the Escherichia coli tryptophan operon. J Bacteriol. 1984 Feb;157(2):363–367. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.2.363-367.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Allison S. L., Phillips A. T. Nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding the repressor for the histidine utilization genes of Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5470–5476. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5470-5476.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson M. R., Wray L. V., Jr, Fisher S. H. Activation of the Bacillus subtilis hut operon at the onset of stationary growth phase in nutrient sporulation medium results primarily from the relief of amino acid repression of histidine transport. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jul;175(14):4282–4289. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.14.4282-4289.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Atkinson M. R., Wray L. V., Jr, Fisher S. H. Regulation of histidine and proline degradation enzymes by amino acid availability in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):4758–4765. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.4758-4765.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chasin L. A., Magasanik B. Induction and repression of the histidine-degrading enzymes of Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1968 Oct 10;243(19):5165–5178. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. D., Morrison D. A. Cloning of Streptococcus pneumoniae DNA fragments in Escherichia coli requires vectors protected by strong transcriptional terminators. Gene. 1987;55(2-3):179–187. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90278-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donnelly C. E., Sonenshein A. L. Promoter-probe plasmid for Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1984 Mar;157(3):965–967. doi: 10.1128/jb.157.3.965-967.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fouet A., Jin S. F., Raffel G., Sonenshein A. L. Multiple regulatory sites in the Bacillus subtilis citB promoter region. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5408–5415. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5408-5415.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Freier S. M., Kierzek R., Jaeger J. A., Sugimoto N., Caruthers M. H., Neilson T., Turner D. H. Improved free-energy parameters for predictions of RNA duplex stability. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Dec;83(24):9373–9377. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.24.9373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hu L., Phillips A. T. Organization and multiple regulation of histidine utilization genes in Pseudomonas putida. J Bacteriol. 1988 Sep;170(9):4272–4279. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.9.4272-4279.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kendrick K. E., Wheelis M. L. Histidine dissimilation in Streptomyces coelicolor. J Gen Microbiol. 1982 Sep;128(9):2029–2040. doi: 10.1099/00221287-128-9-2029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimhi Y., Magasanik B. Genetic basis of histidine degradation in Bacillus subtilis. J Biol Chem. 1970 Jul 25;245(14):3545–3548. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kroening T. A., Kendrick K. E. Cascading regulation of histidase activity in Streptomyces griseus. J Bacteriol. 1989 Feb;171(2):1100–1105. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.2.1100-1105.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leidigh B. J., Wheelis M. L. Genetic control of the histidine dissimilatory pathway in Pseudomonas putida. Mol Gen Genet. 1973 Feb 2;120(3):201–210. doi: 10.1007/BF00267152. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lessie T. G., Neidhardt F. C. Formation and operation of the histidine-degrading pathway in Pseudomonas aeruginosa. J Bacteriol. 1967 Jun;93(6):1800–1810. doi: 10.1128/jb.93.6.1800-1810.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lopilato J., Bortner S., Beckwith J. Mutations in a new chromosomal gene of Escherichia coli K-12, pcnB, reduce plasmid copy number of pBR322 and its derivatives. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Nov;205(2):285–290. doi: 10.1007/BF00430440. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moran C. P., Jr, Lang N., LeGrice S. F., Lee G., Stephens M., Sonenshein A. L., Pero J., Losick R. Nucleotide sequences that signal the initiation of transcription and translation in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1982;186(3):339–346. doi: 10.1007/BF00729452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neidhardt F. C., Bloch P. L., Smith D. F. Culture medium for enterobacteria. J Bacteriol. 1974 Sep;119(3):736–747. doi: 10.1128/jb.119.3.736-747.1974. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda M., Katagai T., Tomura D., Shoun H., Hoshino T., Furukawa K. Analysis of the transcriptional activity of the hut promoter in Bacillus subtilis and identification of a cis-acting regulatory region associated with catabolite repression downstream from the site of transcription. Mol Microbiol. 1992 Sep;6(18):2573–2582. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1992.tb01434.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oda M., Sugishita A., Furukawa K. Cloning and nucleotide sequences of histidase and regulatory genes in the Bacillus subtilis hut operon and positive regulation of the operon. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jul;170(7):3199–3205. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.7.3199-3205.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds R., Bermúdez-Cruz R. M., Chamberlin M. J. Parameters affecting transcription termination by Escherichia coli RNA polymerase. I. Analysis of 13 rho-independent terminators. J Mol Biol. 1992 Mar 5;224(1):31–51. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90574-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds R., Chamberlin M. J. Parameters affecting transcription termination by Escherichia coli RNA. II. Construction and analysis of hybrid terminators. J Mol Biol. 1992 Mar 5;224(1):53–63. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(92)90575-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg M., Court D. Regulatory sequences involved in the promotion and termination of RNA transcription. Annu Rev Genet. 1979;13:319–353. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.13.120179.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwacha A., Bender R. A. Nucleotide sequence of the gene encoding the repressor for the histidine utilization genes of Klebsiella aerogenes. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5477–5481. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5477-5481.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwacha A., Bender R. A. The product of the Klebsiella aerogenes nac (nitrogen assimilation control) gene is sufficient for activation of the hut operons and repression of the gdh operon. J Bacteriol. 1993 Apr;175(7):2116–2124. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.7.2116-2124.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimotsu H., Henner D. J. Construction of a single-copy integration vector and its use in analysis of regulation of the trp operon of Bacillus subtilis. Gene. 1986;43(1-2):85–94. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90011-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack F. J., Mueller J. P., Sonenshein A. L. Mutations that relieve nutritional repression of the Bacillus subtilis dipeptide permease operon. J Bacteriol. 1993 Aug;175(15):4605–4614. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.15.4605-4614.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slack F. J., Mueller J. P., Strauch M. A., Mathiopoulos C., Sonenshein A. L. Transcriptional regulation of a Bacillus subtilis dipeptide transport operon. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Aug;5(8):1915–1925. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb00815.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wray L. V., Jr, Pettengill F. K., Fisher S. H. Catabolite repression of the Bacillus subtilis hut operon requires a cis-acting site located downstream of the transcription initiation site. J Bacteriol. 1994 Apr;176(7):1894–1902. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.7.1894-1902.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu P. C., Kroening T. A., White P. J., Kendrick K. E. Purification of histidase from Streptomyces griseus and nucleotide sequence of the hutH structural gene. J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(5):1647–1655. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.5.1647-1655.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanofsky C., Platt T., Crawford I. P., Nichols B. P., Christie G. E., Horowitz H., VanCleemput M., Wu A. M. The complete nucleotide sequence of the tryptophan operon of Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Dec 21;9(24):6647–6668. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.24.6647. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yansura D. G., Henner D. J. Use of the Escherichia coli lac repressor and operator to control gene expression in Bacillus subtilis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jan;81(2):439–443. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.2.439. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]