Abstract
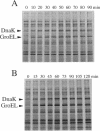
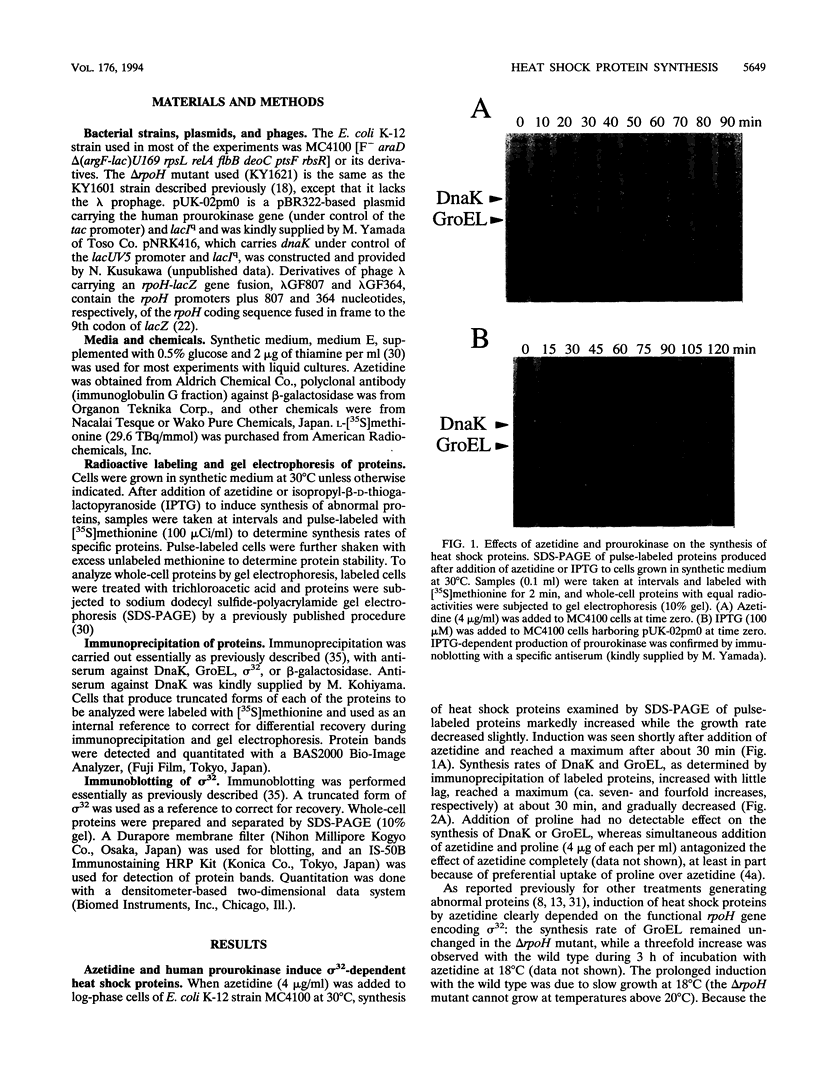
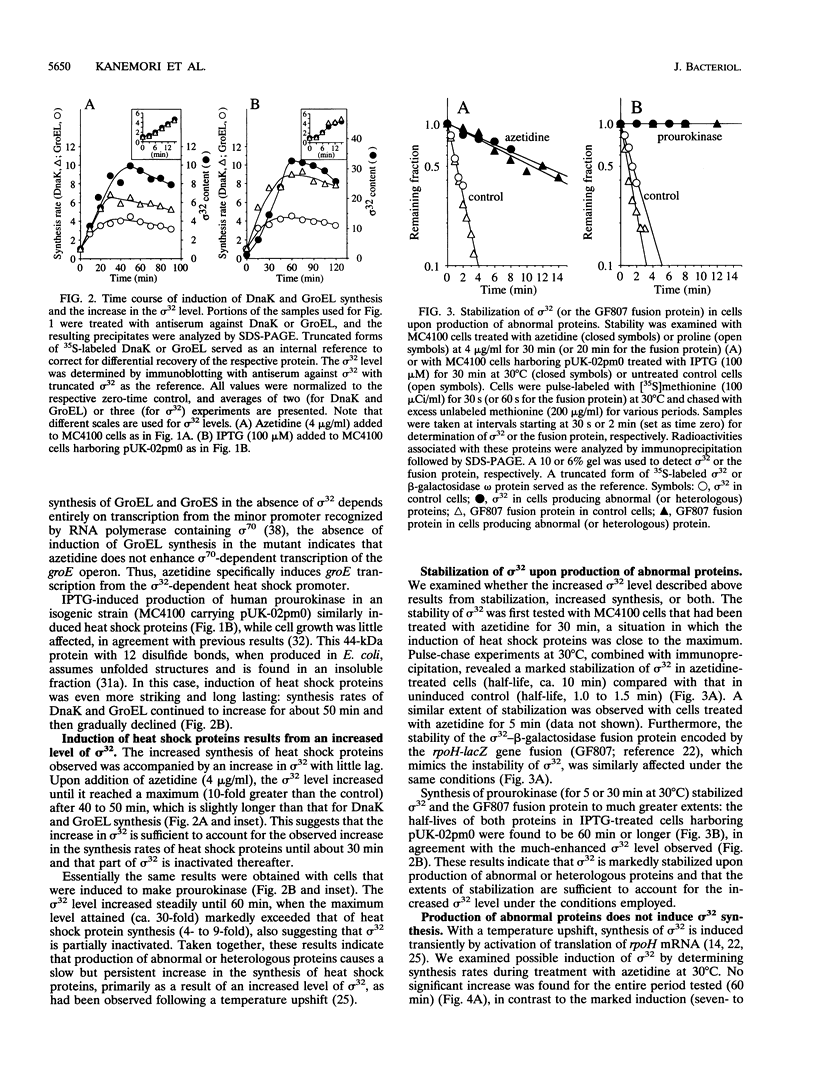
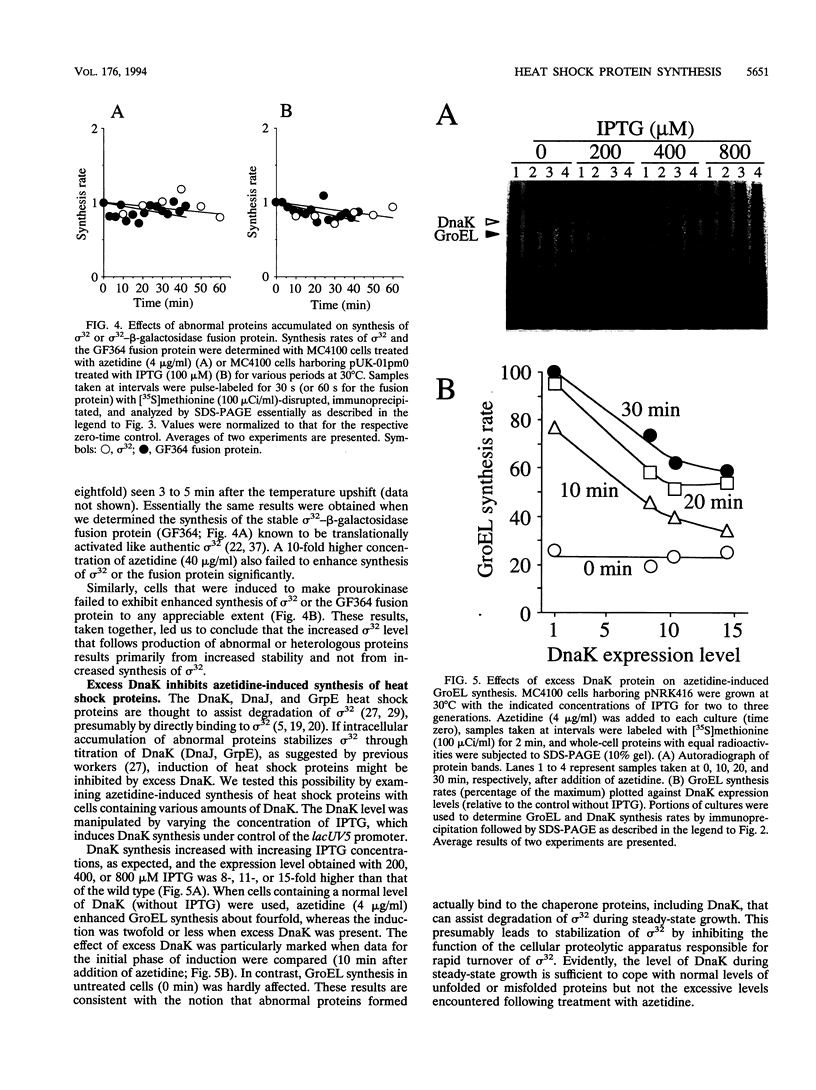
Accumulation of abnormal proteins in cells of bacteria or eukaryotes can induce synthesis of a set of heat shock proteins. We examined such induction following addition of azetidine (a proline analog) or synthesis of a heterologous protein (human prourokinase) in Escherichia coli. Synthesis of heat shock proteins under these conditions increased almost immediately and continued with increasing rates until it reached a maximum after 30 to 60 min at 30 degrees C. The induction was closely accompanied by an increase in the cellular level of sigma 32 specifically required for transcription of heat shock genes. The increase in sigma 32 initially coincided with increased synthesis of heat shock proteins but then exceeded the latter, particularly following accumulation of prourokinase. The sigma 32 level increase upon either treatment was found to result solely from stabilization of sigma 32, which is ordinarily very unstable, and not from increased synthesis of sigma 32. This is in contrast to what had been found when cells were exposed to a higher temperature, at which both increased synthesis and stabilization of sigma 32 contributed to the increased sigma 32 level. On the basis of these and other findings, we propose that abnormal proteins stabilize sigma 32 by a pathway or a mechanism distinct from that used for the induction of sigma 32 synthesis known to occur at the level of translation. Evidence further suggests that the DnaK chaperone plays a crucial regulatory role in induction of the heat shock response by abnormal proteins.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ananthan J., Goldberg A. L., Voellmy R. Abnormal proteins serve as eukaryotic stress signals and trigger the activation of heat shock genes. Science. 1986 Apr 25;232(4749):522–524. doi: 10.1126/science.3083508. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bahl H., Echols H., Straus D. B., Court D., Crowl R., Georgopoulos C. P. Induction of the heat shock response of E. coli through stabilization of sigma 32 by the phage lambda cIII protein. Genes Dev. 1987 Mar;1(1):57–64. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.1.57. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bukau B. Regulation of the Escherichia coli heat-shock response. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Aug;9(4):671–680. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01727.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig E. A., Gross C. A. Is hsp70 the cellular thermometer? Trends Biochem Sci. 1991 Apr;16(4):135–140. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(91)90055-z. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fowden L., Lewis D., Tristram H. Toxic amino acids: their action as antimetabolites. Adv Enzymol Relat Areas Mol Biol. 1967;29:89–163. doi: 10.1002/9780470122747.ch3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gamer J., Bujard H., Bukau B. Physical interaction between heat shock proteins DnaK, DnaJ, and GrpE and the bacterial heat shock transcription factor sigma 32. Cell. 1992 May 29;69(5):833–842. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90294-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Georgopoulos C., Welch W. J. Role of the major heat shock proteins as molecular chaperones. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1993;9:601–634. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.09.110193.003125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff S. A., Goldberg A. L. Production of abnormal proteins in E. coli stimulates transcription of lon and other heat shock genes. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):587–595. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80031-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman A. D., Erickson J. W., Gross C. A. The htpR gene product of E. coli is a sigma factor for heat-shock promoters. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):383–390. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90493-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grossman A. D., Straus D. B., Walter W. A., Gross C. A. Sigma 32 synthesis can regulate the synthesis of heat shock proteins in Escherichia coli. Genes Dev. 1987 Apr;1(2):179–184. doi: 10.1101/gad.1.2.179. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hendrick J. P., Hartl F. U. Molecular chaperone functions of heat-shock proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:349–384. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.002025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ito K., Akiyama Y., Yura T., Shiba K. Diverse effects of the MalE-LacZ hybrid protein on Escherichia coli cell physiology. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jul;167(1):201–204. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.1.201-204.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kamath-Loeb A. S., Gross C. A. Translational regulation of sigma 32 synthesis: requirement for an internal control element. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jun;173(12):3904–3906. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.12.3904-3906.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keller J. A., Simon L. D. Divergent effects of a dnaK mutation on abnormal protein degradation in Escherichia coli. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Jan;2(1):31–41. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00004.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelley P. M., Schlesinger M. J. The effect of amino acid analogues and heat shock on gene expression in chicken embryo fibroblasts. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1277–1286. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90053-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kucharczyk K., Laskowska E., Taylor A. Response of Escherichia coli cell membranes to induction of lambda cl857 prophage by heat shock. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Dec;5(12):2935–2945. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01853.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kusukawa N., Yura T. Heat shock protein GroE of Escherichia coli: key protective roles against thermal stress. Genes Dev. 1988 Jul;2(7):874–882. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.7.874. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liberek K., Galitski T. P., Zylicz M., Georgopoulos C. The DnaK chaperone modulates the heat shock response of Escherichia coli by binding to the sigma 32 transcription factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 15;89(8):3516–3520. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.8.3516. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liberek K., Georgopoulos C. Autoregulation of the Escherichia coli heat shock response by the DnaK and DnaJ heat shock proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Dec 1;90(23):11019–11023. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.23.11019. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nagai H., Yuzawa H., Yura T. Interplay of two cis-acting mRNA regions in translational control of sigma 32 synthesis during the heat shock response of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Dec 1;88(23):10515–10519. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.23.10515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsell D. A., Sauer R. T. Induction of a heat shock-like response by unfolded protein in Escherichia coli: dependence on protein level not protein degradation. Genes Dev. 1989 Aug;3(8):1226–1232. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.8.1226. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus D. B., Walter W. A., Gross C. A. Escherichia coli heat shock gene mutants are defective in proteolysis. Genes Dev. 1988 Dec;2(12B):1851–1858. doi: 10.1101/gad.2.12b.1851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus D. B., Walter W. A., Gross C. A. The heat shock response of E. coli is regulated by changes in the concentration of sigma 32. Nature. 1987 Sep 24;329(6137):348–351. doi: 10.1038/329348a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Straus D., Walter W., Gross C. A. DnaK, DnaJ, and GrpE heat shock proteins negatively regulate heat shock gene expression by controlling the synthesis and stability of sigma 32. Genes Dev. 1990 Dec;4(12A):2202–2209. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.12a.2202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilly K., McKittrick N., Zylicz M., Georgopoulos C. The dnaK protein modulates the heat-shock response of Escherichia coli. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):641–646. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90396-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tilly K., Spence J., Georgopoulos C. Modulation of stability of the Escherichia coli heat shock regulatory factor sigma. J Bacteriol. 1989 Mar;171(3):1585–1589. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.3.1585-1589.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tobe T., Ito K., Yura T. Isolation and physical mapping of temperature-sensitive mutants defective in heat-shock induction of proteins in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;195(1-2):10–16. doi: 10.1007/BF00332716. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wild J., Walter W. A., Gross C. A., Altman E. Accumulation of secretory protein precursors in Escherichia coli induces the heat shock response. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jul;175(13):3992–3997. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.13.3992-3997.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamori T., Yura T. Genetic control of heat-shock protein synthesis and its bearing on growth and thermal resistance in Escherichia coli K-12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(3):860–864. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.3.860. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamori T., Yura T. Temperature-induced synthesis of specific proteins in Escherichia coli: evidence for transcriptional control. J Bacteriol. 1980 Jun;142(3):843–851. doi: 10.1128/jb.142.3.843-851.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yano R., Nagai H., Shiba K., Yura T. A mutation that enhances synthesis of sigma 32 and suppresses temperature-sensitive growth of the rpoH15 mutant of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1990 Apr;172(4):2124–2130. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.4.2124-2130.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yura T., Nagai H., Mori H. Regulation of the heat-shock response in bacteria. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1993;47:321–350. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.47.100193.001541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuzawa H., Nagai H., Mori H., Yura T. Heat induction of sigma 32 synthesis mediated by mRNA secondary structure: a primary step of the heat shock response in Escherichia coli. Nucleic Acids Res. 1993 Nov 25;21(23):5449–5455. doi: 10.1093/nar/21.23.5449. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhou Y. N., Kusukawa N., Erickson J. W., Gross C. A., Yura T. Isolation and characterization of Escherichia coli mutants that lack the heat shock sigma factor sigma 32. J Bacteriol. 1988 Aug;170(8):3640–3649. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.8.3640-3649.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]