Abstract
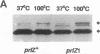
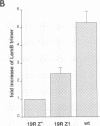
Reversion analysis has been employed to isolate suppressors that restore export of a unique LamB signal sequence mutant. The mutation results in a substitution of Arg for Met at position 19, which prevents LamB export to the outer membrane and leads to a Dex- phenotype. Unlike other LamB signal sequence mutants utilized for reversion analysis, LamB19R becomes stably associated with the inner membrane in an export-specific manner. In this study, Dex+ revertants were selected and various suppressors were isolated. One of the extragenic suppressors, designated prlZ1, was chosen for further study. prlZ1 maps to 69 min on the Escherichia coli chromosome. The suppressor is dominant and SecB dependent. In addition to its effect on lamB19R, prlZ1 suppresses the export defect of signal sequence point mutations at positions 12, 15, and 16, as well as several point mutations in the maltose-binding protein signal sequence. prlZ1 does not suppress deletion mutations in either signal sequence. This pattern of suppression can be explained by interaction of a helical LamB signal sequence with the suppressor.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bachmann B. J. Pedigrees of some mutant strains of Escherichia coli K-12. Bacteriol Rev. 1972 Dec;36(4):525–557. doi: 10.1128/br.36.4.525-557.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bankaitis V. A., Bassford P. J., Jr Proper interaction between at least two components is required for efficient export of proteins to the Escherichia coli cell envelope. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):169–178. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.169-178.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benson S. A., Decloux A. Isolation and characterization of outer membrane permeability mutants in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):361–367. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.361-367.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Briggs M. S., Cornell D. G., Dluhy R. A., Gierasch L. M. Conformations of signal peptides induced by lipids suggest initial steps in protein export. Science. 1986 Jul 11;233(4760):206–208. doi: 10.1126/science.2941862. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bruch M. D., Gierasch L. M. Comparison of helix stability in wild-type and mutant LamB signal sequences. J Biol Chem. 1990 Mar 5;265(7):3851–3858. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casadaban M. J. Transposition and fusion of the lac genes to selected promoters in Escherichia coli using bacteriophage lambda and Mu. J Mol Biol. 1976 Jul 5;104(3):541–555. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(76)90119-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DePamphilis M. L. Dissociation and reassembly of Escherichia coli outer membrane and of lipopolysaccharide, and their reassembly onto flagellar basal bodies. J Bacteriol. 1971 Mar;105(3):1184–1199. doi: 10.1128/jb.105.3.1184-1199.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Derman A. I., Puziss J. W., Bassford P. J., Jr, Beckwith J. A signal sequence is not required for protein export in prlA mutants of Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):879–888. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05728.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emr S. D., Hanley-Way S., Silhavy T. J. Suppressor mutations that restore export of a protein with a defective signal sequence. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):79–88. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90272-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emr S. D., Silhavy T. J. Importance of secondary structure in the signal sequence for protein secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(15):4599–4603. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.15.4599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emr S. D., Silhavy T. J. Mutations affecting localization of an Escherichia coli outer membrane protein, the bacteriophage lambda receptor. J Mol Biol. 1980 Jul 25;141(1):63–90. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(80)80029-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gardel C., Benson S., Hunt J., Michaelis S., Beckwith J. secD, a new gene involved in protein export in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1286–1290. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1286-1290.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiino D. R., Silhavy T. J. Mutation prlF1 relieves the lethality associated with export of beta-galactosidase hybrid proteins in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jun;158(3):878–883. doi: 10.1128/jb.158.3.878-883.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kumamoto C. A., Beckwith J. Evidence for specificity at an early step in protein export in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):267–274. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.267-274.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Low B. Rapid mapping of conditional and auxotrophic mutations in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1973 Feb;113(2):798–812. doi: 10.1128/jb.113.2.798-812.1973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishiyama K., Mizushima S., Tokuda H. A novel membrane protein involved in protein translocation across the cytoplasmic membrane of Escherichia coli. EMBO J. 1993 Sep;12(9):3409–3415. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06015.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborne R. S., Silhavy T. J. PrlA suppressor mutations cluster in regions corresponding to three distinct topological domains. EMBO J. 1993 Sep;12(9):3391–3398. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb06013.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schnaitman C. A. Effect of ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid, Triton X-100, and lysozyme on the morphology and chemical composition of isolate cell walls of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1971 Oct;108(1):553–563. doi: 10.1128/jb.108.1.553-563.1971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Singer M., Baker T. A., Schnitzler G., Deischel S. M., Goel M., Dove W., Jaacks K. J., Grossman A. D., Erickson J. W., Gross C. A. A collection of strains containing genetically linked alternating antibiotic resistance elements for genetic mapping of Escherichia coli. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Mar;53(1):1–24. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.1.1-24.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stader J., Benson S. A., Silhavy T. J. Kinetic analysis of lamB mutants suggests the signal sequence plays multiple roles in protein export. J Biol Chem. 1986 Nov 15;261(32):15075–15080. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stader J., Gansheroff L. J., Silhavy T. J. New suppressors of signal-sequence mutations, prlG, are linked tightly to the secE gene of Escherichia coli. Genes Dev. 1989 Jul;3(7):1045–1052. doi: 10.1101/gad.3.7.1045. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stader J., Justice S. Export and trimerization pathways of maltoporin overlap in the inner membrane of Escherichia coli. J Mol Biol. 1994 May 13;238(4):555–562. doi: 10.1006/jmbi.1994.1314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stader J., Silhavy T. J. A progenitor of the outer membrane LamB trimer. J Bacteriol. 1988 Apr;170(4):1973–1974. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.4.1973-1974.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomoyasu T., Yuki T., Morimura S., Mori H., Yamanaka K., Niki H., Hiraga S., Ogura T. The Escherichia coli FtsH protein is a prokaryotic member of a protein family of putative ATPases involved in membrane functions, cell cycle control, and gene expression. J Bacteriol. 1993 Mar;175(5):1344–1351. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.5.1344-1351.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trun N. J., Silhavy T. J. Characterization and in vivo cloning of prlC, a suppressor of signal sequence mutations in Escherichia coli K12. Genetics. 1987 Aug;116(4):513–521. doi: 10.1093/genetics/116.4.513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trun N. J., Silhavy T. J. PrlC, a suppressor of signal sequence mutations in Escherichia coli, can direct the insertion of the signal sequence into the membrane. J Mol Biol. 1989 Feb 20;205(4):665–676. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(89)90312-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trun N. J., Stader J., Lupas A., Kumamoto C., Silhavy T. J. Two cellular components, PrlA and SecB, that recognize different sequence determinants are required for efficient protein export. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5928–5930. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5928-5930.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vos-Scheperkeuter G. H., Witholt B. Assembly pathway of newly synthesized LamB protein an outer membrane protein of Escherichia coli K-12. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jun 5;175(4):511–528. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90182-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wanner B. L. Novel regulatory mutants of the phosphate regulon in Escherichia coli K-12. J Mol Biol. 1986 Sep 5;191(1):39–58. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90421-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei S. Q., Stader J. Two distinct regions of the LamB signal sequence function in different steps in export. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 21;269(3):1648–1653. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]