Abstract
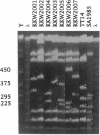
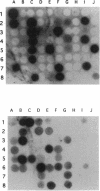
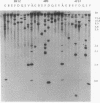
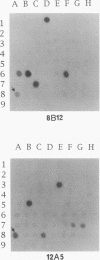
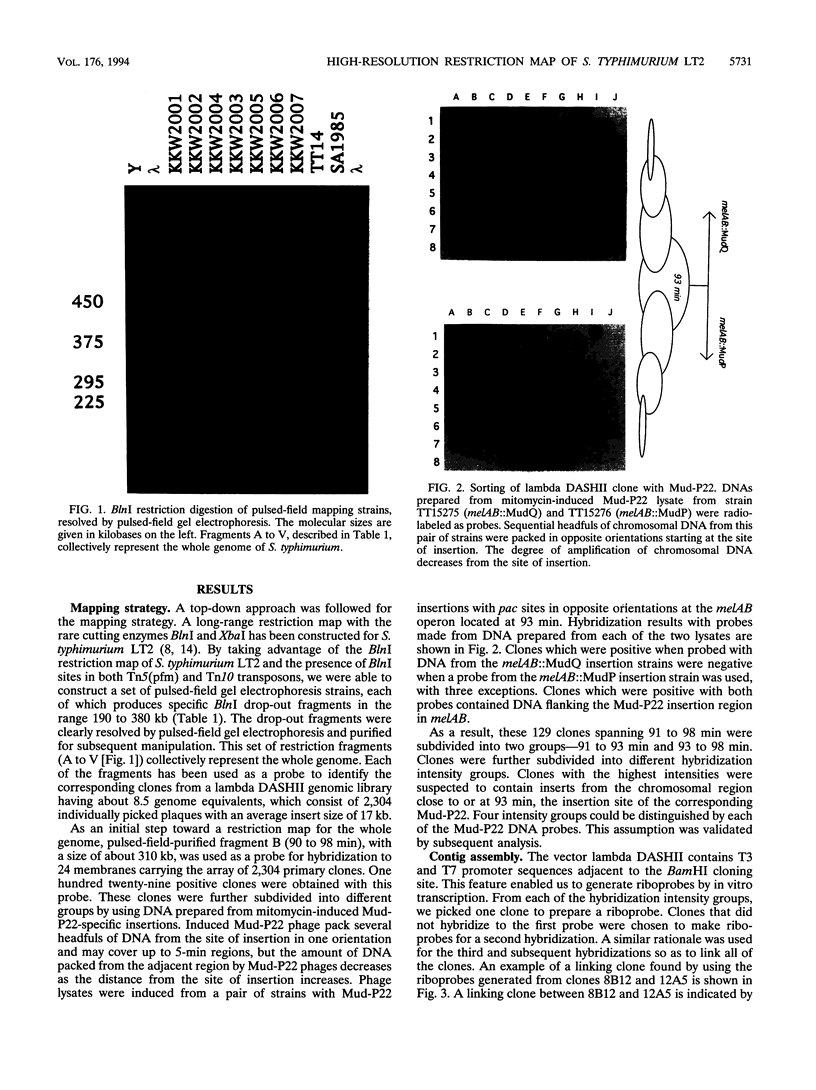
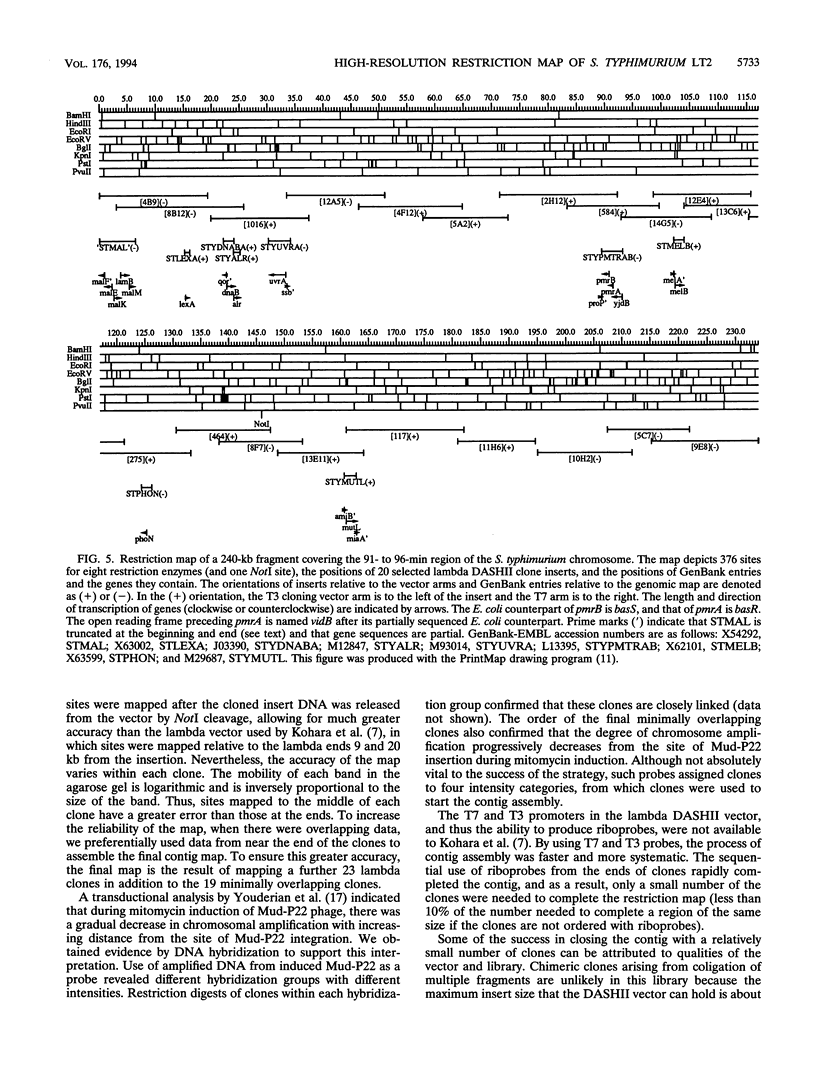
A hierarchical approach allows the completion of contiguous sets of overlapping clones for small regions of a genome, one at a time rather than tackling the whole genome at once. On the basis of the BlnI restriction map for Salmonella typhimurium LT2, we dissected the chromosome into 21 different fragments by using a Tn5 transposon carrying a BlnI site. Dissected chromosomal fragments were purified by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis and used as probes for sorting a lambda DASHII genomic library of 2,304 primary clones. A total of 129 clones identified as spanning the region from 91 min to 98 min were partly ordered on the basis of the intensity of hybridization with mitomycin-induced Mud-P22 phage DNAs from insertions with pac sites in opposite orientations at 93 min used as probes. Decreased signal intensity with the Mud-P22 probes corresponded to the increased distance of the clone from the site of Mud-P22 insertion and allowed the clones to be placed in two groups from 91 min to 93 min and from 93 min to 98 min and into four intensity categories within the two groups. A member of each category was used to generate a riboprobe from the T3 promoter flanking the insert. This probe identified overlapping clones among the 129 clones. This subchromosomal library was then screened again with riboprobes from nonoverlapping clones. After four cycles of this strategy, a minimal contiguous sequence of 19 partly overlapping clones was selected for restriction mapping. A detailed map of 378 sites for eight restriction enzymes is presented for a region of about 240 kb. Working clockwise, the following genes were placed on this physical map on the basis of their restriction maps: malFEK, lamB, malM, lexA, qor, dnaB, alr, uvrA, proP, pmrB, pmrA, melA, melB, phoN, amiB, mutL, and miaA.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benson N. R., Goldman B. S. Rapid mapping in Salmonella typhimurium with Mud-P22 prophages. J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(5):1673–1681. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.5.1673-1681.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels D. L., Plunkett G., 3rd, Burland V., Blattner F. R. Analysis of the Escherichia coli genome: DNA sequence of the region from 84.5 to 86.5 minutes. Science. 1992 Aug 7;257(5071):771–778. doi: 10.1126/science.1379743. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graña D., Youderian P., Susskind M. M. Mutations that improve the ant promoter of Salmonella phage P22. Genetics. 1985 May;110(1):1–16. doi: 10.1093/genetics/110.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Groisman E. A., Sturmoski M. A., Solomon F. R., Lin R., Ochman H. Molecular, functional, and evolutionary analysis of sequences specific to Salmonella. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 1;90(3):1033–1037. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.3.1033. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kajitani M., Ishihama A. Identification and sequence determination of the host factor gene for bacteriophage Q beta. Nucleic Acids Res. 1991 Mar 11;19(5):1063–1066. doi: 10.1093/nar/19.5.1063. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kleckner N., Chan R. K., Tye B. K., Botstein D. Mutagenesis by insertion of a drug-resistance element carrying an inverted repetition. J Mol Biol. 1975 Oct 5;97(4):561–575. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80059-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohara Y., Akiyama K., Isono K. The physical map of the whole E. coli chromosome: application of a new strategy for rapid analysis and sorting of a large genomic library. Cell. 1987 Jul 31;50(3):495–508. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(87)90503-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu S. L., Sanderson K. E. A physical map of the Salmonella typhimurium LT2 genome made by using XbaI analysis. J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(5):1662–1672. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.5.1662-1672.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanderson K. E., Roth J. R. Linkage map of Salmonella typhimurium, edition VII. Microbiol Rev. 1988 Dec;52(4):485–532. doi: 10.1128/mr.52.4.485-532.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. K., McClelland M. A BlnI restriction map of the Salmonella typhimurium LT2 genome. J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(5):1656–1661. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.5.1656-1661.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. K., McClelland M. Dissection of the Salmonella typhimurium genome by use of a Tn5 derivative carrying rare restriction sites. J Bacteriol. 1992 Jun;174(11):3807–3811. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.11.3807-3811.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong K. K., Suen K. L., Kwan H. S. Transcription of pfl is regulated by anaerobiosis, catabolite repression, pyruvate, and oxrA: pfl::Mu dA operon fusions of Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1989 Sep;171(9):4900–4905. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.9.4900-4905.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Youderian P., Sugiono P., Brewer K. L., Higgins N. P., Elliott T. Packaging specific segments of the Salmonella chromosome with locked-in Mud-P22 prophages. Genetics. 1988 Apr;118(4):581–592. doi: 10.1093/genetics/118.4.581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]