Abstract
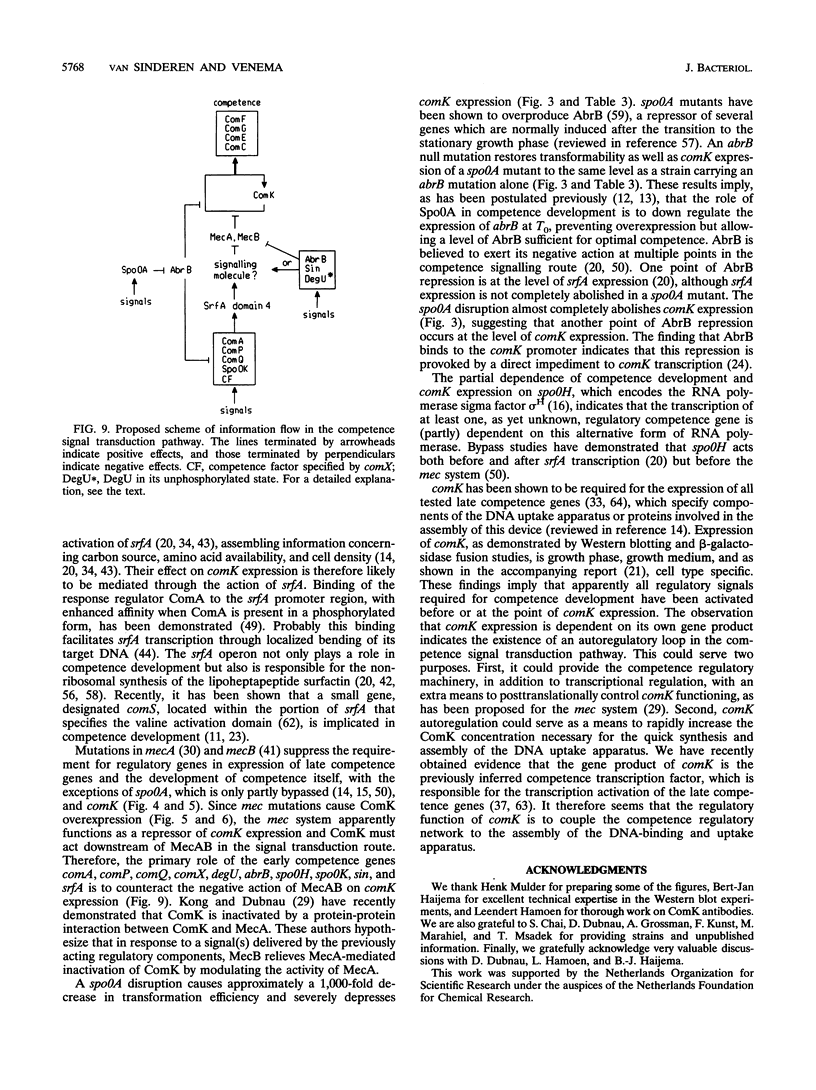
The comK gene is a regulatory transcription unit which is essential for the development of genetic competence in Bacillus subtilis. The transcription of comK is under strict nutritional and growth phase-dependent control and has been shown to depend on the gene products of comA and srfA. In this report, we show that expression of comK is dependent on its own gene product as well as on the gene products of all other tested regulatory genes known to be involved in competence development (abrB, comA, comP, degU, sin, spo0A, spo0H, spo0K, and srfA). A mecA mutation is able to suppress the competence deficiency of mutations in any of these regulatory loci except for mutations in spo0A and, as we show here, in comK. Furthermore, we show that the presence of comK on a multiple copy plasmid leads to derepression of comK expression, causing an almost constitutive expression of competence in minimal medium as well as permitting competence development in complex medium. We infer from these results that the signals which trigger competence development, after having been received and processed by the various components of the competence signal transduction pathway, all converge at the level of comK expression. As soon as derepression of comK expression occurs, the positive autoregulation rapidly results in accumulation of the comK gene product, which subsequently induces competence.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albano M., Hahn J., Dubnau D. Expression of competence genes in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1987 Jul;169(7):3110–3117. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.7.3110-3117.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bai U., Mandic-Mulec I., Smith I. SinI modulates the activity of SinR, a developmental switch protein of Bacillus subtilis, by protein-protein interaction. Genes Dev. 1993 Jan;7(1):139–148. doi: 10.1101/gad.7.1.139. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Biswal N., Kleinschmidt A. K., Spatz H. C., Trautner T. A. Physical properties of the DNA of bacteriophage SP50. Mol Gen Genet. 1967;100(1):39–55. doi: 10.1007/BF00425774. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bron S., Venema G. Ultraviolet inactivation and excision-repair in Bacillus subtilis. I. Construction and characterization of a transformable eightfold auxotrophic strain and two ultraviolet-sensitive derivatives. Mutat Res. 1972 May;15(1):1–10. doi: 10.1016/0027-5107(72)90086-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burbulys D., Trach K. A., Hoch J. A. Initiation of sporulation in B. subtilis is controlled by a multicomponent phosphorelay. Cell. 1991 Feb 8;64(3):545–552. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(91)90238-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton Z., Burgess R. R., Lin J., Moore D., Holder S., Gross C. A. The nucleotide sequence of the cloned rpoD gene for the RNA polymerase sigma subunit from E coli K12. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jun 25;9(12):2889–2903. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.12.2889. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang S., Cohen S. N. High frequency transformation of Bacillus subtilis protoplasts by plasmid DNA. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 Jan 5;168(1):111–115. doi: 10.1007/BF00267940. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chomczynski P., Qasba P. K. Alkaline transfer of DNA to plastic membrane. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jul 18;122(1):340–344. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90480-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cosmina P., Rodriguez F., de Ferra F., Grandi G., Perego M., Venema G., van Sinderen D. Sequence and analysis of the genetic locus responsible for surfactin synthesis in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol. 1993 May;8(5):821–831. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01629.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl M. K., Msadek T., Kunst F., Rapoport G. Mutational analysis of the Bacillus subtilis DegU regulator and its phosphorylation by the DegS protein kinase. J Bacteriol. 1991 Apr;173(8):2539–2547. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.8.2539-2547.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubnau D. Genetic competence in Bacillus subtilis. Microbiol Rev. 1991 Sep;55(3):395–424. doi: 10.1128/mr.55.3.395-424.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubnau D., Roggiani M. Growth medium-independent genetic competence mutants of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):4048–4055. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.4048-4055.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubnau D. The regulation of genetic competence in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jan;5(1):11–18. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01820.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubnau E., Weir J., Nair G., Carter L., 3rd, Moran C., Jr, Smith I. Bacillus sporulation gene spo0H codes for sigma 30 (sigma H). J Bacteriol. 1988 Mar;170(3):1054–1062. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.3.1054-1062.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaur N. K., Dubnau E., Smith I. Characterization of a cloned Bacillus subtilis gene that inhibits sporulation in multiple copies. J Bacteriol. 1986 Nov;168(2):860–869. doi: 10.1128/jb.168.2.860-869.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gaur N. K., Oppenheim J., Smith I. The Bacillus subtilis sin gene, a regulator of alternate developmental processes, codes for a DNA-binding protein. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(2):678–686. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.2.678-686.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn J., Dubnau D. Growth stage signal transduction and the requirements for srfA induction in development of competence. J Bacteriol. 1991 Nov;173(22):7275–7282. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.22.7275-7282.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn J., Kong L., Dubnau D. The regulation of competence transcription factor synthesis constitutes a critical control point in the regulation of competence in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1994 Sep;176(18):5753–5761. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.18.5753-5761.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haima P., Bron S., Venema G. The effect of restriction on shotgun cloning and plasmid stability in Bacillus subtilis Marburg. Mol Gen Genet. 1987 Sep;209(2):335–342. doi: 10.1007/BF00329663. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henner D. J., Yang M., Ferrari E. Localization of Bacillus subtilis sacU(Hy) mutations to two linked genes with similarities to the conserved procaryotic family of two-component signalling systems. J Bacteriol. 1988 Nov;170(11):5102–5109. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.11.5102-5109.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Joenje H., Gruber M., Venema G. Stimulation of the development of competence by culture fluids in Bacillus subtilis transformation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Mar 14;262(2):189–199. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(72)90232-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kong L., Siranosian K. J., Grossman A. D., Dubnau D. Sequence and properties of mecA, a negative regulator of genetic competence in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Jul;9(2):365–373. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01697.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kunst F., Debarbouille M., Msadek T., Young M., Mauel C., Karamata D., Klier A., Rapoport G., Dedonder R. Deduced polypeptides encoded by the Bacillus subtilis sacU locus share homology with two-component sensor-regulator systems. J Bacteriol. 1988 Nov;170(11):5093–5101. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.11.5093-5101.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Londoño-Vallejo J. A., Dubnau D. comF, a Bacillus subtilis late competence locus, encodes a protein similar to ATP-dependent RNA/DNA helicases. Mol Microbiol. 1993 Jul;9(1):119–131. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01674.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mandel M., Higa A. Calcium-dependent bacteriophage DNA infection. J Mol Biol. 1970 Oct 14;53(1):159–162. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90051-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mohan S., Dubnau D. Transcriptional regulation of comC: evidence for a competence-specific transcription factor in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):4064–4071. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.4064-4071.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Msadek T., Kunst F., Henner D., Klier A., Rapoport G., Dedonder R. Signal transduction pathway controlling synthesis of a class of degradative enzymes in Bacillus subtilis: expression of the regulatory genes and analysis of mutations in degS and degU. J Bacteriol. 1990 Feb;172(2):824–834. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.2.824-834.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Msadek T., Kunst F., Klier A., Rapoport G. DegS-DegU and ComP-ComA modulator-effector pairs control expression of the Bacillus subtilis pleiotropic regulatory gene degQ. J Bacteriol. 1991 Apr;173(7):2366–2377. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.7.2366-2377.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Msadek T., Kunst F., Rapoport G. MecB of Bacillus subtilis, a member of the ClpC ATPase family, is a pleiotropic regulator controlling competence gene expression and growth at high temperature. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 21;91(13):5788–5792. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.13.5788. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano M. M., Magnuson R., Myers A., Curry J., Grossman A. D., Zuber P. srfA is an operon required for surfactin production, competence development, and efficient sporulation in Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1991 Mar;173(5):1770–1778. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.5.1770-1778.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakano M. M., Zuber P. The primary role of comA in establishment of the competent state in Bacillus subtilis is to activate expression of srfA. J Bacteriol. 1991 Nov;173(22):7269–7274. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.22.7269-7274.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ostroff G. R., Pène J. J. Molecular cloning with bifunctional plasmid vectors in Bacillus subtilis: isolation of a spontaneous mutant of Bacillus subtilis with enhanced transformability for Escherichia coli-propagated chimeric plasmid DNA. J Bacteriol. 1983 Nov;156(2):934–936. doi: 10.1128/jb.156.2.934-936.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perego M., Higgins C. F., Pearce S. R., Gallagher M. P., Hoch J. A. The oligopeptide transport system of Bacillus subtilis plays a role in the initiation of sporulation. Mol Microbiol. 1991 Jan;5(1):173–185. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1991.tb01838.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perego M., Spiegelman G. B., Hoch J. A. Structure of the gene for the transition state regulator, abrB: regulator synthesis is controlled by the spo0A sporulation gene in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol. 1988 Nov;2(6):689–699. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1988.tb00079.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson J. B., Gocht M., Marahiel M. A., Zuber P. AbrB, a regulator of gene expression in Bacillus, interacts with the transcription initiation regions of a sporulation gene and an antibiotic biosynthesis gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8457–8461. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8457. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roggiani M., Dubnau D. ComA, a phosphorylated response regulator protein of Bacillus subtilis, binds to the promoter region of srfA. J Bacteriol. 1993 May;175(10):3182–3187. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.10.3182-3187.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roggiani M., Hahn J., Dubnau D. Suppression of early competence mutations in Bacillus subtilis by mec mutations. J Bacteriol. 1990 Jul;172(7):4056–4063. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.7.4056-4063.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudner D. Z., LeDeaux J. R., Ireton K., Grossman A. D. The spo0K locus of Bacillus subtilis is homologous to the oligopeptide permease locus and is required for sporulation and competence. J Bacteriol. 1991 Feb;173(4):1388–1398. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.4.1388-1398.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sadaie Y., Kada T. Formation of competent Bacillus subtilis cells. J Bacteriol. 1983 Feb;153(2):813–821. doi: 10.1128/jb.153.2.813-821.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaeffer P., Millet J., Aubert J. P. Catabolic repression of bacterial sporulation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Sep;54(3):704–711. doi: 10.1073/pnas.54.3.704. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spizizen J. TRANSFORMATION OF BIOCHEMICALLY DEFICIENT STRAINS OF BACILLUS SUBTILIS BY DEOXYRIBONUCLEATE. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1958 Oct 15;44(10):1072–1078. doi: 10.1073/pnas.44.10.1072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J. B., Ninfa A. J., Stock A. M. Protein phosphorylation and regulation of adaptive responses in bacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1989 Dec;53(4):450–490. doi: 10.1128/mr.53.4.450-490.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauch M. A., Spiegelman G. B., Perego M., Johnson W. C., Burbulys D., Hoch J. A. The transition state transcription regulator abrB of Bacillus subtilis is a DNA binding protein. EMBO J. 1989 May;8(5):1615–1621. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb03546.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauch M., Webb V., Spiegelman G., Hoch J. A. The SpoOA protein of Bacillus subtilis is a repressor of the abrB gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(5):1801–1805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.5.1801. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trowsdale J., Chen S. M., Hoch J. A. Genetic analysis of a class of polymyxin resistant partial revertants of stage O sporulation mutants of Bacillus subtilis: map of the chromosome region near the origin of replication. Mol Gen Genet. 1979 May 23;173(1):61–70. doi: 10.1007/BF00267691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- VENEMA G., PRITCHARD R. H., VENEMA-SCHROEDER T. FATE OF TRANSFORMING DEOXYRIBONUCLEIC ACID IN BACILLUS SUBTILIS. J Bacteriol. 1965 May;89:1250–1255. doi: 10.1128/jb.89.5.1250-1255.1965. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinrauch Y., Guillen N., Dubnau D. A. Sequence and transcription mapping of Bacillus subtilis competence genes comB and comA, one of which is related to a family of bacterial regulatory determinants. J Bacteriol. 1989 Oct;171(10):5362–5375. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.10.5362-5375.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinrauch Y., Msadek T., Kunst F., Dubnau D. Sequence and properties of comQ, a new competence regulatory gene of Bacillus subtilis. J Bacteriol. 1991 Sep;173(18):5685–5693. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.18.5685-5693.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinrauch Y., Penchev R., Dubnau E., Smith I., Dubnau D. A Bacillus subtilis regulatory gene product for genetic competence and sporulation resembles sensor protein members of the bacterial two-component signal-transduction systems. Genes Dev. 1990 May;4(5):860–872. doi: 10.1101/gad.4.5.860. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weinstock G. M., Berman M. L., Silhavy T. J. Chimeric genetics with beta-galactosidase. Gene Amplif Anal. 1983;3:27–64. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Sinderen D., Galli G., Cosmina P., de Ferra F., Withoff S., Venema G., Grandi G. Characterization of the srfA locus of Bacillus subtilis: only the valine-activating domain of srfA is involved in the establishment of genetic competence. Mol Microbiol. 1993 May;8(5):833–841. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01630.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Sinderen D., Withoff S., Boels H., Venema G. Isolation and characterization of comL, a transcription unit involved in competence development of Bacillus subtilis. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Dec;224(3):396–404. doi: 10.1007/BF00262434. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Sinderen D., ten Berge A., Hayema B. J., Hamoen L., Venema G. Molecular cloning and sequence of comK, a gene required for genetic competence in Bacillus subtilis. Mol Microbiol. 1994 Feb;11(4):695–703. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1994.tb00347.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]