Abstract
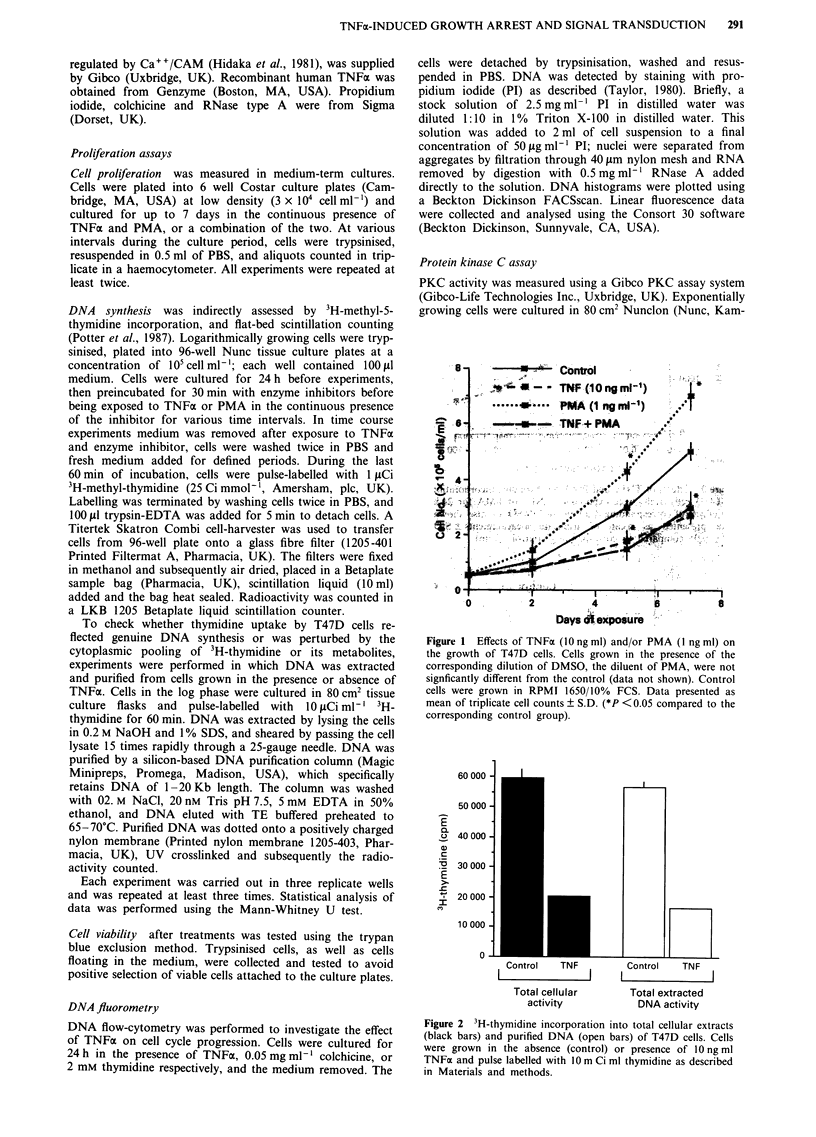
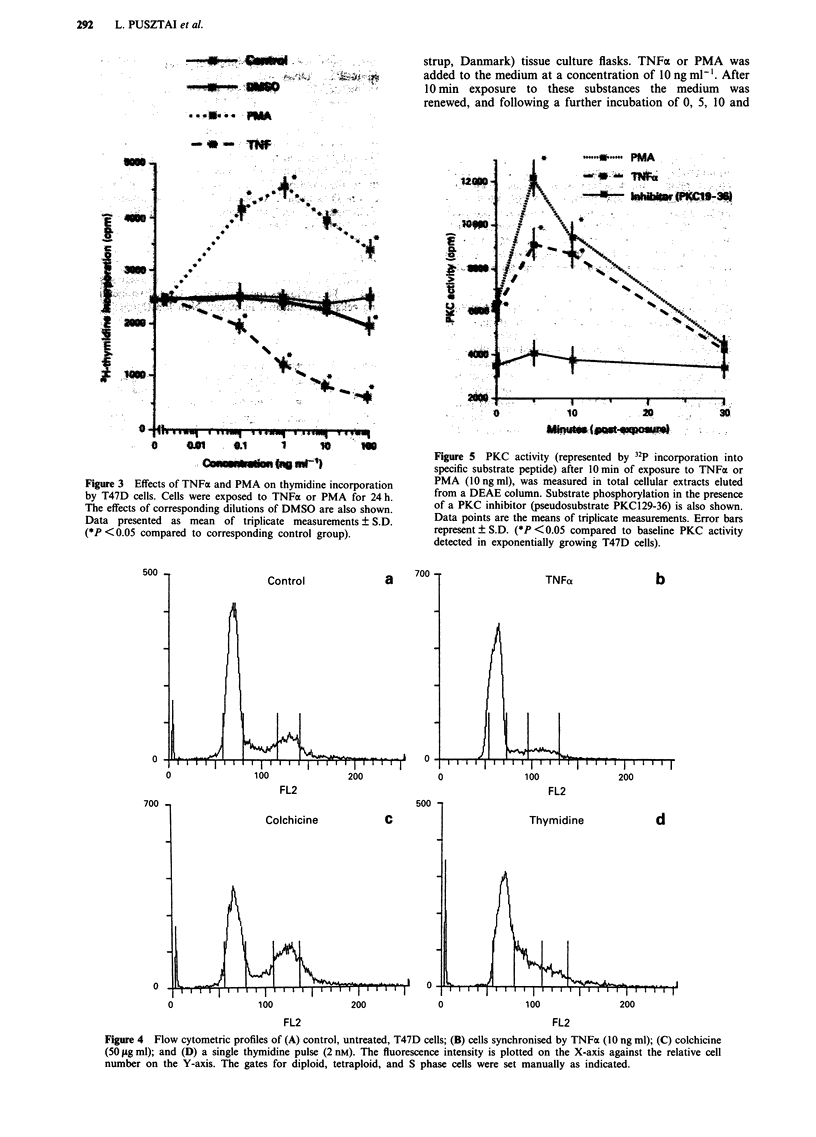
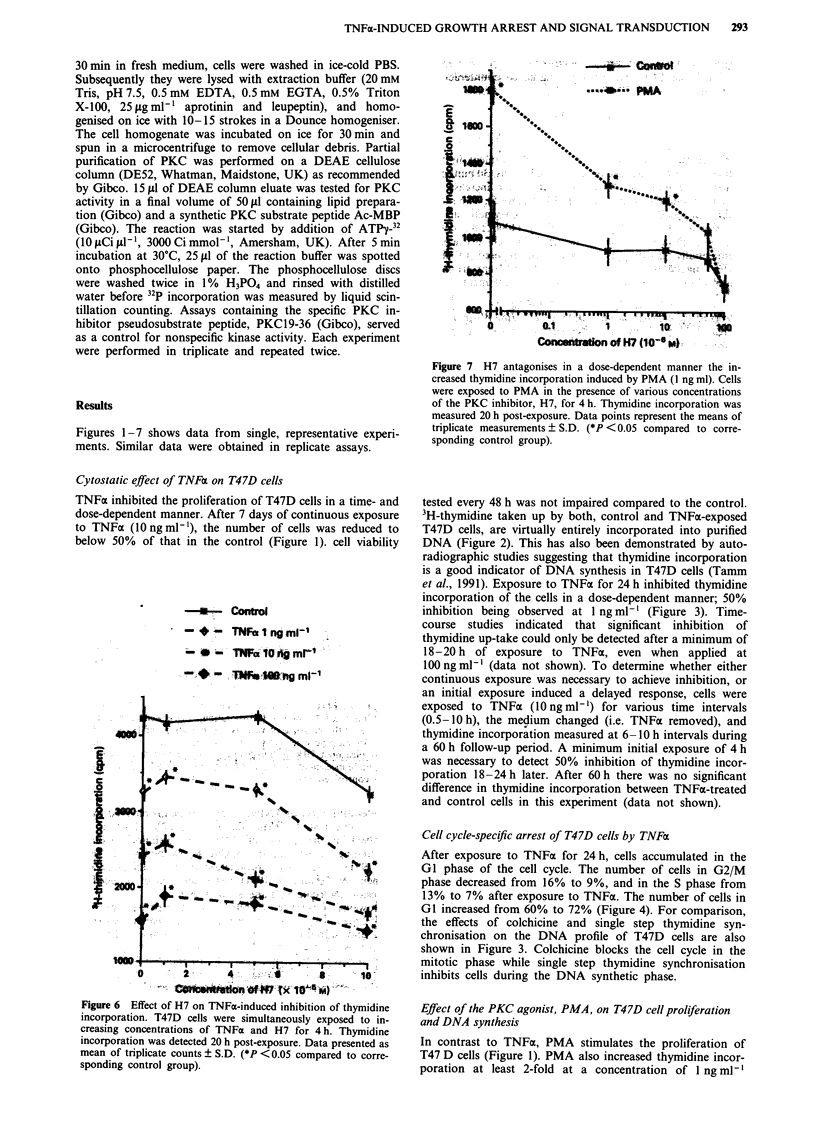
The effects of tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF alpha) on the growth and DNA synthesis of the human breast cell line, T47D, were studied. A dose-dependent, reversible inhibition of thymidine incorporation and cell growth was observed in the range of 0.1 ng ml-1 to 100 ng ml-1 of TNF alpha. Cell viability was not impaired in any of the experiments. Flow-cytometric DNA analysis demonstrated that after 24 h exposure to TNF alpha, T47D cells accumulated in the G1 phase of the cell cycle, and were depleted in the G2/M and S phases, suggesting a block in the progression of the G1/S transition. The involvement of protein kinases (PK) and protein phosphatases in TNF alpha-induced signal transduction was also investigated. A transient and rapid 2-fold increase in total cellular protein kinase C (PKC) activity was detected after 10 min exposure to TNF alpha. To study the role of the observed PKC activation in the cytostatic effect of TNF alpha, T47D cells were exposed to the cytokine in the presence of the potent PKC inhibitor, H7. The inhibitory effect of TNF alpha on thymidine incorporation was not affected by exposure to H7 at concentrations sufficient to block the stimulation of thymidine up-take induced by the PKC agonist, phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate (PMA). The involvement of other signalling pathways was addressed using the cyclic nucleotide-dependent PK inhibitor, H8; the calmodulin-dependent PK inhibitor, W7; and the inhibitor of protein phosphatases PP1 and PP2B, okadaic acid. Exposure of T47D cells to these enzyme inhibitors failed to antagonise the inhibition of thymidine incorporation by TNF alpha. Taken together, these results indicate that the cytostatic effect of TNF alpha on T47D cells occurs at the G1/S transition of the cell cycle, and is mediated by an intracellular pathway which does not involve the activity of protein kinases C and A, nor protein phosphatases PP1, PP2B.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Arrigo A. P. Tumor necrosis factor induces the rapid phosphorylation of the mammalian heat shock protein hsp28. Mol Cell Biol. 1990 Mar;10(3):1276–1280. doi: 10.1128/mcb.10.3.1276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Belizario J. E., Dinarello C. A. Interleukin 1, interleukin 6, tumor necrosis factor, and transforming growth factor beta increase cell resistance to tumor necrosis factor cytotoxicity by growth arrest in the G1 phase of the cell cycle. Cancer Res. 1991 May 1;51(9):2379–2385. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boscá L., Junco M., Díaz-Guerra M. J. Substrate specificity of protein kinase C inhibitors. Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1990 Dec;11(12):477–477. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(90)90136-v. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brockhaus M., Schoenfeld H. J., Schlaeger E. J., Hunziker W., Lesslauer W., Loetscher H. Identification of two types of tumor necrosis factor receptors on human cell lines by monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Apr;87(8):3127–3131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.8.3127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Browning J., Ribolini A. Studies on the differing effects of tumor necrosis factor and lymphotoxin on the growth of several human tumor lines. J Immunol. 1989 Sep 15;143(6):1859–1867. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen P., Holmes C. F., Tsukitani Y. Okadaic acid: a new probe for the study of cellular regulation. Trends Biochem Sci. 1990 Mar;15(3):98–102. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(90)90192-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darzynkiewicz Z., Williamson B., Carswell E. A., Old L. J. Cell cycle-specific effects of tumor necrosis factor. Cancer Res. 1984 Jan;44(1):83–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Das U. N., Padma M., Sagar P. S., Ramesh G., Koratkar R. Stimulation of free radical generation in human leukocytes by various agents including tumor necrosis factor is a calmodulin dependent process. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Mar 30;167(3):1030–1036. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)90626-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dealtry G. B., Naylor M. S., Fiers W., Balkwill F. R. The effect of recombinant human tumour necrosis factor on growth and macromolecular synthesis of human epithelial cells. Exp Cell Res. 1987 Jun;170(2):428–438. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(87)90318-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elbaz O., Budel L. M., Hoogerbrugge H., Touw I. P., Delwel R., Mahmoud L. A., Löwenberg B. Tumor necrosis factor downregulates granulocyte-colony-stimulating factor receptor expression on human acute myeloid leukemia cells and granulocytes. J Clin Invest. 1991 Mar;87(3):838–841. doi: 10.1172/JCI115087. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feuillard J., Gouy H., Bismuth G., Lee L. M., Debré P., Körner M. NF-kappa B activation by tumor necrosis factor alpha in the Jurkat T cell line is independent of protein kinase A, protein kinase C, and Ca(2+)-regulated kinases. Cytokine. 1991 May;3(3):257–265. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(91)90025-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fransen L., Van der Heyden J., Ruysschaert R., Fiers W. Recombinant tumor necrosis factor: its effect and its synergism with interferon-gamma on a variety of normal and transformed human cell lines. Eur J Cancer Clin Oncol. 1986 Apr;22(4):419–426. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(86)90107-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hepburn A., Demolle D., Boeynaems J. m., Fiers W., Dumont J. E. Rapid phosphorylation of a 27 kDa protein induced by tumor necrosis factor. FEBS Lett. 1988 Jan 25;227(2):175–178. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(88)80892-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Inagaki M., Kawamoto S., Sasaki Y. Isoquinolinesulfonamides, novel and potent inhibitors of cyclic nucleotide dependent protein kinase and protein kinase C. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):5036–5041. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hidaka H., Sasaki Y., Tanaka T., Endo T., Ohno S., Fujii Y., Nagata T. N-(6-aminohexyl)-5-chloro-1-naphthalenesulfonamide, a calmodulin antagonist, inhibits cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4354–4357. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4354. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane T. A., Lamkin G. E., Wancewicz E. V. Protein kinase C inhibitors block the enhanced expression of intercellular adhesion molecule-1 on endothelial cells activated by interleukin-1, lipopolysaccharide and tumor necrosis factor. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1990 Nov 15;172(3):1273–1281. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(90)91587-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larrick J. W., Wright S. C. Cytotoxic mechanism of tumor necrosis factor-alpha. FASEB J. 1990 Nov;4(14):3215–3223. doi: 10.1096/fasebj.4.14.2172061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantovani L., Henschler R., Brach M. A., Mertelsmann R. H., Herrmann F. Regulation of gene expression of macrophage-colony stimulating factor in human fibroblasts by the acute phase response mediators interleukin (IL)-1 beta, tumor necrosis factor-alpha and IL-6. FEBS Lett. 1991 Mar 11;280(1):97–102. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80213-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mantovani L., Henschler R., Brach M. A., Wieser R., Lübbert M., Lindemann A., Mertelsmann R. H., Herrmann F. Differential regulation of interleukin-6 expression in human fibroblasts by tumor necrosis factor-alpha and lymphotoxin. FEBS Lett. 1990 Sep 17;270(1-2):152–156. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)81256-n. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marino M. W., Pfeffer L. M., Guidon P. T., Jr, Donner D. B. Tumor necrosis factor induces phosphorylation of a 28-kDa mRNA cap-binding protein in human cervical carcinoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(21):8417–8421. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.21.8417. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsubara N., Fuchimoto S., Orita K. Differing roles of protein kinase C on the antiproliferative effects of tumor necrosis factor alpha and beta on LoVo cells. Pathobiology. 1990;58(3):168–171. doi: 10.1159/000163578. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meichle A., Schütze S., Hensel G., Brunsing D., Krönke M. Protein kinase C-independent activation of nuclear factor kappa B by tumor necrosis factor. J Biol Chem. 1990 May 15;265(14):8339–8343. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muro M., Naomoto Y., Orita K. Mechanism of the combined antitumor effect of natural human tumor necrosis factor-alpha and natural human interferon-alpha on cell cycle progression. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1991 Jan;82(1):118–126. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1991.tb01754.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oka S., Arita H. Inflammatory factors stimulate expression of group II phospholipase A2 in rat cultured astrocytes. Two distinct pathways of the gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 25;266(15):9956–9960. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paciotti G. F., Tamarkin L. Interleukin-1 alpha differentially synchronizes estrogen-dependent and estrogen-independent human breast cancer cells in the G0/G1 phase of the cell cycle. Anticancer Res. 1991 Jan-Feb;11(1):25–31. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter C. G., Gotch F., Warner G. T., Oestrup J. Lymphocyte proliferation and cytotoxic assays using flat-bed scintillation counting. J Immunol Methods. 1987 Dec 24;105(2):171–177. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(87)90263-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ritchie A. J., Johnson D. R., Ewenstein B. M., Pober J. S. Tumor necrosis factor induction of endothelial cell surface antigens is independent of protein kinase C activation or inactivation. Studies with phorbol myristate acetate and staurosporine. J Immunol. 1991 May 1;146(9):3056–3062. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruggiero V., Latham K., Baglioni C. Cytostatic and cytotoxic activity of tumor necrosis factor on human cancer cells. J Immunol. 1987 Apr 15;138(8):2711–2717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancho-Tello M., Terranova P. F. Involvement of protein kinase C in regulating tumor necrosis factor alpha-stimulated progesterone production in rat preovulatory follicles in vitro. Endocrinology. 1991 Mar;128(3):1223–1228. doi: 10.1210/endo-128-3-1223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schütze S., Nottrott S., Pfizenmaier K., Krönke M. Tumor necrosis factor signal transduction. Cell-type-specific activation and translocation of protein kinase C. J Immunol. 1990 Apr 1;144(7):2604–2608. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schütze S., Scheurich P., Pfizenmaier K., Krönke M. Tumor necrosis factor signal transduction. Tissue-specific serine phosphorylation of a 26-kDa cytosolic protein. J Biol Chem. 1989 Feb 25;264(6):3562–3567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sugarman B. J., Aggarwal B. B., Hass P. E., Figari I. S., Palladino M. A., Jr, Shepard H. M. Recombinant human tumor necrosis factor-alpha: effects on proliferation of normal and transformed cells in vitro. Science. 1985 Nov 22;230(4728):943–945. doi: 10.1126/science.3933111. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tamm I., Cardinale I., Sehgal P. B. Interleukin-6 and 12-O-tetradecanoyl phorbol-13-acetate act synergistically in inducing cell-cell separation and migration of human breast carcinoma cells. Cytokine. 1991 May;3(3):212–223. doi: 10.1016/1043-4666(91)90019-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor I. W. A rapid single step staining technique for DNA analysis by flow microfluorimetry. J Histochem Cytochem. 1980 Sep;28(9):1021–1024. doi: 10.1177/28.9.6157714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zhang Y. H., Lin J. X., Yip Y. K., Vilcek J. Enhancement of cAMP levels and of protein kinase activity by tumor necrosis factor and interleukin 1 in human fibroblasts: role in the induction of interleukin 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Sep;85(18):6802–6805. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.18.6802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zucali J. R., Morse C., Dinarello C. A. The role of protein kinase C in interleukin 1 and tumor necrosis factor alpha induction of fibroblasts to produce and release granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating activity. Exp Hematol. 1990 Sep;18(8):888–892. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



