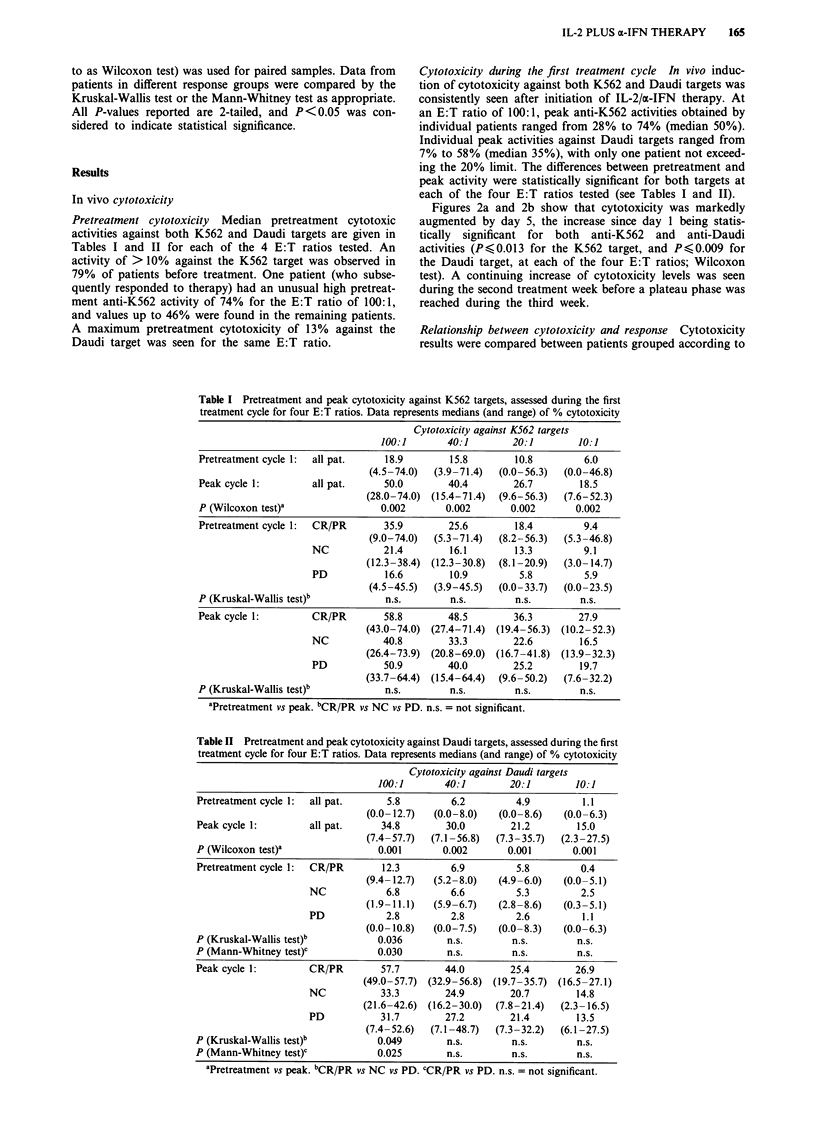
Abstract
Treatment with combined IL-2 and alpha-IFN has resulted in synergistic antitumour efficacy in animal studies. The mechanisms responsible for this synergy remain unclear. In this study, several immune parameters which might be involved in mediating antitumour activity have been monitored serially in 15 patients with advanced malignant melanoma or renal cell cancer during treatment with concurrent IL-2 and alpha-IFN. Both drugs were given subcutaneously in low to moderate (outpatient) dosages but for a prolonged duration. This treatment resulted in remarkable immunomodulation. In vivo induction of cytotoxicity against K562 and Daudi target cells was consistently seen, and percentages of peripheral blood cells expressing CD 25 (IL-2 receptor) and CD 56 (Leu-19) increased. In vitro proliferation of lymphocytes in response to IL-2 was enhanced during the treatment periods, whereas spontaneous proliferation was inhibited. Moreover, correlations between immune parameters and subsequent clinical responses were present in the early phase of the study. Cytotoxicity levels generated in vivo as well as the percentage of CD 56+ lymphocytes were higher in patients who responded to treatment than in non-responders. In contrast, responders had lower levels of CD 25+ cells. These findings indicate that it might be possible to select patients who are likely to benefit from prolonged immunotherapy.
Full text
PDF






Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkins M. B., Gould J. A., Allegretta M., Li J. J., Dempsey R. A., Rudders R. A., Parkinson D. R., Reichlin S., Mier J. W. Phase I evaluation of recombinant interleukin-2 in patients with advanced malignant disease. J Clin Oncol. 1986 Sep;4(9):1380–1391. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1986.4.9.1380. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bich-Thuy L. T., Lane H. C., Fauci A. S. Recombinant interleukin-2-induced polyclonal proliferation of in vitro unstimulated human peripheral blood lymphocytes. Cell Immunol. 1986 Apr 1;98(2):396–410. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(86)90299-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blay J. Y., Bertoglio J., Fradelizi D., Chouaib S. Functional interactions of IL2 and TNF in the differentiation of LGL into LAK effectors. Int J Cancer. 1989 Oct 15;44(4):598–604. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910440407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunda M. J., Bellantoni D., Sulich V. In vivo anti-tumor activity of combinations of interferon alpha and interleukin-2 in a murine model. Correlation of efficacy with the induction of cytotoxic cells resembling natural killer cells. Int J Cancer. 1987 Sep 15;40(3):365–371. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910400314. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brunda M. J., Tarnowski D., Davatelis V. Interaction of recombinant interferons with recombinant interleukin-2: differential effects on natural killer cell activity and interleukin-2-activated killer cells. Int J Cancer. 1986 May 15;37(5):787–793. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910370522. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Budd G. T., Osgood B., Barna B., Boyett J. M., Finke J., Medendorp S. V., Murthy S., Novak C., Sergi J., Tubbs R. Phase I clinical trial of interleukin 2 and alpha-interferon: toxicity and immunologic effects. Cancer Res. 1989 Nov 15;49(22):6432–6436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron R. B., McIntosh J. K., Rosenberg S. A. Synergistic antitumor effects of combination immunotherapy with recombinant interleukin-2 and a recombinant hybrid alpha-interferon in the treatment of established murine hepatic metastases. Cancer Res. 1988 Oct 15;48(20):5810–5817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chikkala N. F., Lewis I., Ulchaker J., Stanley J., Tubbs R., Finke J. H. Interactive effects of alpha-interferon A/D and interleukin 2 on murine lymphokine-activated killer activity: analysis at the effector and precursor level. Cancer Res. 1990 Feb 15;50(4):1176–1182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creekmore S. P., Harris J. E., Ellis T. M., Braun D. P., Cohen I. I., Bhoopalam N., Jassak P. F., Cahill M. A., Canzoneri C. L., Fisher R. I. A phase I clinical trial of recombinant interleukin-2 by periodic 24-hour intravenous infusions. J Clin Oncol. 1989 Feb;7(2):276–284. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1989.7.2.276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Czarniecki C. W., Fennie C. W., Powers D. B., Estell D. A. Synergistic antiviral and antiproliferative activities of Escherichia coli-derived human alpha, beta, and gamma interferons. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):490–496. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.490-496.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Di Raimondo F., LaPushin R., Hersh E. M. Synergism between alpha-interferon and interleukin-2-activated killer cells: in vitro studies. Acta Haematol. 1987;78 (Suppl 1):77–83. doi: 10.1159/000205908. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis T. M., Creekmore S. P., McMannis J. D., Braun D. P., Harris J. A., Fisher R. I. Appearance and phenotypic characterization of circulating Leu 19+ cells in cancer patients receiving recombinant interleukin 2. Cancer Res. 1988 Nov 15;48(22):6597–6602. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fidler I. J., Heicappell R., Saiki I., Grutter M. G., Horisberger M. A., Nuesch J. Direct antiproliferative effects of recombinant human interferon-alpha B/D hybrids on human tumor cell lines. Cancer Res. 1987 Apr 15;47(8):2020–2027. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gambacorti-Passerini C., Radrizzani M., Marolda R., Belli F., Sciorelli G., Galazka A. R., Schindler J. D., Cascinelli N., Parmiani G. In vivo activation of lymphocytes in melanoma patients receiving escalating doses of recombinant interleukin 2. Int J Cancer. 1988 May 15;41(5):700–706. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910410511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh A. K., Dazzi H., Thatcher N., Moore M. Lack of correlation between peripheral blood lymphokine-activated killer (LAK) cell function and clinical response in patients with advanced malignant melanoma receiving recombinant interleukin 2. Int J Cancer. 1989 Mar 15;43(3):410–414. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910430311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giacomini P., Aguzzi A., Pestka S., Fisher P. B., Ferrone S. Modulation by recombinant DNA leukocyte (alpha) and fibroblast (beta) interferons of the expression and shedding of HLA- and tumor-associated antigens by human melanoma cells. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1649–1655. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenberg A. H., Miller V., Jablonski T., Pohajdak B. Suppression of NK-mediated natural resistance by interferon treatment of murine lymphomas. J Immunol. 1984 Apr;132(4):2129–2134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grimm E. A., Mazumder A., Zhang H. Z., Rosenberg S. A. Lymphokine-activated killer cell phenomenon. Lysis of natural killer-resistant fresh solid tumor cells by interleukin 2-activated autologous human peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Exp Med. 1982 Jun 1;155(6):1823–1841. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.6.1823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henney C. S., Kuribayashi K., Kern D. E., Gillis S. Interleukin-2 augments natural killer cell activity. Nature. 1981 May 28;291(5813):335–338. doi: 10.1038/291335a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herberman R. B., Ortaldo J. R., Mantovani A., Hobbs D. S., Kung H. F., Pestka S. Effect of human recombinant interferon on cytotoxic activity of natural killer (NK) cells and monocytes. Cell Immunol. 1982 Feb;67(1):160–167. doi: 10.1016/0008-8749(82)90208-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hicks N. J., Morris A. G., Burke D. C. Partial reversion of the transformed phenotype of murine sarcoma virus-transformed cells in the presence of interferon: a possible mechanism for the anti-tumour effect of interferon. J Cell Sci. 1981 Jun;49:225–236. doi: 10.1242/jcs.49.1.225. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hänninen E. L., Körfer A., Hadam M., Schneekloth C., Dallmann I., Menzel T., Kirchner H., Poliwoda H., Atzpodien J. Biological monitoring of low-dose interleukin 2 in humans: soluble interleukin 2 receptors, cytokines, and cell surface phenotypes. Cancer Res. 1991 Dec 1;51(23 Pt 1):6312–6316. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim B., Warnaka P., Imbembo A. Interleukin-2 and alpha interferon therapy of advanced pulmonary metastases. Eur Surg Res. 1989;21(5):260–266. doi: 10.1159/000129035. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirchner H., Körfer A., Palmer P. A., Evers P., De Riese W., Knüver-Hopf J., Hadam M., Goldman U., Franks C. R., Poliwoda H. Subcutaneous interleukin-2 and interferon-alpha 2b in patients with metastatic renal cell cancer: the German outpatient experience. Mol Biother. 1990 Sep;2(3):145–154. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klasa R. J., Silver H. K., Kong S. In vivo induction of lymphokine-activated killer cells by interleukin-2 splenic artery perfusion in advanced malignancy. Cancer Res. 1990 Aug 15;50(16):4906–4910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kohler P. C., Hank J. A., Moore K. H., Storer B., Bechhofer R., Hong R., Sondel P. M. Phase 1 clinical trial of recombinant interleukin-2: a comparison of bolus and continuous intravenous infusion. Cancer Invest. 1989;7(3):213–223. doi: 10.3109/07357908909039840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konrad M. W., Hemstreet G., Hersh E. M., Mansell P. W., Mertelsmann R., Kolitz J. E., Bradley E. C. Pharmacokinetics of recombinant interleukin 2 in humans. Cancer Res. 1990 Apr 1;50(7):2009–2017. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krigel R. L., Padavic-Shaller K. A., Rudolph A. R., Konrad M., Bradley E. C., Comis R. L. Renal cell carcinoma: treatment with recombinant interleukin-2 plus beta-interferon. J Clin Oncol. 1990 Mar;8(3):460–467. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1990.8.3.460. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lamers H. J., Gratama J. W., van Putten W. L., Stoter G., Bolhuis R. L. Exogenous interleukin 2 recruits in vitro lymphokine-activated killer activity by in vivo activated lymphocytes. Cancer Res. 1991 May 1;51(9):2324–2328. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lanier L. L., Le A. M., Civin C. I., Loken M. R., Phillips J. H. The relationship of CD16 (Leu-11) and Leu-19 (NKH-1) antigen expression on human peripheral blood NK cells and cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1986 Jun 15;136(12):4480–4486. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ligo M., Nakajima Y., Nishikata K., Hoshi A. Effects of interleukin-2 and interferon-alpha A/D treatment on lymphocytes from tumour-bearing mice. Br J Cancer. 1989 Jun;59(6):883–888. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1989.187. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lotze M. T., Custer M. C., Sharrow S. O., Rubin L. A., Nelson D. L., Rosenberg S. A. In vivo administration of purified human interleukin-2 to patients with cancer: development of interleukin-2 receptor positive cells and circulating soluble interleukin-2 receptors following interleukin-2 administration. Cancer Res. 1987 Apr 15;47(8):2188–2195. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMannis J. D., Fisher R. I., Creekmore S. P., Braun D. P., Harris J. E., Ellis T. M. In vivo effects of recombinant IL-2. I. Isolation of circulating Leu-19+ lymphokine-activated killer effector cells from cancer patients receiving recombinant IL-2. J Immunol. 1988 Feb 15;140(4):1335–1340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mulé J. J., Yang J., Shu S., Rosenberg S. A. The anti-tumor efficacy of lymphokine-activated killer cells and recombinant interleukin 2 in vivo: direct correlation between reduction of established metastases and cytolytic activity of lymphokine-activated killer cells. J Immunol. 1986 May 15;136(10):3899–3909. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortaldo J. R., Longo D. L. Human natural lymphocyte effector cells: definition, analysis of activity, and clinical effectiveness. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1988 Sep 7;80(13):999–1010. doi: 10.1093/jnci/80.13.999. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ortaldo J. R., Mason A., Overton R. Lymphokine-activated killer cells. Analysis of progenitors and effectors. J Exp Med. 1986 Oct 1;164(4):1193–1205. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.4.1193. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paciucci P. A., Holland J. F., Ryder J. S., Konefal R. G., Bekesi G. J., Odchimar R., Gordon R. Immunotherapy with interleukin-2 by constant infusion with and without adoptive cell transfer and with weekly doxorubicin. Cancer Treat Rev. 1989 Jun;16 (Suppl A):67–81. doi: 10.1016/0305-7372(89)90026-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phillips J. H., Lanier L. L. Dissection of the lymphokine-activated killer phenomenon. Relative contribution of peripheral blood natural killer cells and T lymphocytes to cytolysis. J Exp Med. 1986 Sep 1;164(3):814–825. doi: 10.1084/jem.164.3.814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pichert G., Jost L. M., Fierz W., Stahel R. A. Clinical and immune modulatory effects of alternative weekly interleukin-2 and interferon alfa-2a in patients with advanced renal cell carcinoma and melanoma. Br J Cancer. 1991 Feb;63(2):287–292. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1991.67. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramsdell F. J., Shau H., Golub S. H. Role of proliferation in LAK cell development. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1988;26(2):139–144. doi: 10.1007/BF00205607. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robertson M. J., Ritz J. Biology and clinical relevance of human natural killer cells. Blood. 1990 Dec 15;76(12):2421–2438. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg S. A., Schwarz S. L., Spiess P. J. Combination immunotherapy for cancer: synergistic antitumor interactions of interleukin-2, alfa interferon, and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1988 Nov 2;80(17):1393–1397. doi: 10.1093/jnci/80.17.1393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenthal N. S., Hank J. A., Kohler P. C., Minkoff D. Z., Moore K. H., Bechhofer R., Hong R., Storer B., Sondel P. M. The in vitro function of lymphocytes from 25 cancer patients receiving four to seven consecutive days of recombinant IL-2. J Biol Response Mod. 1988 Apr;7(2):123–139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sondel P. M., Hank J. A., Kohler P. C., Chen B. P., Minkoff D. Z., Molenda J. A. Destruction of autologous human lymphocytes by interleukin 2-activated cytotoxic cells. J Immunol. 1986 Jul 15;137(2):502–511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sondel P. M., Kohler P. C., Hank J. A., Moore K. H., Rosenthal N. S., Sosman J. A., Bechhofer R., Storer B. Clinical and immunological effects of recombinant interleukin 2 given by repetitive weekly cycles to patients with cancer. Cancer Res. 1988 May 1;48(9):2561–2567. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sone S., Utsugi T., Nii A., Ogura T. Differential effects of recombinant interferons alpha, beta, and gamma on induction of human lymphokine (IL-2)-activated killer activity. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1988 May 18;80(6):425–431. doi: 10.1093/jnci/80.6.425. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sosman J. A., Kohler P. C., Hank J. A., Moore K. H., Bechhofer R., Storer B., Sondel P. M. Repetitive weekly cycles of interleukin-2. II. Clinical and immunologic effects of dose, schedule, and addition of indomethacin. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1988 Nov 16;80(18):1451–1461. doi: 10.1093/jnci/80.18.1451. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. A., Lee D. J., Cox W. W., Lindgren C. G., Collins C., Neraas K. A., Dennin R. A., Fefer A. Recombinant interleukin 2 toxicity, pharmacokinetics, and immunomodulatory effects in a phase I trial. Cancer Res. 1987 Aug 1;47(15):4202–4207. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson J. A., Lee D. J., Lindgren C. G., Benz L. A., Collins C., Shuman W. P., Levitt D., Fefer A. Influence of schedule of interleukin 2 administration on therapy with interleukin 2 and lymphokine activated killer cells. Cancer Res. 1989 Jan 1;49(1):235–240. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuda Y., Ebina N., Golub S. H. The inhibitory effect of human interferon alpha on the generation of lymphokine-activated killer activity. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1989;30(4):205–212. doi: 10.1007/BF01665006. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G., Granato D., Perussia B. Interferon-induced resistance of fibroblasts to cytolysis mediated by natural killer cells: specificity and mechanism. J Immunol. 1981 Jan;126(1):335–340. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinchieri G., Matsumoto-Kobayashi M., Clark S. C., Seehra J., London L., Perussia B. Response of resting human peripheral blood natural killer cells to interleukin 2. J Exp Med. 1984 Oct 1;160(4):1147–1169. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.4.1147. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber J. S., Rosenberg S. A. Modulation of murine tumor major histocompatibility antigens by cytokines in vivo and in vitro. Cancer Res. 1988 Oct 15;48(20):5818–5824. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weil-Hillman G., Fisch P., Prieve A. F., Sosman J. A., Hank J. A., Sondel P. M. Lymphokine-activated killer activity induced by in vivo interleukin 2 therapy: predominant role for lymphocytes with increased expression of CD2 and leu19 antigens but negative expression of CD16 antigens. Cancer Res. 1989 Jul 1;49(13):3680–3688. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada S., Ruscetti F. W., Overton W. R., Herberman R. B., Birchenall-Sparks M. C., Ortaldo J. R. Regulation of human large granular lymphocyte and T cell growth and function by recombinant interleukin 2: induction of interleukin 2 receptor and promotion of growth of cells with enhanced cytotoxicity. J Leukoc Biol. 1987 Jun;41(6):505–517. doi: 10.1002/jlb.41.6.505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yasumoto K., Mivazaki K., Nagashima A., Ishida T., Kuda T., Yano T., Sugimachi K., Nomoto K. Induction of lymphokine-activated killer cells by intrapleural instillations of recombinant interleukin-2 in patients with malignant pleurisy due to lung cancer. Cancer Res. 1987 Apr 15;47(8):2184–2187. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



