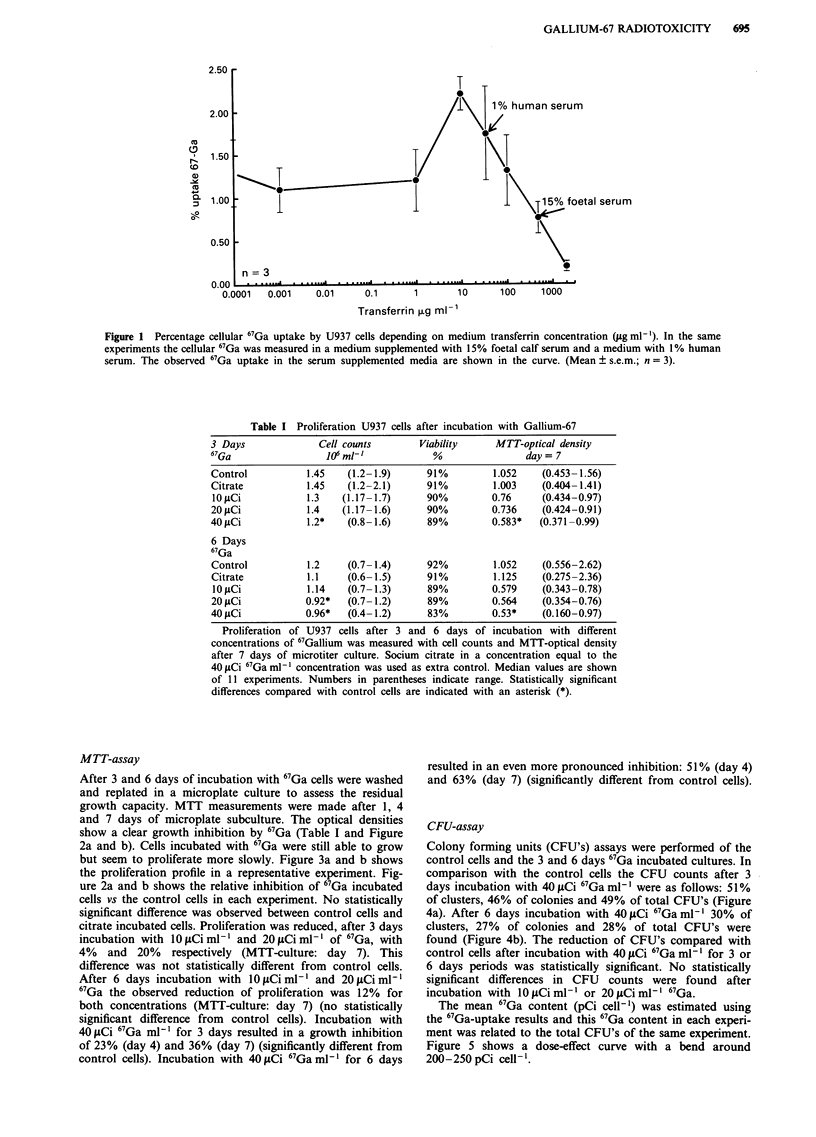
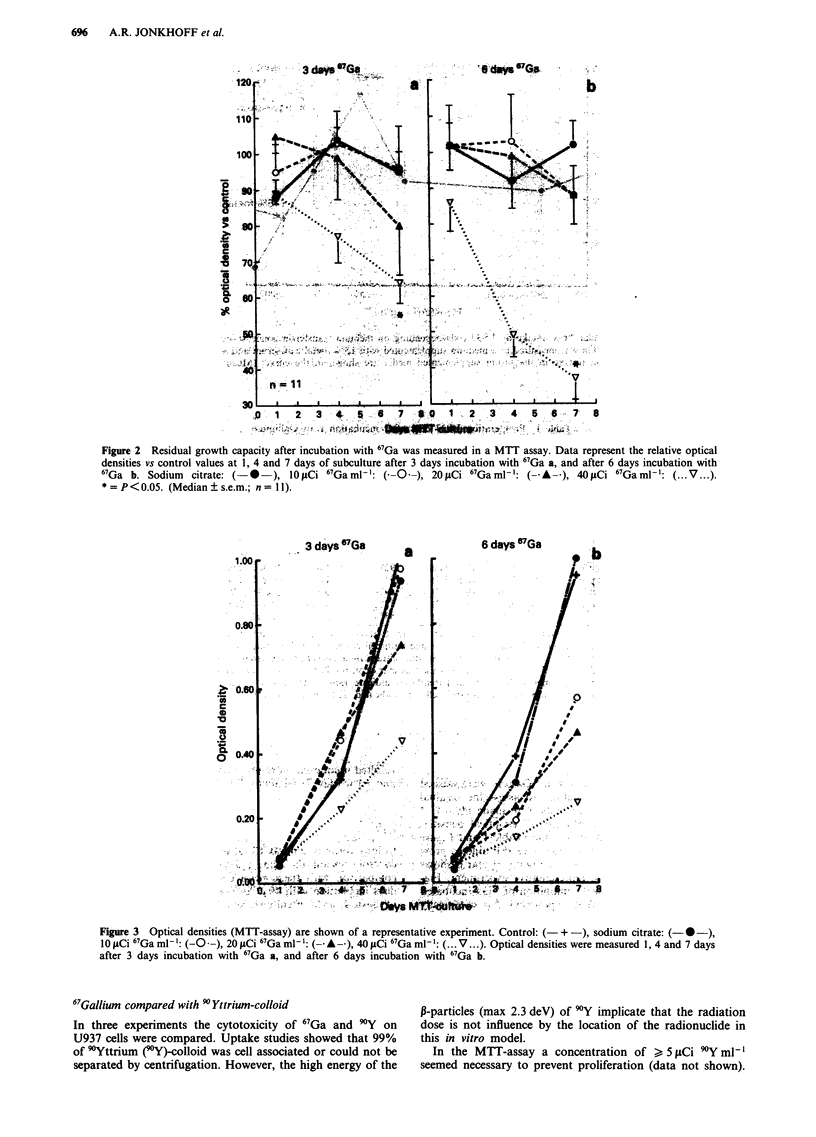
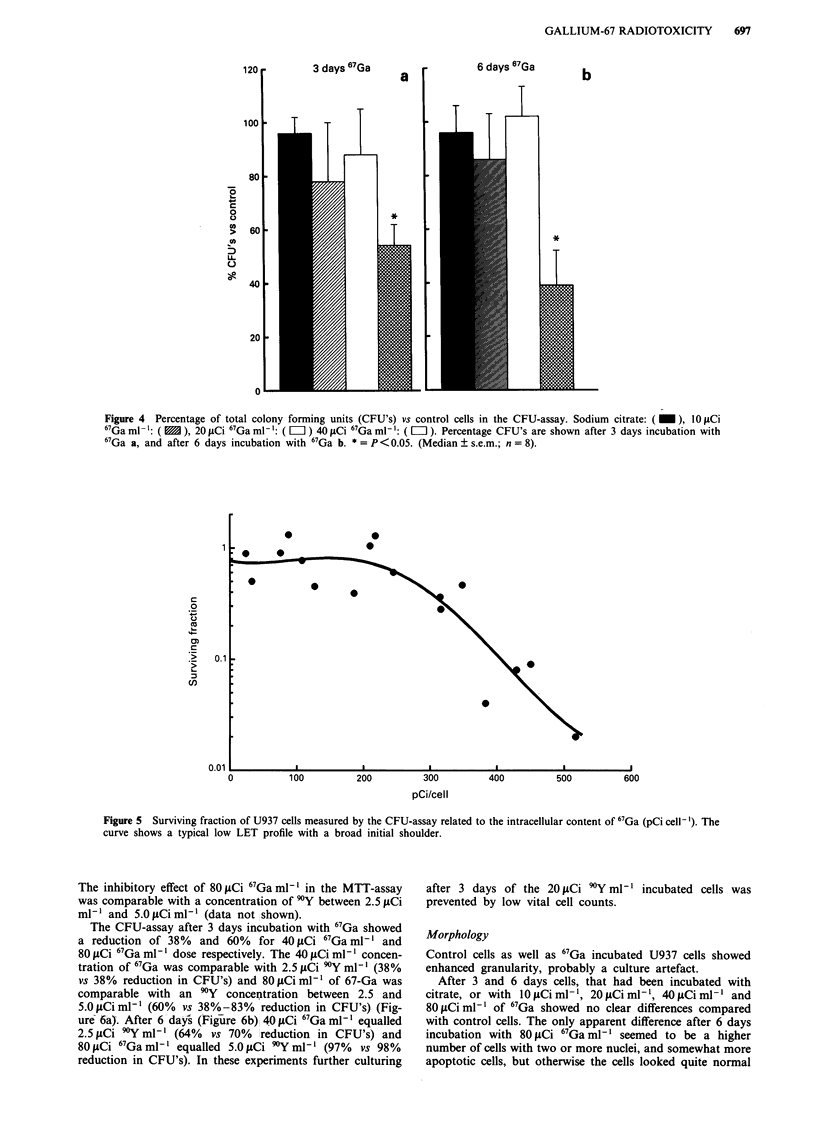
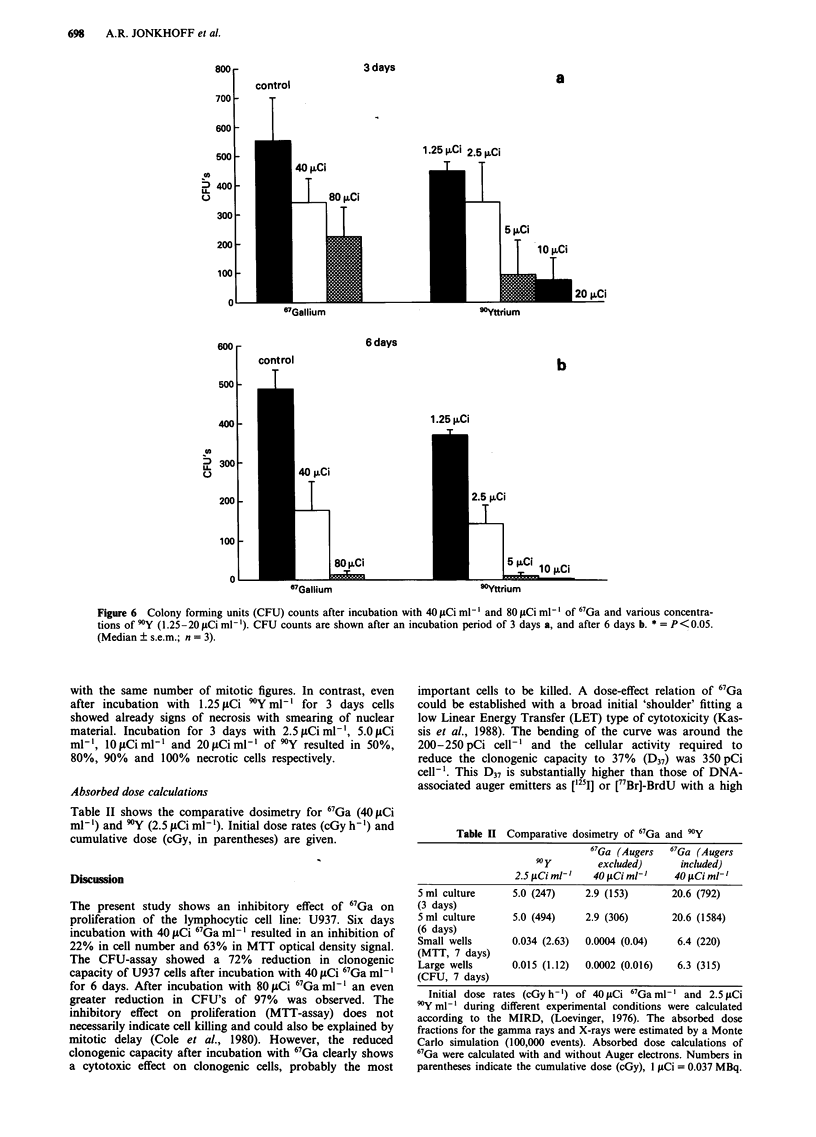
Abstract
Promising clinical results have been obtained with radiolabeled antibodies in lymphoma patients. The higher uptake by lymphomas of 67Gallium (67Ga) compared with monoclonal antibodies makes selective radiotherapy by the widely available 67Ga appealing. However, the gamma radiation of 67Ga used in scintigraphy is considered to be almost non-toxic to lymphoma cells. However, in addition to photon radiation 67Ga emits low energy Auger electrons and 80-90 keV conversion electrons which could be cytotoxic. The objective of the present study was the assessment of radiotoxicity of 67Ga on a lymphoid cell line: U937. Proliferation (MTT-assay) and clonogenic capacity (CFU-assay) were measured after 3 and 6 days incubation with 10, 20 and 40 microCi ml-1 67Ga. Growth inhibition was 36% after 3 days incubation and 63% after 6 days incubation with 40 microCi 67Ga ml-1. Clonogenic capacity was reduced by 51% after 3 days and 72% after 6 days incubation with 40 microCi ml-1 67Ga. A survival curve showed an initial shoulder and became steeper beyond 200-250 pCi cell-1 (low linear energy transfer type). Iso-effect doses of 67Ga and 90Yttrium (90Y) were determined. The iso-effect dose of 40 microCi 67Ga ml-1 (cumulative dose of conversion electrons 306 cGy) was 2.5 microCi 90Y ml-1 (cumulative dose 494 cGy) and the iso-effect dose of 80 microCi 67Ga ml-1 was 5.0 microCi 90Y/ml. The main cytotoxic effect of 67Ga seems to be induced by the 80 keV conversion electrons. We conclude that the conversion electrons of 67Ga have a cytotoxic effect on U937 cells and that in our experiments a 16-fold higher microCi-dose of 67Ga than of 90Y was needed for the same cytotoxic effect. We believe that 67Ga holds promise for therapeutic use.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bloomer W. D., McLaughlin W. H., Lambrecht R. M., Atcher R. W., Mirzadeh S., Madara J. L., Milius R. A., Zalutsky M. R., Adelstein S. J., Wolf A. P. 211At radiocolloid therapy: further observations and comparison with radiocolloids of 32P, 165Dy, and 90Y. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1984 Mar;10(3):341–348. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(84)90052-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bunn P. A., Jr, Carrasquillo J. A., Keenan A. M., Schroff R. W., Foon K. A., Hsu S. M., Gazdar A. F., Reynolds J. C., Perentesis P., Larson S. M. Imaging of T-cell lymphoma by radiolabelled monoclonal antibody. Lancet. 1984 Nov 24;2(8413):1219–1221. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)92781-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carrasquillo J. A., Bunn P. A., Jr, Keenan A. M., Reynolds J. C., Schroff R. W., Foon K. A., Su M. H., Gazdar A. F., Mulshine J. L., Oldham R. K. Radioimmunodetection of cutaneous T-cell lymphoma with 111In-labeled T101 monoclonal antibody. N Engl J Med. 1986 Sep 11;315(11):673–680. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198609113151104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldenberg D. M., Horowitz J. A., Sharkey R. M., Hall T. C., Murthy S., Goldenberg H., Lee R. E., Stein R., Siegel J. A., Izon D. O. Targeting, dosimetry, and radioimmunotherapy of B-cell lymphomas with iodine-131-labeled LL2 monoclonal antibody. J Clin Oncol. 1991 Apr;9(4):548–564. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1991.9.4.548. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofer K. G., Harris C. R., Smith J. M. Rdiotoxicity of intracellular 67Ga, 125I and 3H. Nuclear versus cytoplasmic radiation effects in murine L1210 leukaemia. Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1975 Sep;28(3):225–241. doi: 10.1080/09553007514550991. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassis A. I., Fayad F., Kinsey B. M., Sastry K. S., Adelstein S. J. Radiotoxicity of an 125I-labeled DNA intercalator in mammalian cells. Radiat Res. 1989 May;118(2):283–294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson B., Hayes R. L., Edwards C. L., Kniseley R. M., Andrews G. A. Distribution of gallium in human tissues after intravenous administration. J Nucl Med. 1972 Jan;13(1):92–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Press O. W., Eary J. F., Badger C. C., Martin P. J., Appelbaum F. R., Levy R., Miller R., Brown S., Nelp W. B., Krohn K. A. Treatment of refractory non-Hodgkin's lymphoma with radiolabeled MB-1 (anti-CD37) antibody. J Clin Oncol. 1989 Aug;7(8):1027–1038. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1989.7.8.1027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Price P., McMillan T. J. Use of the tetrazolium assay in measuring the response of human tumor cells to ionizing radiation. Cancer Res. 1990 Mar 1;50(5):1392–1396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shipley W. U., Jennings M., Gerweck L. E., Ling C. C. Prolonged "ultra" low-dose-rate irradiation: effects on Chinese hamster cell population growth, survival, and radiation sensitivity. Radiat Res. 1981 Jan;85(1):150–160. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Twentyman P. R., Fox N. E., Rees J. K. Chemosensitivity testing of fresh leukaemia cells using the MTT colorimetric assay. Br J Haematol. 1989 Jan;71(1):19–24. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1989.tb06268.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vriesendorp H. M., Herpst J. M., Germack M. A., Klein J. L., Leichner P. K., Loudenslager D. M., Order S. E. Phase I-II studies of yttrium-labeled antiferritin treatment for end-stage Hodgkin's disease, including Radiation Therapy Oncology Group 87-01. J Clin Oncol. 1991 Jun;9(6):918–928. doi: 10.1200/JCO.1991.9.6.918. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vriesendorp H. M., Herpst J. M., Leichner P. K., Klein J. L., Order S. E. Polyclonal 90Yttrium labeled antiferritin for refractory Hodgkin's disease. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1989 Oct;17(4):815–821. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(89)90072-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson E. E., Cloutier R. J., Gibbs W. D. Whole-body retention of 67Ga-citrate. J Nucl Med. 1973 Nov;14(11):840–842. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


