Abstract
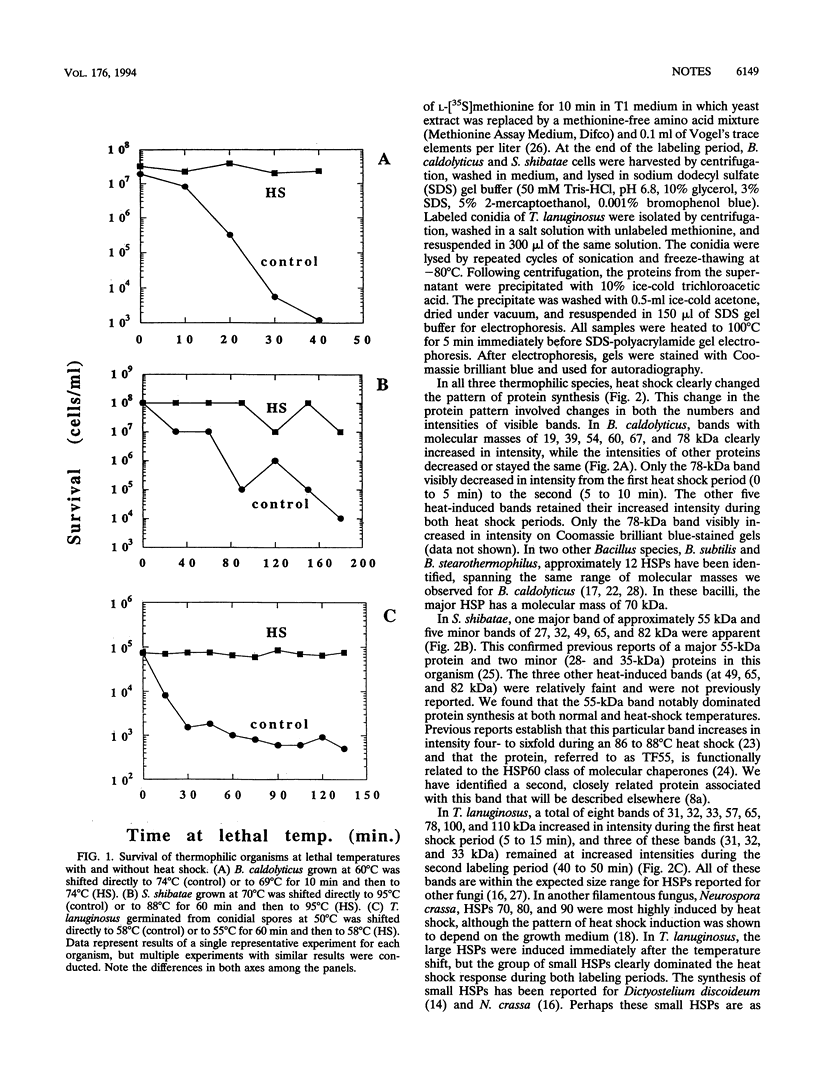
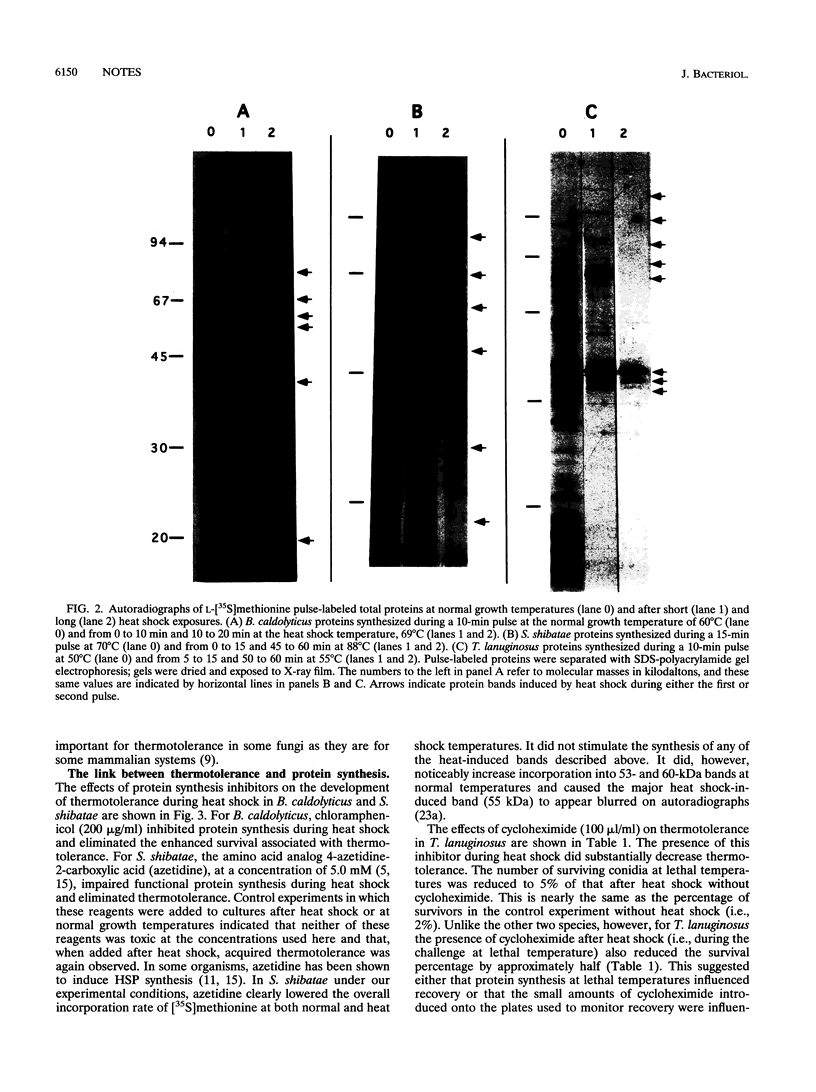
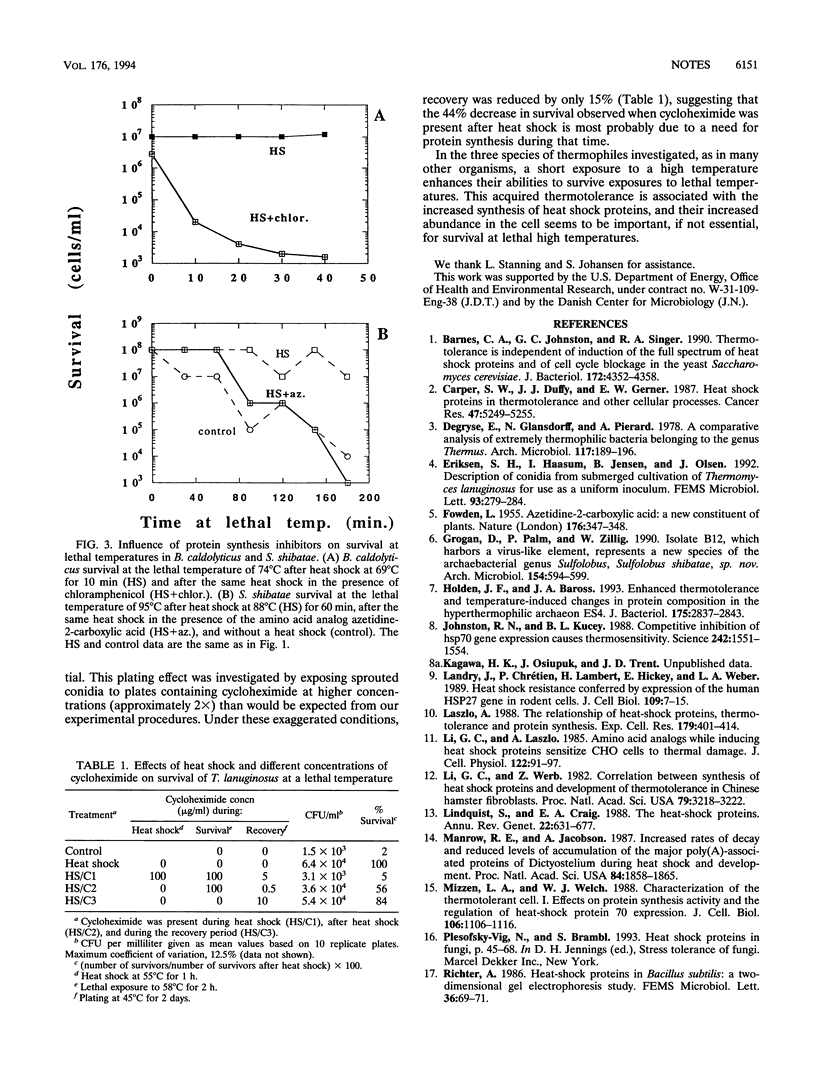
Thermophilic organisms from each of the three phylogenetic domains (Bacteria, Archaea, and Eucarya) acquired thermotolerance after heat shock. Bacillus caldolyticus grown at 60 degrees C and heat shocked at 69 degrees C for 10 min showed thermotolerance at 74 degrees C, Sulfolobus shibatae grown at 70 degrees C and heat shocked at 88 degrees C for 60 min showed thermotolerance at 95 degrees C, and Thermomyces lanuginosus grown at 50 degrees C and heat shocked at 55 degrees C for 60 min showed thermotolerance at 58 degrees C. Determinations of protein synthesis during heat shock revealed differences in the dominant heat shock proteins for each species. For B. caldolyticus, a 70-kDa protein dominated while for S. shibatae, a 55-kDa protein dominated and for T. lanuginosus, 31- to 33-kDa proteins dominated. Reagents that disrupted normal protein synthesis during heat shock prevented the enhanced thermotolerance.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes C. A., Johnston G. C., Singer R. A. Thermotolerance is independent of induction of the full spectrum of heat shock proteins and of cell cycle blockage in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1990 Aug;172(8):4352–4358. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.8.4352-4358.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carper S. W., Duffy J. J., Gerner E. W. Heat shock proteins in thermotolerance and other cellular processes. Cancer Res. 1987 Oct 15;47(20):5249–5255. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Degryse E., Glansdorff N., Piérard A. A comparative analysis of extreme thermophilic bacteria belonging to the genus Thermus. Arch Microbiol. 1978 May 30;117(2):189–196. doi: 10.1007/BF00402307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eriksen S. H., Haasum I., Jensen B., Olsen J. Description of conidia from submerged cultivation of Thermomyces lanuginosus for use as a uniform inoculum. FEMS Microbiol Lett. 1992 Jun 15;72(3):279–283. doi: 10.1016/0378-1097(92)90475-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grogan D., Palm P., Zillig W. Isolate B12, which harbours a virus-like element, represents a new species of the archaebacterial genus Sulfolobus, Sulfolobus shibatae, sp. nov. Arch Microbiol. 1990;154(6):594–599. doi: 10.1007/BF00248842. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holden J. F., Baross J. A. Enhanced thermotolerance and temperature-induced changes in protein composition in the hyperthermophilic archaeon ES4. J Bacteriol. 1993 May;175(10):2839–2843. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.10.2839-2843.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston R. N., Kucey B. L. Competitive inhibition of hsp70 gene expression causes thermosensitivity. Science. 1988 Dec 16;242(4885):1551–1554. doi: 10.1126/science.3201244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landry J., Chrétien P., Lambert H., Hickey E., Weber L. A. Heat shock resistance conferred by expression of the human HSP27 gene in rodent cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Jul;109(1):7–15. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.1.7. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laszlo A. The relationship of heat-shock proteins, thermotolerance, and protein synthesis. Exp Cell Res. 1988 Oct;178(2):401–414. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(88)90409-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li G. C., Laszlo A. Amino acid analogs while inducing heat shock proteins sensitize CHO cells to thermal damage. J Cell Physiol. 1985 Jan;122(1):91–97. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1041220114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li G. C., Werb Z. Correlation between synthesis of heat shock proteins and development of thermotolerance in Chinese hamster fibroblasts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(10):3218–3222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.10.3218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindquist S., Craig E. A. The heat-shock proteins. Annu Rev Genet. 1988;22:631–677. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.22.120188.003215. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manrow R. E., Jacobson A. Increased rates of decay and reduced levels of accumulation of the major poly(A)-associated proteins of Dictyostelium during heat shock and development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Apr;84(7):1858–1862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.7.1858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizzen L. A., Welch W. J. Characterization of the thermotolerant cell. I. Effects on protein synthesis activity and the regulation of heat-shock protein 70 expression. J Cell Biol. 1988 Apr;106(4):1105–1116. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.4.1105. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roychowdhury H. S., Kapoor M. Ethanol and carbon-source starvation enhance the accumulation of HSP80 in Neurospora crassa. Can J Microbiol. 1988 Feb;34(2):162–168. doi: 10.1139/m88-031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanchez Y., Taulien J., Borkovich K. A., Lindquist S. Hsp104 is required for tolerance to many forms of stress. EMBO J. 1992 Jun;11(6):2357–2364. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1992.tb05295.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanders B. M. Stress proteins in aquatic organisms: an environmental perspective. Crit Rev Toxicol. 1993;23(1):49–75. doi: 10.3109/10408449309104074. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Streips U. N., Polio F. W. Heat shock proteins in bacilli. J Bacteriol. 1985 Apr;162(1):434–437. doi: 10.1128/jb.162.1.434-437.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trent J. D., Nimmesgern E., Wall J. S., Hartl F. U., Horwich A. L. A molecular chaperone from a thermophilic archaebacterium is related to the eukaryotic protein t-complex polypeptide-1. Nature. 1991 Dec 12;354(6353):490–493. doi: 10.1038/354490a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trent J. D., Osipiuk J., Pinkau T. Acquired thermotolerance and heat shock in the extremely thermophilic archaebacterium Sulfolobus sp. strain B12. J Bacteriol. 1990 Mar;172(3):1478–1484. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.3.1478-1484.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson K. Microbial stress proteins. Adv Microb Physiol. 1990;31:183–223. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2911(08)60122-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wu L., Welker N. E. Temperature-induced protein synthesis in Bacillus stearothermophilus NUB36. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(15):4889–4892. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.15.4889-4892.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]