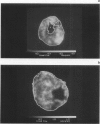
Abstract
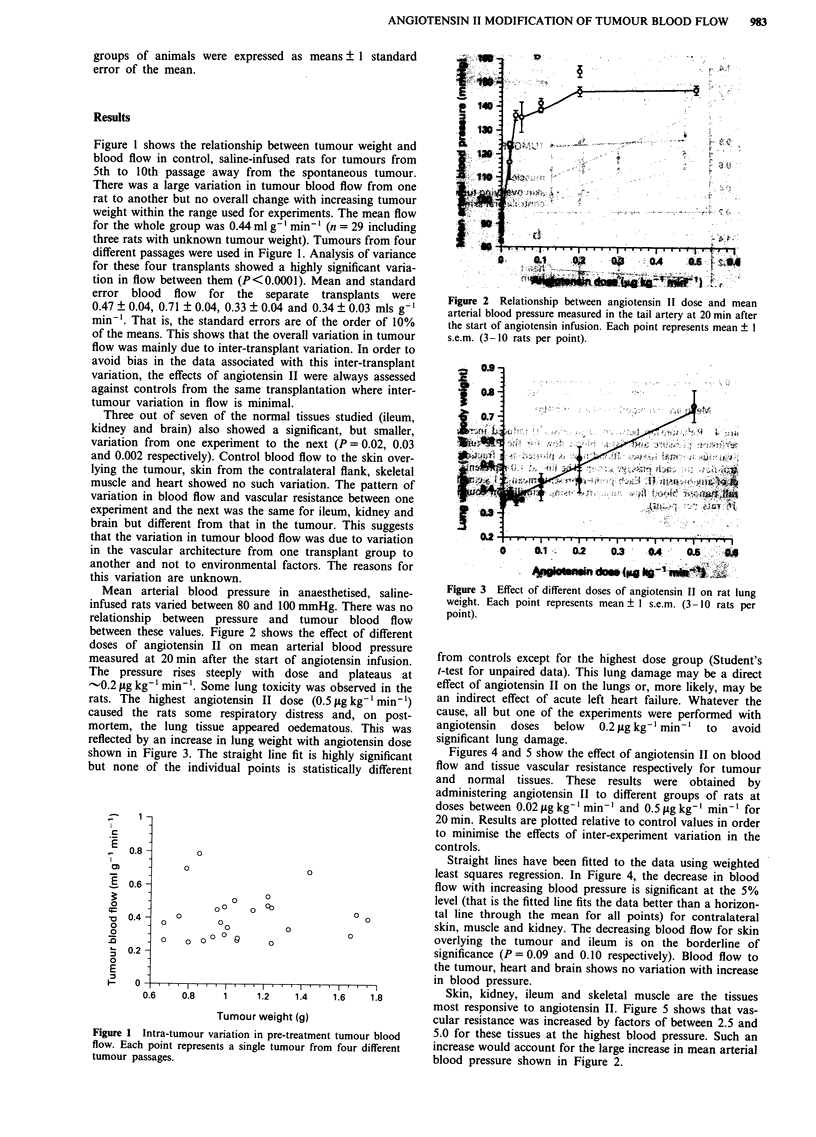
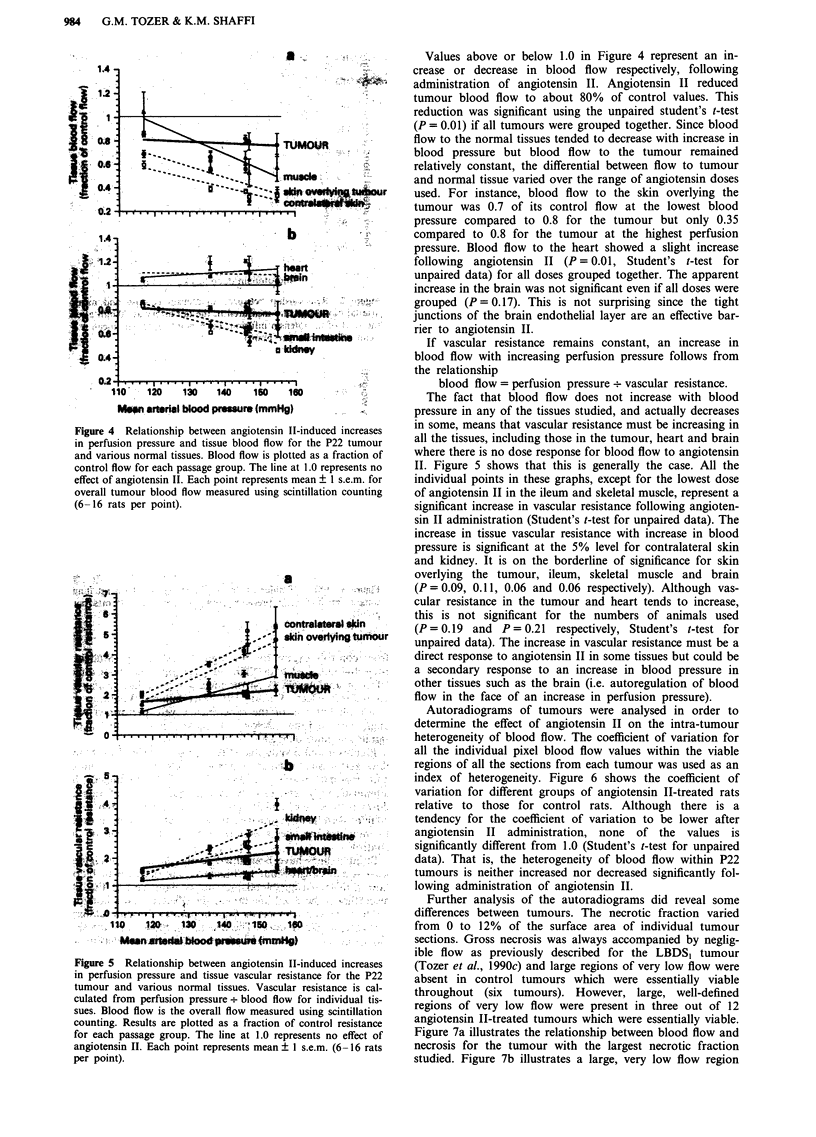
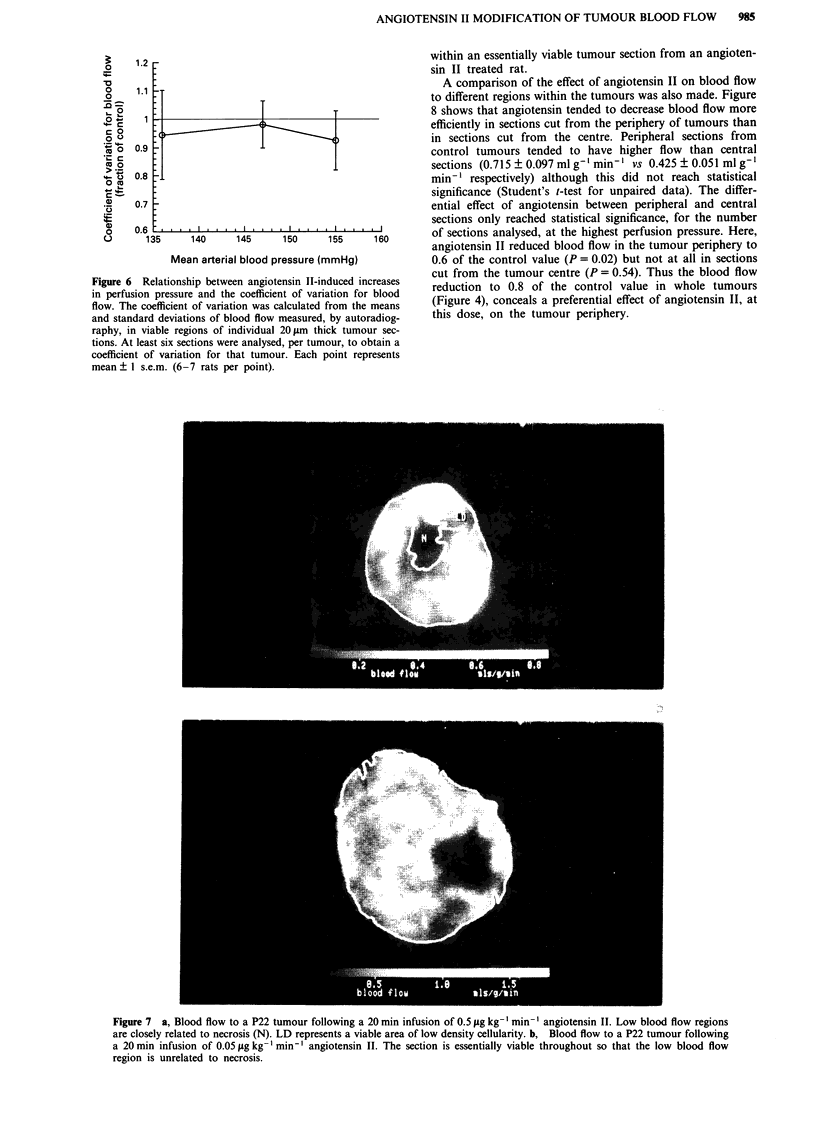
The effects of different doses of angiotensin II (0.02 to 0.5 microgram kg-1 min-1 on mean arterial blood pressure, tissue blood flow and tissue vascular resistance were investigated in BD9 rats. Blood flow was measured using the uptake of 125I- or 14C-labelled iodoantipyrine (125I-IAP and 14C-IAP). Spatial heterogeneity of blood flow within tumours, before and after angiotensin II infusion, was also measured using 14C-IAP and an autoradiographic procedure. Mean arterial blood pressure rose steeply with angiotensin II dose. Blood flow to skeletal muscle, skin overlying the tumour, contralateral skin, small intestine and kidney tended to decline in a dose-dependent manner. Blood flow to the tumour was also reduced (to 80% of control values) but there was no dose response. Blood flow to the heart was slightly increased and blood flow to the brain was unaffected by angiotensin II. Vascular resistance, in all tissues, was increased by angiotensin II infusion. The increase in tumour tissue was similar to that found in skeletal muscle and small intestine and is likely to be caused by a direct vasoconstricting effect of the drug rather than autoregulation of tumour blood flow in the face of an increase in perfusion pressure. The reduction in overall blood flow at the highest perfusion pressure was due to a preferential effect of angiotensin II at the tumour periphery. These results show that some tumours, at least, can respond directly to the effects of vasoactive agents.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson J. H., Willmott N., Bessent R., Angerson W. J., Kerr D. J., McArdle C. S. Regional chemotherapy for inoperable renal carcinoma: a method of targeting therapeutic microspheres to tumour. Br J Cancer. 1991 Aug;64(2):365–368. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1991.308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boucher Y., Baxter L. T., Jain R. K. Interstitial pressure gradients in tissue-isolated and subcutaneous tumors: implications for therapy. Cancer Res. 1990 Aug 1;50(15):4478–4484. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burton M. A., Gray B. N., Self G. W., Heggie J. C., Townsend P. S. Manipulation of experimental rat and rabbit liver tumor blood flow with angiotensin II. Cancer Res. 1985 Nov;45(11 Pt 1):5390–5393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekelund L., Lunderquist A. Pharmacoangiography with angiotensin. Radiology. 1974 Mar;110(3):533–540. doi: 10.1148/110.3.533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldberg J. A., Murray T., Kerr D. J., Willmott N., Bessent R. G., McKillop J. H., McArdle C. S. The use of angiotensin II as a potential method of targeting cytotoxic microspheres in patients with intrahepatic tumour. Br J Cancer. 1991 Feb;63(2):308–310. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1991.71. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hemingway D. M., Cooke T. G., Chang D., Grime S. J., Jenkins S. A. The effects of intra-arterial vasoconstrictors on the distribution of a radiolabelled low molecular weight marker in an experimental model of liver tumour. Br J Cancer. 1991 Apr;63(4):495–498. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1991.118. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirst D. G., Hirst V. K., Shaffi K. M., Prise V. E., Joiner B. The influence of vasoactive agents on the perfusion of tumours growing in three sites in the mouse. Int J Radiat Biol. 1991 Jul-Aug;60(1-2):211–218. doi: 10.1080/09553009114551861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori K., Suzuki M., Abe I., Saito S., Sato H. Increase in tumor vascular area due to increased blood flow by angiotensin II in rats. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1985 Feb;74(2):453–459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hori K., Suzuki M., Tanda S., Saito S., Shinozaki M., Zhang Q. H. Fluctuations in tumor blood flow under normotension and the effect of angiotensin II-induced hypertension. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1991 Nov;82(11):1309–1316. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1991.tb01797.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horsman M. R., Christensen K. L., Overgaard J. Hydralazine-induced enhancement of hyperthermic damage in a C3H mammary carcinoma in vivo. Int J Hyperthermia. 1989 Mar-Apr;5(2):123–136. doi: 10.3109/02656738909140442. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jirtle R., Clifton K. H., Rankin J. H. Effects of several vasoactive drugs on the vascular resistance of MT-W9B tumors in W/Fu rats. Cancer Res. 1978 Aug;38(8):2385–2390. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaplan J. H., Bookstein J. J. Abdominal visceral pharmacoangiography with angiotensin. Radiology. 1972 Apr;103(1):79–83. doi: 10.1148/103.1.79. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H., Hasuda K., Aoki K., Taniguchi S., Baba T. Systemic chemotherapy in tumor-bearing rats using high-dose cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II) with low nephrotoxicity in combination with angiotensin II and sodium thiosulfate. Int J Cancer. 1990 May 15;45(5):940–944. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910450527. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kobayashi H., Hasuda K., Taniguchi S., Baba T. Therapeutic efficacy of two-route chemotherapy using cis-diamminedichloroplatinum(II) and its antidote, sodium thiosulfate, combined with the angiotensin-II-induced hypertension method in a rat uterine tumor. Int J Cancer. 1991 Apr 1;47(6):893–898. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910470618. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noguchi S., Miyauchi K., Nishizawa Y., Sasaki Y., Imaoka S., Iwanaga T., Koyama H., Terasawa T. Augmentation of anticancer effect with angiotensin II in intraarterial infusion chemotherapy for breast carcinoma. Cancer. 1988 Aug 1;62(3):467–473. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19880801)62:3<467::aid-cncr2820620304>3.0.co;2-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasaki Y., Imaoka S., Hasegawa Y., Nakano S., Ishikawa O., Ohigashi H., Taniguchi K., Koyama H., Iwanaga T., Terasawa T. Changes in distribution of hepatic blood flow induced by intra-arterial infusion of angiotensin II in human hepatic cancer. Cancer. 1985 Jan 15;55(2):311–316. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19850115)55:2<311::aid-cncr2820550202>3.0.co;2-m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki M., Hori K., Abe I., Saito S., Sato H. A new approach to cancer chemotherapy: selective enhancement of tumor blood flow with angiotensin II. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1981 Sep;67(3):663–669. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki N., Sako K., Yonemasu Y. Effects of induced hypertension on blood flow and capillary permeability in rats with experimental brain tumors. J Neurooncol. 1991 Jun;10(3):213–218. doi: 10.1007/BF00177533. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takematsu H., Tomita Y., Kato T. Angiotensin-induced hypertension and chemotherapy for multiple lesions of malignant melanoma. Br J Dermatol. 1985 Oct;113(4):463–465. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2133.1985.tb02361.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tanda S., Hori K., Saito S., Shinozaki M., Zhang Q. H., Suzuki M. Comparison of the effects of intravenously bolus-administered endothelin-1 and infused angiotensin II on the subcutaneous tumor blood flow in anesthetized rats. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1991 Aug;82(8):958–963. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1991.tb01927.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuda K., Abe H., Aida T., Sugimoto S., Kaneko S. Modification of tumor blood flow and enhancement of therapeutic effect of ACNU on experimental rat gliomas with angiotensin II. J Neurooncol. 1990 Jun;8(3):205–212. doi: 10.1007/BF00177353. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tozer G. M., Lewis S., Michalowski A., Aber V. The relationship between regional variations in blood flow and histology in a transplanted rat fibrosarcoma. Br J Cancer. 1990 Feb;61(2):250–257. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1990.46. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tozer G. M., Maxwell R. J., Griffiths J. R., Pham P. Modification of the 31P magnetic resonance spectra of a rat tumour using vasodilators and its relationship to hypotension. Br J Cancer. 1990 Oct;62(4):553–560. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1990.329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tozer G. M., Morris C. C. Blood flow and blood volume in a transplanted rat fibrosarcoma: comparison with various normal tissues. Radiother Oncol. 1990 Feb;17(2):153–165. doi: 10.1016/0167-8140(90)90103-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trotter M. J., Chaplin D. J., Olive P. L. Effect of angiotensin II on intermittent tumour blood flow and acute hypoxia in the murine SCCVII carcinoma. Eur J Cancer. 1991;27(7):887–893. doi: 10.1016/0277-5379(91)90140-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tveit E., Weiss L., Lundstam S., Hultborn R. Perfusion characteristics and norepinephrine reactivity of human renal carcinoma. Cancer Res. 1987 Sep 1;47(17):4709–4713. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaupel P. Interrelationship between mean arterial blood pressure, blood flow, and vascular resistance in solid tumor tissue of DS-carcinosarcoma. Experientia. 1975 May 15;31(5):587–589. doi: 10.1007/BF01932474. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss L., Tveit E., Jansson I., Hultborn R. Vascular reactivity to norepinephrine of 7,12-dimethylbenz(a)anthracene-induced rat mammary tumors and normal tissue as studied in vitro. Cancer Res. 1986 Jul;46(7):3254–3257. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiig H., Tveit E., Hultborn R., Reed R. K., Weiss L. Interstitial fluid pressure in DMBA-induced rat mammary tumours. Scand J Clin Lab Invest. 1982 Apr;42(2):159–164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]