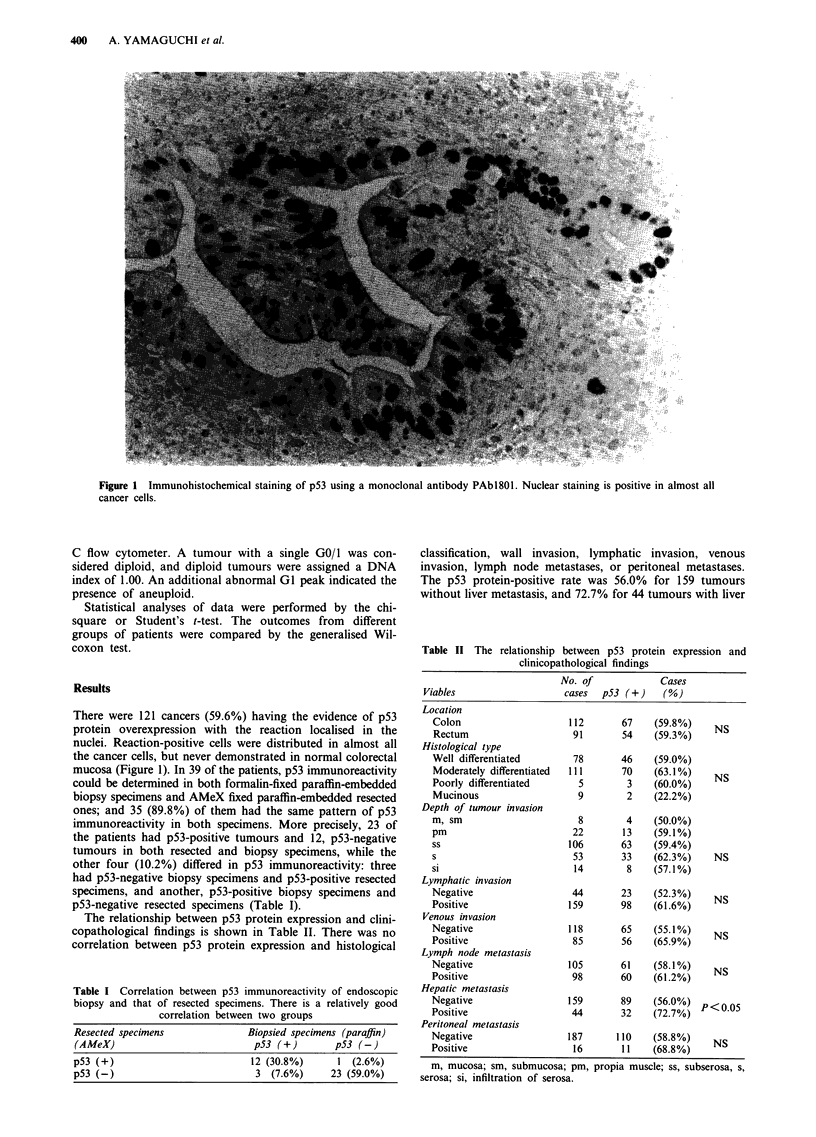
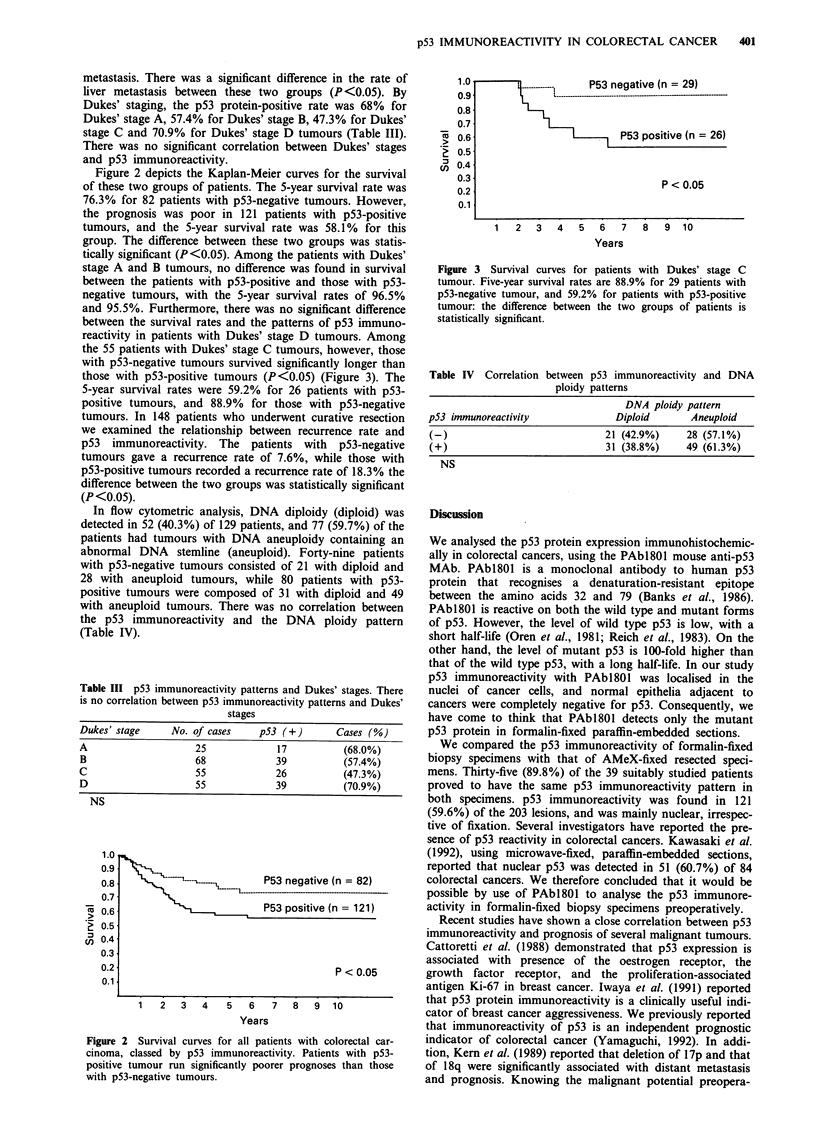
Abstract
The expression of p53 protein was immunohistochemically studied in formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded biopsy specimens of 203 colorectal carcinomas by use of a monoclonal antibody specific for the p53 protein. PAb1801. p53 protein expression with its reactivity localised in nuclei was found in 121 (59.6%) of the cancers. There was no correlation of p53 immunoreactivity with histological classification, wall invasion, lymphatic invasion, venous invasion, lymph node metastases, or peritoneal metastases. p53-positive cancers were more frequently associated with liver metastasis than p53-negative ones. Patients with p53-positive tumours had significantly poorer prognoses than those with p53-negative tumours. The 5 year survival rate was 58.1% for patients with p53-positive tumours, and 76.3% for those with p53-negative tumours. In Dukes' stage C tumours, an especially good correlation was found between p53 immunoreactivity and prognosis. In addition, patients with p53-positive tumours had higher recurrence rates. The results indicate that p53 immunoreactivity may be a useful prognostic marker of colorectal cancers.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Armitage N. C., Robins R. A., Evans D. F., Turner D. R., Baldwin R. W., Hardcastle J. D. The influence of tumour cell DNA abnormalities on survival in colorectal cancer. Br J Surg. 1985 Oct;72(10):828–830. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800721018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks L., Matlashewski G., Crawford L. Isolation of human-p53-specific monoclonal antibodies and their use in the studies of human p53 expression. Eur J Biochem. 1986 Sep 15;159(3):529–534. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1986.tb09919.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cattoretti G., Rilke F., Andreola S., D'Amato L., Delia D. P53 expression in breast cancer. Int J Cancer. 1988 Feb 15;41(2):178–183. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910410204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford L. V., Pim D. C., Gurney E. G., Goodfellow P., Taylor-Papadimitriou J. Detection of a common feature in several human tumor cell lines--a 53,000-dalton protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):41–45. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.41. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford L. V., Pim D. C., Lamb P. The cellular protein p53 in human tumours. Mol Biol Med. 1984 Aug;2(4):261–272. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fearon E. R., Vogelstein B. A genetic model for colorectal tumorigenesis. Cell. 1990 Jun 1;61(5):759–767. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90186-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iggo R., Gatter K., Bartek J., Lane D., Harris A. L. Increased expression of mutant forms of p53 oncogene in primary lung cancer. Lancet. 1990 Mar 24;335(8691):675–679. doi: 10.1016/0140-6736(90)90801-b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iwaya K., Tsuda H., Hiraide H., Tamaki K., Tamakuma S., Fukutomi T., Mukai K., Hirohashi S. Nuclear p53 immunoreaction associated with poor prognosis of breast cancer. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1991 Jul;82(7):835–840. doi: 10.1111/j.1349-7006.1991.tb02710.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawasaki Y., Monden T., Morimoto H., Murotani M., Miyoshi Y., Kobayashi T., Shimano T., Mori T. Immunohistochemical study of p53 expression in microwave-fixed, paraffin-embedded sections of colorectal carcinoma and adenoma. Am J Clin Pathol. 1992 Feb;97(2):244–249. doi: 10.1093/ajcp/97.2.244. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kern S. E., Fearon E. R., Tersmette K. W., Enterline J. P., Leppert M., Nakamura Y., White R., Vogelstein B., Hamilton S. R. Clinical and pathological associations with allelic loss in colorectal carcinoma [corrected]. JAMA. 1989 Jun 2;261(21):3099–3103. doi: 10.1001/jama.261.21.3099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane D. P., Crawford L. V. T antigen is bound to a host protein in SV40-transformed cells. Nature. 1979 Mar 15;278(5701):261–263. doi: 10.1038/278261a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levine A. J. Tumor suppressor genes. Bioessays. 1990 Feb;12(2):60–66. doi: 10.1002/bies.950120203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mercer W. E., Nelson D., DeLeo A. B., Old L. J., Baserga R. Microinjection of monoclonal antibody to protein p53 inhibits serum-induced DNA synthesis in 3T3 cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(20):6309–6312. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.20.6309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oren M., Maltzman W., Levine A. J. Post-translational regulation of the 54K cellular tumor antigen in normal and transformed cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1981 Feb;1(2):101–110. doi: 10.1128/mcb.1.2.101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purdie C. A., O'Grady J., Piris J., Wyllie A. H., Bird C. C. p53 expression in colorectal tumors. Am J Pathol. 1991 Apr;138(4):807–813. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich N. C., Levine A. J. Growth regulation of a cellular tumour antigen, p53, in nontransformed cells. Nature. 1984 Mar 8;308(5955):199–201. doi: 10.1038/308199a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich N. C., Oren M., Levine A. J. Two distinct mechanisms regulate the levels of a cellular tumor antigen, p53. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Dec;3(12):2143–2150. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.12.2143. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rotter V., Abutbul H., Ben-Ze'ev A. P53 transformation-related protein accumulates in the nucleus of transformed fibroblasts in association with the chromatin and is found in the cytoplasm of non-transformed fibroblasts. EMBO J. 1983;2(7):1041–1047. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1983.tb01543.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato Y., Mukai K., Watanabe S., Goto M., Shimosato Y. The AMeX method. A simplified technique of tissue processing and paraffin embedding with improved preservation of antigens for immunostaining. Am J Pathol. 1986 Dec;125(3):431–435. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scott N., Sagar P., Stewart J., Blair G. E., Dixon M. F., Quirke P. p53 in colorectal cancer: clinicopathological correlation and prognostic significance. Br J Cancer. 1991 Feb;63(2):317–319. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1991.74. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolley R. C., Schreiber K., Koss L. G., Karas M., Sherman A. DNA distribution in human colon carcinomas and its relationship to clinical behavior. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1982 Jul;69(1):15–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi A., Kurosaka Y., Fushida S., Kanno M., Yonemura Y., Miwa K., Miyazaki I. Expression of p53 protein in colorectal cancer and its relationship to short-term prognosis. Cancer. 1992 Dec 15;70(12):2778–2784. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19921215)70:12<2778::aid-cncr2820701209>3.0.co;2-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]