Abstract
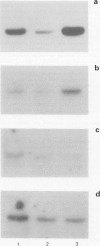
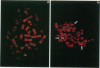
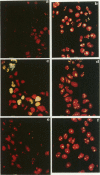
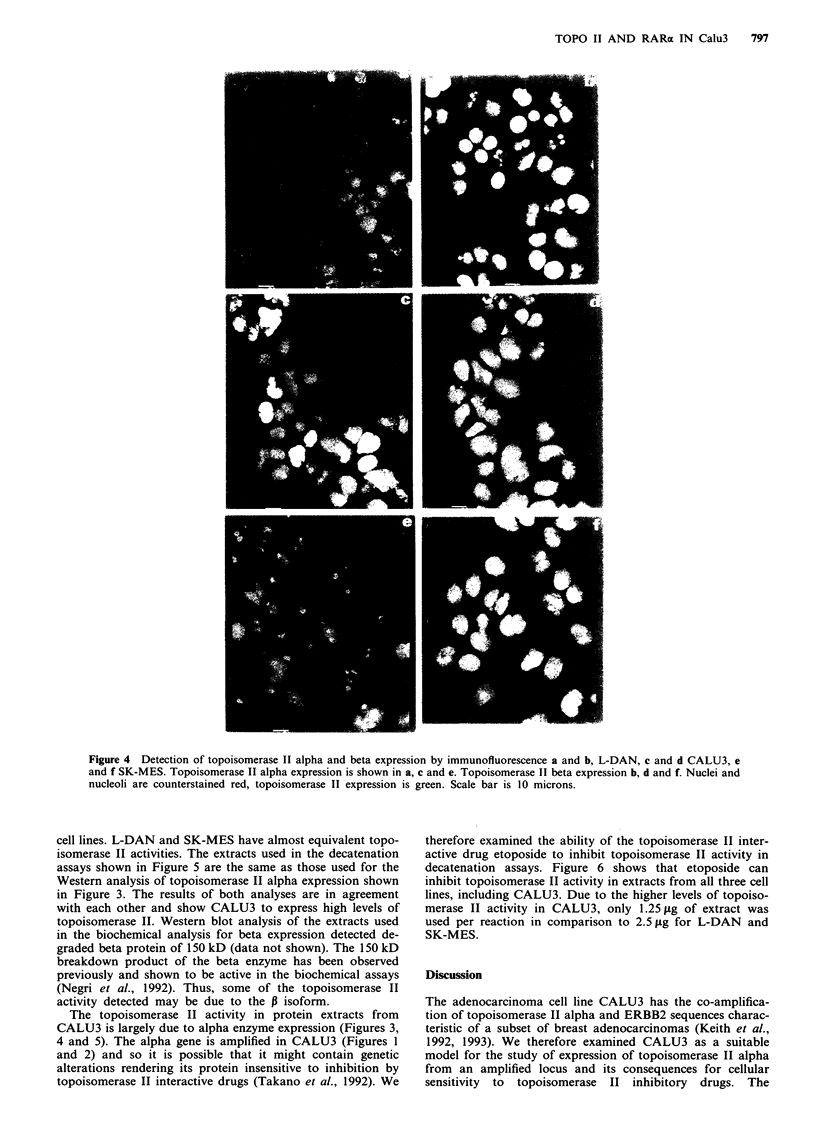
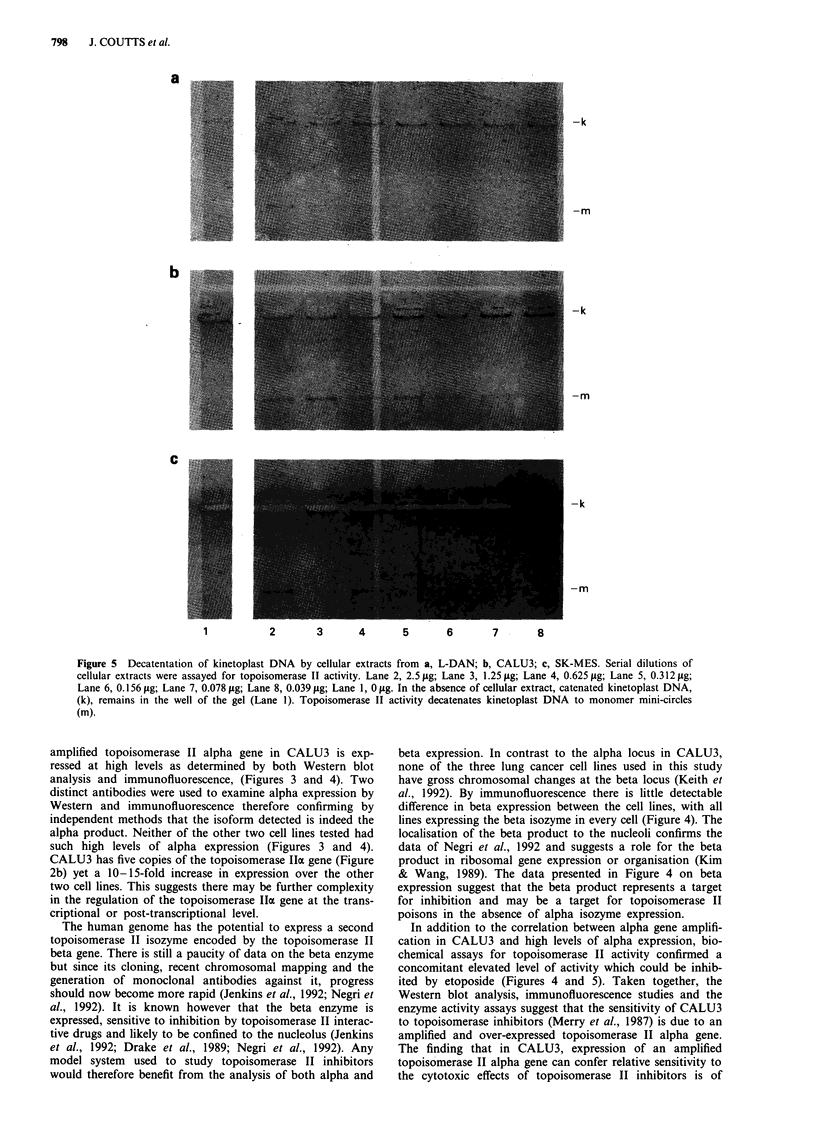
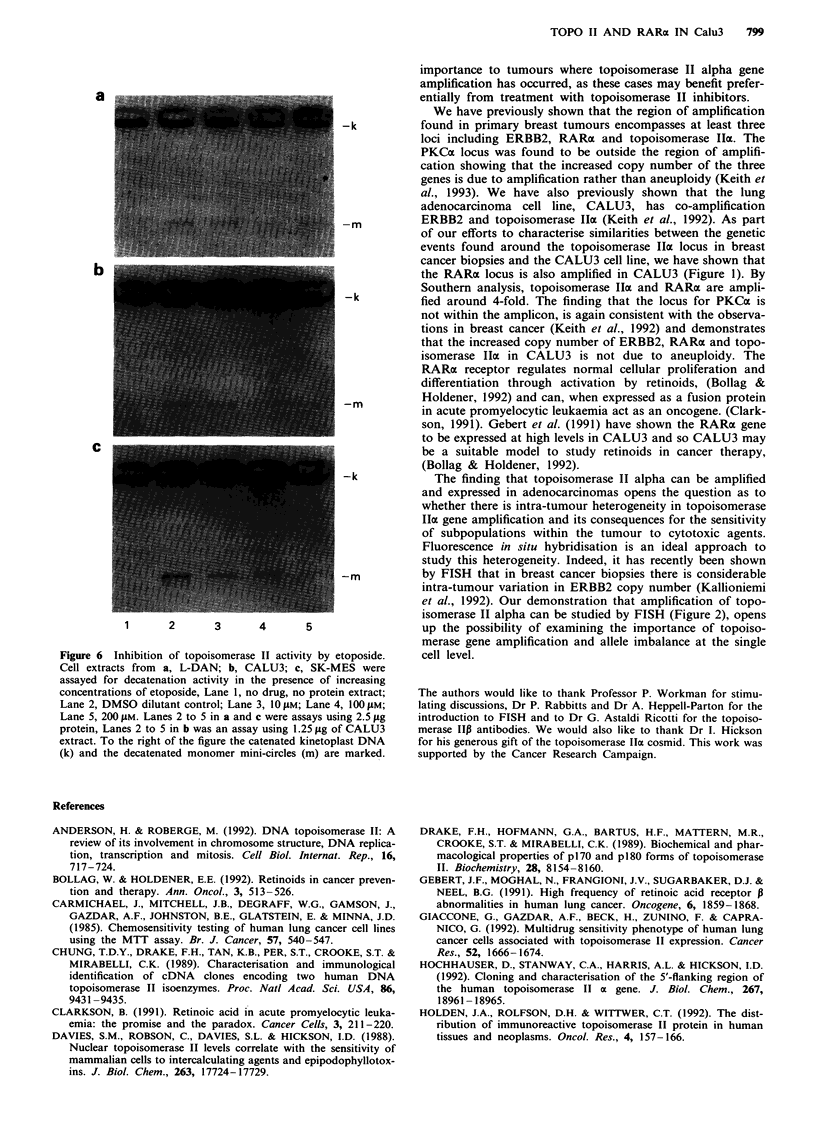
Human topoisomerase II enzymes are targets for a number of widely used anticancer agents. We have analysed a lung adenocarcinoma cell line CALU3, which has co-amplified topoisomerase II alpha and ERBB2 sequences, for the structure of the amplicon and for expression of both topoisomerase II alpha and beta. The region of chromosome 17q amplified in CALU3 also includes the retinoic acid receptor alpha locus and is therefore similar to the amplicon observed in breast cancers carrying amplified topoisomerase II alpha and retinoic acid receptor sequences. The use of fluorescence in situ hybridisation localises the amplified topoisomerase II alpha sequences to a cluster on one chromosome with single copies localised to others. CALU3 express high levels of topoisomerase II alpha is determined by Western blot, immunofluorescence and enzyme activity. The enzyme activity extracted from CALU3 is sensitive to inhibition by the topoisomerase II poison etoposide. Topoisomerase II beta expression was observed in three lung cancer cell lines including CALU3 and was confined to the nucleoli. Thus, the CALU3 cell line is an ideal model to study the amplification and expression of topoisomerase II alpha in adenocarcinomas.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson H. J., Roberge M. DNA topoisomerase II: a review of its involvement in chromosome structure, DNA replication, transcription and mitosis. Cell Biol Int Rep. 1992 Aug;16(8):717–724. doi: 10.1016/s0309-1651(05)80016-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bollag W., Holdener E. E. Retinoids in cancer prevention and therapy. Ann Oncol. 1992 Jul;3(7):513–526. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.annonc.a058252. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carmichael J., Mitchell J. B., DeGraff W. G., Gamson J., Gazdar A. F., Johnson B. E., Glatstein E., Minna J. D. Chemosensitivity testing of human lung cancer cell lines using the MTT assay. Br J Cancer. 1988 Jun;57(6):540–547. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1988.125. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung T. D., Drake F. H., Tan K. B., Per S. R., Crooke S. T., Mirabelli C. K. Characterization and immunological identification of cDNA clones encoding two human DNA topoisomerase II isozymes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(23):9431–9435. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.23.9431. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarkson B. Retinoic acid in acute promyelocytic leukemia: the promise and the paradox. Cancer Cells. 1991 Jun;3(6):211–220. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies S. M., Robson C. N., Davies S. L., Hickson I. D. Nuclear topoisomerase II levels correlate with the sensitivity of mammalian cells to intercalating agents and epipodophyllotoxins. J Biol Chem. 1988 Nov 25;263(33):17724–17729. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Drake F. H., Hofmann G. A., Bartus H. F., Mattern M. R., Crooke S. T., Mirabelli C. K. Biochemical and pharmacological properties of p170 and p180 forms of topoisomerase II. Biochemistry. 1989 Oct 3;28(20):8154–8160. doi: 10.1021/bi00446a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gebert J. F., Moghal N., Frangioni J. V., Sugarbaker D. J., Neel B. G. High frequency of retinoic acid receptor beta abnormalities in human lung cancer. Oncogene. 1991 Oct;6(10):1859–1868. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giaccone G., Gazdar A. F., Beck H., Zunino F., Capranico G. Multidrug sensitivity phenotype of human lung cancer cells associated with topoisomerase II expression. Cancer Res. 1992 Apr 1;52(7):1666–1674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hochhauser D., Stanway C. A., Harris A. L., Hickson I. D. Cloning and characterization of the 5'-flanking region of the human topoisomerase II alpha gene. J Biol Chem. 1992 Sep 15;267(26):18961–18965. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holden J. A., Rolfson D. H., Wittwer C. T. The distribution of immunoreactive topoisomerase II Protein in human tissues and neoplasms. Oncol Res. 1992;4(4-5):157–166. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jenkins J. R., Ayton P., Jones T., Davies S. L., Simmons D. L., Harris A. L., Sheer D., Hickson I. D. Isolation of cDNA clones encoding the beta isozyme of human DNA topoisomerase II and localisation of the gene to chromosome 3p24. Nucleic Acids Res. 1992 Nov 11;20(21):5587–5592. doi: 10.1093/nar/20.21.5587. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kallioniemi O. P., Kallioniemi A., Kurisu W., Thor A., Chen L. C., Smith H. S., Waldman F. M., Pinkel D., Gray J. W. ERBB2 amplification in breast cancer analyzed by fluorescence in situ hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Jun 15;89(12):5321–5325. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.12.5321. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
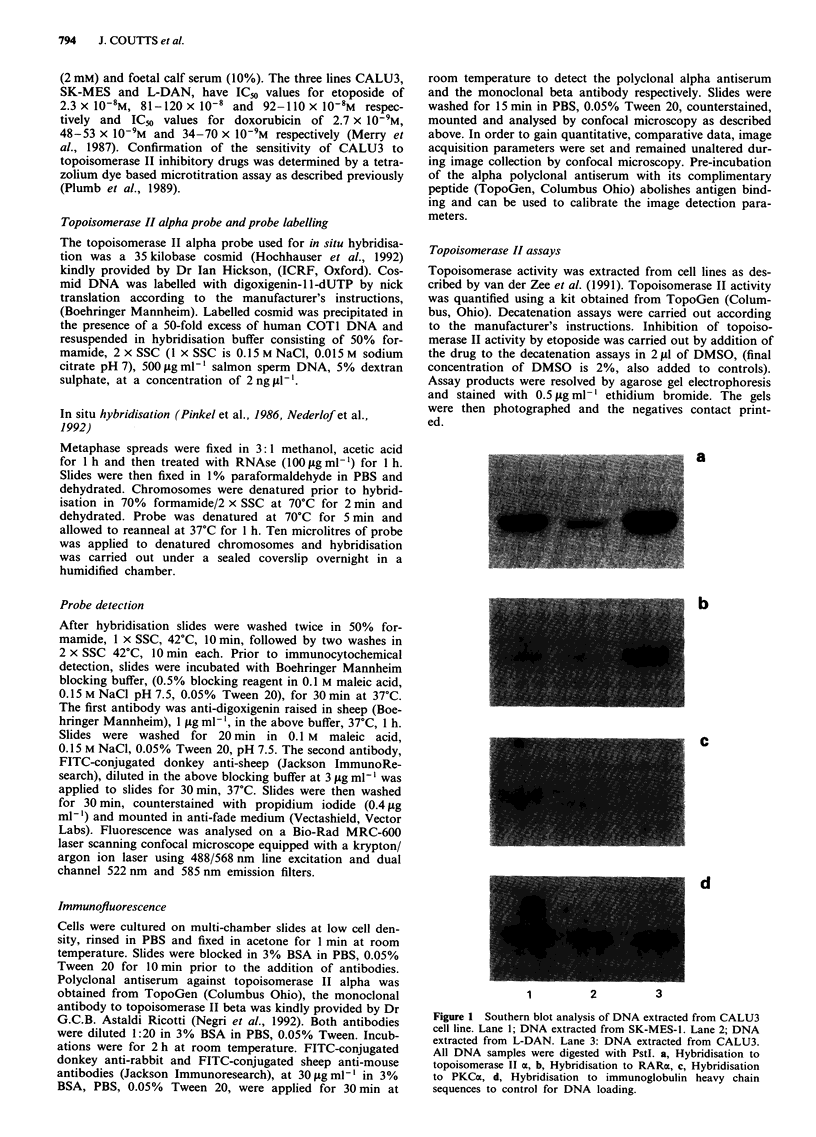
- Keith W. N., Tan K. B., Brown R. Amplification of the topoisomerase II alpha gene in a non-small cell lung cancer cell line and characterisation of polymorphisms at the human topoisomerase II alpha and beta loci in normal tissue. Genes Chromosomes Cancer. 1992 Mar;4(2):169–175. doi: 10.1002/gcc.2870040211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim R. A., Wang J. C. A subthreshold level of DNA topoisomerases leads to the excision of yeast rDNA as extrachromosomal rings. Cell. 1989 Jun 16;57(6):975–985. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90336-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu L. F. DNA topoisomerase poisons as antitumor drugs. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:351–375. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.002031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattei M. G., Petkovich M., Mattei J. F., Brand N., Chambon P. Mapping of the human retinoic acid receptor to the q21 band of chromosome 17. Hum Genet. 1988 Oct;80(2):186–188. doi: 10.1007/BF00702866. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
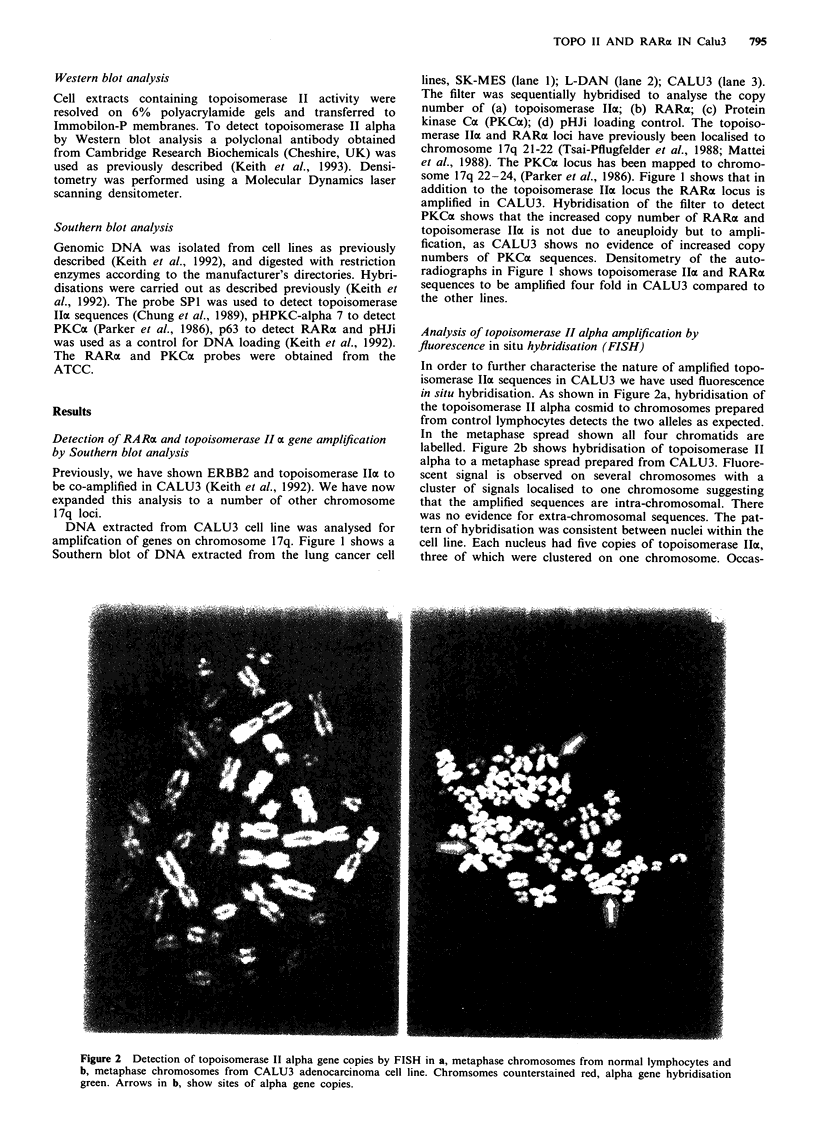
- Merry S., Courtney E. R., Fetherston C. A., Kaye S. B., Freshney R. I. Circumvention of drug resistance in human non-small cell lung cancer in vitro by verapamil. Br J Cancer. 1987 Oct;56(4):401–405. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1987.214. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nederlof P. M., van der Flier S., Raap A. K., Tanke H. J. Quantification of inter- and intra-nuclear variation of fluorescence in situ hybridization signals. Cytometry. 1992;13(8):831–838. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990130805. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
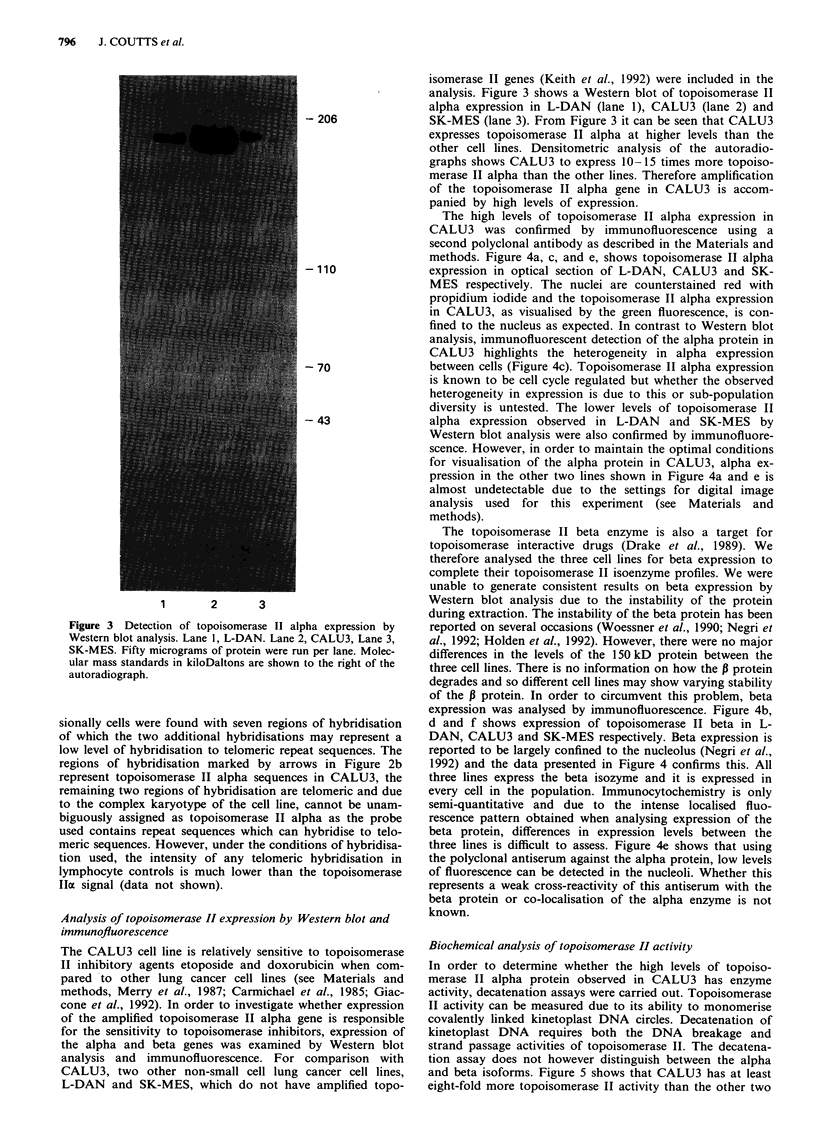
- Negri C., Chiesa R., Cerino A., Bestagno M., Sala C., Zini N., Maraldi N. M., Astaldi Ricotti G. C. Monoclonal antibodies to human DNA topoisomerase I and the two isoforms of DNA topoisomerase II: 170- and 180-kDa isozymes. Exp Cell Res. 1992 Jun;200(2):452–459. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(92)90195-e. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nitiss J. L., Liu Y. X., Harbury P., Jannatipour M., Wasserman R., Wang J. C. Amsacrine and etoposide hypersensitivity of yeast cells overexpressing DNA topoisomerase II. Cancer Res. 1992 Aug 15;52(16):4467–4472. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parker P. J., Coussens L., Totty N., Rhee L., Young S., Chen E., Stabel S., Waterfield M. D., Ullrich A. The complete primary structure of protein kinase C--the major phorbol ester receptor. Science. 1986 Aug 22;233(4766):853–859. doi: 10.1126/science.3755547. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pinkel D., Straume T., Gray J. W. Cytogenetic analysis using quantitative, high-sensitivity, fluorescence hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 May;83(9):2934–2938. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.9.2934. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plumb J. A., Milroy R., Kaye S. B. Effects of the pH dependence of 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl-tetrazolium bromide-formazan absorption on chemosensitivity determined by a novel tetrazolium-based assay. Cancer Res. 1989 Aug 15;49(16):4435–4440. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takano H., Kohno K., Matsuo K., Matsuda T., Kuwano M. DNA topoisomerase-targeting antitumor agents and drug resistance. Anticancer Drugs. 1992 Aug;3(4):323–330. doi: 10.1097/00001813-199208000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tan K. B., Dorman T. E., Falls K. M., Chung T. D., Mirabelli C. K., Crooke S. T., Mao J. Topoisomerase II alpha and topoisomerase II beta genes: characterization and mapping to human chromosomes 17 and 3, respectively. Cancer Res. 1992 Jan 1;52(1):231–234. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsai-Pflugfelder M., Liu L. F., Liu A. A., Tewey K. M., Whang-Peng J., Knutsen T., Huebner K., Croce C. M., Wang J. C. Cloning and sequencing of cDNA encoding human DNA topoisomerase II and localization of the gene to chromosome region 17q21-22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Oct;85(19):7177–7181. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.19.7177. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woessner R. D., Chung T. D., Hofmann G. A., Mattern M. R., Mirabelli C. K., Drake F. H., Johnson R. K. Differences between normal and ras-transformed NIH-3T3 cells in expression of the 170kD and 180kD forms of topoisomerase II. Cancer Res. 1990 May 15;50(10):2901–2908. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woessner R. D., Mattern M. R., Mirabelli C. K., Johnson R. K., Drake F. H. Proliferation- and cell cycle-dependent differences in expression of the 170 kilodalton and 180 kilodalton forms of topoisomerase II in NIH-3T3 cells. Cell Growth Differ. 1991 Apr;2(4):209–214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van der Zee A. G., Hollema H., de Jong S., Boonstra H., Gouw A., Willemse P. H., Zijlstra J. G., de Vries E. G. P-glycoprotein expression and DNA topoisomerase I and II activity in benign tumors of the ovary and in malignant tumors of the ovary, before and after platinum/cyclophosphamide chemotherapy. Cancer Res. 1991 Nov 1;51(21):5915–5920. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]