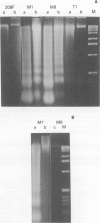
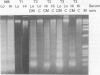
Abstract
Oncogenes and oncosuppressors can deregulate cell replication in tumours, and recently have been shown to influence the probability of apoptosis. The effects of human c-myc and mutated (T24) Ha-ras oncogenes on susceptibility to apoptosis were investigated by introducing them into immortalised rat fibroblasts. The resulting family of transfectants showed closely similar measures of proliferation, but widely divergent rates of apoptosis, differing by up to fifteen-fold, that correlated inversely with population expansion rates in vitro. T24-ras transfectants with moderate or high p21ras expression showed reduced apoptosis, and this was reversed by pharmacological inhibition of membrane localisation of p21ras by mevinolin. In contrast, c-myc stimulated apoptosis, and this was further enhanced by serum deprivation. Inducibility of effector proteins represents one possible mechanism of genetic control of the susceptibility to apoptosis, and its investigation showed that c-myc was associated with expression by viable cells of latent calcium/magnesium sensitive endonuclease activity characteristic of apoptosis. In contrast, endonuclease activity was not detected in viable cells of a T24-ras transfectant expressing high levels of p21ras. Thus, there appeared to be differential regulation of susceptibility to apoptosis, positively by c-myc and negatively by activated ras, and this was associated with availability of endonuclease activity. Genetic modulation of apoptosis in human neoplasms is likely to influence net growth rate, retention of cells acquiring new mutations and response to certain chemotherapeutic agents.
Full text
PDF






Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Andrejauskas E., Moroni C. Reversible abrogation of IL-3 dependence by an inducible H-ras oncogene. EMBO J. 1989 Sep;8(9):2575–2581. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1989.tb08396.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arends M. J., Morris R. G., Wyllie A. H. Apoptosis. The role of the endonuclease. Am J Pathol. 1990 Mar;136(3):593–608. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arends M. J., Wyllie A. H. Apoptosis: mechanisms and roles in pathology. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1991;32:223–254. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-364932-4.50010-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Askew D. S., Ashmun R. A., Simmons B. C., Cleveland J. L. Constitutive c-myc expression in an IL-3-dependent myeloid cell line suppresses cell cycle arrest and accelerates apoptosis. Oncogene. 1991 Oct;6(10):1915–1922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertrand R., Sarang M., Jenkin J., Kerrigan D., Pommier Y. Differential induction of secondary DNA fragmentation by topoisomerase II inhibitors in human tumor cell lines with amplified c-myc expression. Cancer Res. 1991 Dec 1;51(23 Pt 1):6280–6285. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissonnette R. P., Echeverri F., Mahboubi A., Green D. R. Apoptotic cell death induced by c-myc is inhibited by bcl-2. Nature. 1992 Oct 8;359(6395):552–554. doi: 10.1038/359552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bos J. L., Fearon E. R., Hamilton S. R., Verlaan-de Vries M., van Boom J. H., van der Eb A. J., Vogelstein B. Prevalence of ras gene mutations in human colorectal cancers. 1987 May 28-Jun 3Nature. 327(6120):293–297. doi: 10.1038/327293a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown K., Quintanilla M., Ramsden M., Kerr I. B., Young S., Balmain A. v-ras genes from Harvey and BALB murine sarcoma viruses can act as initiators of two-stage mouse skin carcinogenesis. Cell. 1986 Aug 1;46(3):447–456. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90665-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Buchmann A., Ruggeri B., Klein-Szanto A. J., Balmain A. Progression of squamous carcinoma cells to spindle carcinomas of mouse skin is associated with an imbalance of H-ras alleles on chromosome 7. Cancer Res. 1991 Aug 1;51(15):4097–4101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke A. R., Maandag E. R., van Roon M., van der Lugt N. M., van der Valk M., Hooper M. L., Berns A., te Riele H. Requirement for a functional Rb-1 gene in murine development. Nature. 1992 Sep 24;359(6393):328–330. doi: 10.1038/359328a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clarke A. R., Purdie C. A., Harrison D. J., Morris R. G., Bird C. C., Hooper M. L., Wyllie A. H. Thymocyte apoptosis induced by p53-dependent and independent pathways. Nature. 1993 Apr 29;362(6423):849–852. doi: 10.1038/362849a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen J. J., Duke R. C. Glucocorticoid activation of a calcium-dependent endonuclease in thymocyte nuclei leads to cell death. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):38–42. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeClue J. E., Vass W. C., Papageorge A. G., Lowy D. R., Willumsen B. M. Inhibition of cell growth by lovastatin is independent of ras function. Cancer Res. 1991 Jan 15;51(2):712–717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evan G. I., Wyllie A. H., Gilbert C. S., Littlewood T. D., Land H., Brooks M., Waters C. M., Penn L. Z., Hancock D. C. Induction of apoptosis in fibroblasts by c-myc protein. Cell. 1992 Apr 3;69(1):119–128. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90123-t. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans C. A., Owen-Lynch P. J., Whetton A. D., Dive C. Activation of the Abelson tyrosine kinase activity is associated with suppression of apoptosis in hemopoietic cells. Cancer Res. 1993 Apr 15;53(8):1735–1738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans D. L., Dive C. Effects of cisplatin on the induction of apoptosis in proliferating hepatoma cells and nonproliferating immature thymocytes. Cancer Res. 1993 May 1;53(9):2133–2139. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fanidi A., Harrington E. A., Evan G. I. Cooperative interaction between c-myc and bcl-2 proto-oncogenes. Nature. 1992 Oct 8;359(6395):554–556. doi: 10.1038/359554a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Field J. K., Spandidos D. A. The role of ras and myc oncogenes in human solid tumours and their relevance in diagnosis and prognosis (review). Anticancer Res. 1990 Jan-Feb;10(1):1–22. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Furth M. E., Davis L. J., Fleurdelys B., Scolnick E. M. Monoclonal antibodies to the p21 products of the transforming gene of Harvey murine sarcoma virus and of the cellular ras gene family. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):294–304. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.294-304.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Going J. J., Anderson T. J., Wyllie A. H. Ras p21 in breast tissue: associations with pathology and cellular localisation. Br J Cancer. 1992 Jan;65(1):45–50. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1992.9. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Going J. J., Williams A. R., Wyllie A. H., Anderson T. J., Piris J. Optimal preservation of p21 ras immunoreactivity and morphology in paraffin-embedded tissue. J Pathol. 1988 Jul;155(3):185–190. doi: 10.1002/path.1711550302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hancock J. F., Magee A. I., Childs J. E., Marshall C. J. All ras proteins are polyisoprenylated but only some are palmitoylated. Cell. 1989 Jun 30;57(7):1167–1177. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(89)90054-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hengartner M. O., Ellis R. E., Horvitz H. R. Caenorhabditis elegans gene ced-9 protects cells from programmed cell death. Nature. 1992 Apr 9;356(6369):494–499. doi: 10.1038/356494a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hockenbery D., Nuñez G., Milliman C., Schreiber R. D., Korsmeyer S. J. Bcl-2 is an inner mitochondrial membrane protein that blocks programmed cell death. Nature. 1990 Nov 22;348(6299):334–336. doi: 10.1038/348334a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacks T., Fazeli A., Schmitt E. M., Bronson R. T., Goodell M. A., Weinberg R. A. Effects of an Rb mutation in the mouse. Nature. 1992 Sep 24;359(6393):295–300. doi: 10.1038/359295a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kerr J. F., Wyllie A. H., Currie A. R. Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide-ranging implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer. 1972 Aug;26(4):239–257. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1972.33. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kita T., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L. Feedback regulation of 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase in livers of mice treated with mevinolin, a competitive inhibitor of the reductase. J Clin Invest. 1980 Nov;66(5):1094–1100. doi: 10.1172/JCI109938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee E. Y., Chang C. Y., Hu N., Wang Y. C., Lai C. C., Herrup K., Lee W. H., Bradley A. Mice deficient for Rb are nonviable and show defects in neurogenesis and haematopoiesis. Nature. 1992 Sep 24;359(6393):288–294. doi: 10.1038/359288a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConkey D. J., Hartzell P., Amador-Pérez J. F., Orrenius S., Jondal M. Calcium-dependent killing of immature thymocytes by stimulation via the CD3/T cell receptor complex. J Immunol. 1989 Sep 15;143(6):1801–1806. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConkey D. J., Hartzell P., Duddy S. K., Håkansson H., Orrenius S. 2,3,7,8-Tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin kills immature thymocytes by Ca2+-mediated endonuclease activation. Science. 1988 Oct 14;242(4876):256–259. doi: 10.1126/science.3262923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McConkey D. J., Nicotera P., Hartzell P., Bellomo G., Wyllie A. H., Orrenius S. Glucocorticoids activate a suicide process in thymocytes through an elevation of cytosolic Ca2+ concentration. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1989 Feb 15;269(1):365–370. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(89)90119-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nuñez G., London L., Hockenbery D., Alexander M., McKearn J. P., Korsmeyer S. J. Deregulated Bcl-2 gene expression selectively prolongs survival of growth factor-deprived hemopoietic cell lines. J Immunol. 1990 May 1;144(9):3602–3610. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perotti M., Toddei F., Mirabelli F., Vairetti M., Bellomo G., McConkey D. J., Orrenius S. Calcium-dependent DNA fragmentation in human synovial cells exposed to cold shock. FEBS Lett. 1990 Jan 1;259(2):331–334. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(90)80040-p. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Quade K. Transformation of mammalian cells by avian myelocytomatosis virus and avian erythroblastosis virus. Virology. 1979 Oct 30;98(2):461–465. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(79)90569-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos E., Tronick S. R., Aaronson S. A., Pulciani S., Barbacid M. T24 human bladder carcinoma oncogene is an activated form of the normal human homologue of BALB- and Harvey-MSV transforming genes. Nature. 1982 Jul 22;298(5872):343–347. doi: 10.1038/298343a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schafer W. R., Kim R., Sterne R., Thorner J., Kim S. H., Rine J. Genetic and pharmacological suppression of oncogenic mutations in ras genes of yeast and humans. Science. 1989 Jul 28;245(4916):379–385. doi: 10.1126/science.2569235. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Servomaa K., Rytömaa T. Suicidal death of rat chloroleukaemia cells by activation of the long interspersed repetitive DNA element (L1Rn). Cell Tissue Kinet. 1988 Jan;21(1):33–43. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2184.1988.tb00769.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw P., Bovey R., Tardy S., Sahli R., Sordat B., Costa J. Induction of apoptosis by wild-type p53 in a human colon tumor-derived cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 May 15;89(10):4495–4499. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.10.4495. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith C. A., Williams G. T., Kingston R., Jenkinson E. J., Owen J. J. Antibodies to CD3/T-cell receptor complex induce death by apoptosis in immature T cells in thymic cultures. Nature. 1989 Jan 12;337(6203):181–184. doi: 10.1038/337181a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spandidos D. A., Wilkie N. M. Malignant transformation of early passage rodent cells by a single mutated human oncogene. Nature. 1984 Aug 9;310(5977):469–475. doi: 10.1038/310469a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Umansky S. R., Korol' B. A., Nelipovich P. A. In vivo DNA degradation in thymocytes of gamma-irradiated or hydrocortisone-treated rats. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1981 Aug 27;655(1):9–17. doi: 10.1016/0005-2787(81)90060-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vaux D. L., Cory S., Adams J. M. Bcl-2 gene promotes haemopoietic cell survival and cooperates with c-myc to immortalize pre-B cells. Nature. 1988 Sep 29;335(6189):440–442. doi: 10.1038/335440a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vindeløv L. L., Christensen I. J., Nissen N. I. Standardization of high-resolution flow cytometric DNA analysis by the simultaneous use of chicken and trout red blood cells as internal reference standards. Cytometry. 1983 Mar;3(5):328–331. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990030504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker P. R., Smith C., Youdale T., Leblanc J., Whitfield J. F., Sikorska M. Topoisomerase II-reactive chemotherapeutic drugs induce apoptosis in thymocytes. Cancer Res. 1991 Feb 15;51(4):1078–1085. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams A. R., Piris J., Spandidos D. A., Wyllie A. H. Immunohistochemical detection of the ras oncogene p21 product in an experimental tumour and in human colorectal neoplasms. Br J Cancer. 1985 Nov;52(5):687–693. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1985.244. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H., Arends M. J., Morris R. G., Walker S. W., Evan G. The apoptosis endonuclease and its regulation. Semin Immunol. 1992 Dec;4(6):389–397. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H. Glucocorticoid-induced thymocyte apoptosis is associated with endogenous endonuclease activation. Nature. 1980 Apr 10;284(5756):555–556. doi: 10.1038/284555a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H., Kerr J. F., Currie A. R. Cell death: the significance of apoptosis. Int Rev Cytol. 1980;68:251–306. doi: 10.1016/s0074-7696(08)62312-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H., Morris R. G. Hormone-induced cell death. Purification ad properties of thymocytes undergoing apoptosis after glucocorticoid treatment. Am J Pathol. 1982 Oct;109(1):78–87. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H., Morris R. G., Smith A. L., Dunlop D. Chromatin cleavage in apoptosis: association with condensed chromatin morphology and dependence on macromolecular synthesis. J Pathol. 1984 Jan;142(1):67–77. doi: 10.1002/path.1711420112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H., Rose K. A., Morris R. G., Steel C. M., Foster E., Spandidos D. A. Rodent fibroblast tumours expressing human myc and ras genes: growth, metastasis and endogenous oncogene expression. Br J Cancer. 1987 Sep;56(3):251–259. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1987.186. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyllie A. H. The biology of cell death in tumours. Anticancer Res. 1985 Jan-Feb;5(1):131–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamada T., Ohyama H. Radiation-induced interphase death of rat thymocytes is internally programmed (apoptosis). Int J Radiat Biol Relat Stud Phys Chem Med. 1988 Jan;53(1):65–75. doi: 10.1080/09553008814550431. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yonish-Rouach E., Resnitzky D., Lotem J., Sachs L., Kimchi A., Oren M. Wild-type p53 induces apoptosis of myeloid leukaemic cells that is inhibited by interleukin-6. Nature. 1991 Jul 25;352(6333):345–347. doi: 10.1038/352345a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yuh Y. S., Thompson E. B. Glucocorticoid effect on oncogene/growth gene expression in human T lymphoblastic leukemic cell line CCRF-CEM. Specific c-myc mRNA suppression by dexamethasone. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jun 25;264(18):10904–10910. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Haelst U. Light and electron microscopic study of the normal and pathological thymus of the rat. II. The acute thymic involution. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1967;80(2):153–182. doi: 10.1007/BF00337454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]