Abstract
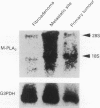
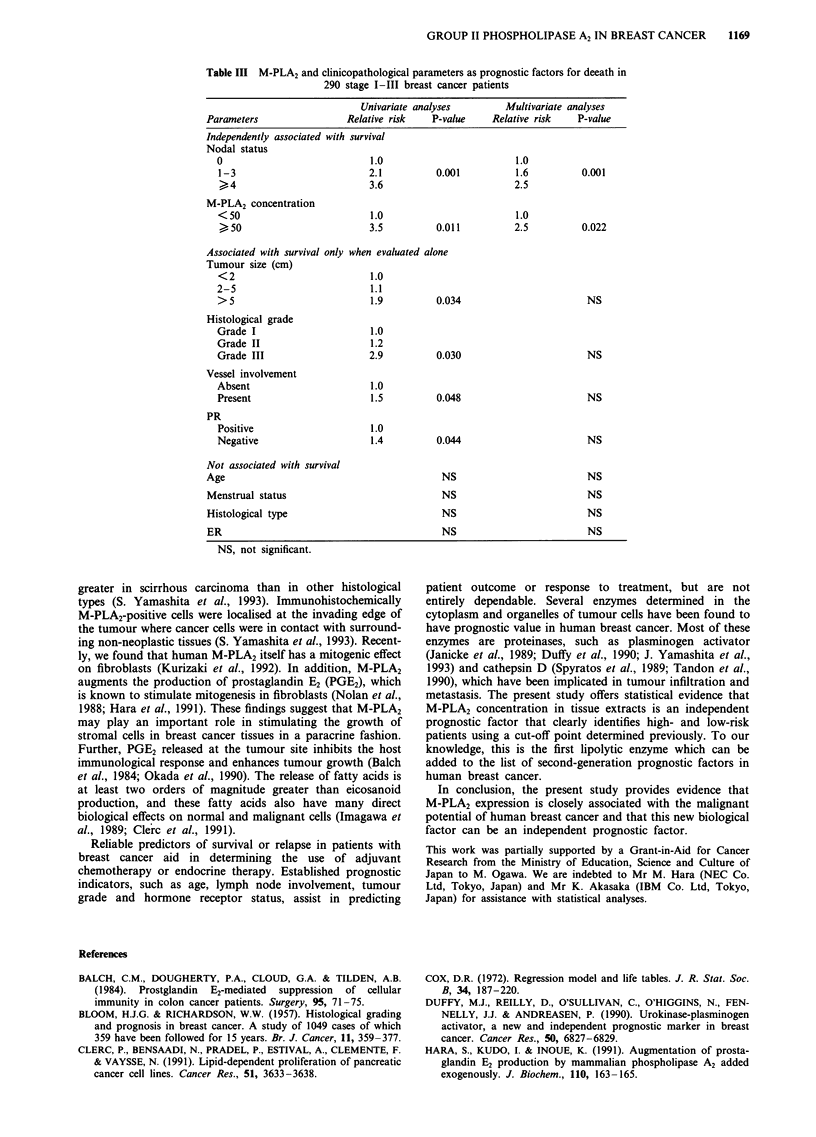
Membrane-associated phospholipase A2 (M-PLA2) is an enzyme that hydrolyses the sn-2 fatty acyl ester bond of phosphoglycerides. We measured M-PLA2 concentration in tissue extracts from 325 human breast cancers using a specific radioimmunoassay recently developed. Correlation analyses between the tissue concentration of M-PLA2 and clinicopathological factors showed that the enzyme level was significantly higher in patients with distant metastasis than in those without. In addition, M-PLA2 concentration was significantly higher in scirrhous carcinoma than in other histological types. No significant association was found between M-PLA2 concentration and age, menstrual status, tumour size, histological grade, vessel involvement or oestrogen receptor (ER) and progesterone receptor (PR) status. The expression of M-PLA2 mRNA was examined in a fibroadenoma, a stage IV breast cancer and its metastatic site of skin. Northern blot analysis showed a clear hybridisation band corresponding to M-PLA2 mRNA in both primary breast cancer and its metastatic site, while the fibroadenoma expressed a faint band corresponding to M-PLA2 mRNA. Breast cancer patients with high M-PLA2 concentrations exhibited significantly shorter disease-free and overall survival than those with low M-PLA2 concentration at the cut-off point of 5 ng 100 mg-1 protein, which was determined in a separate study. In multivariate analysis, M-PLA2 was found to be an independent prognostic factor for disease recurrence and death in human breast cancer. The possible significance of M-PLA2 expression in human breast cancer tissue is discussed.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLOOM H. J., RICHARDSON W. W. Histological grading and prognosis in breast cancer; a study of 1409 cases of which 359 have been followed for 15 years. Br J Cancer. 1957 Sep;11(3):359–377. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1957.43. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Balch C. M., Dougherty P. A., Cloud G. A., Tilden A. B. Prostaglandin E2-mediated suppression of cellular immunity in colon cancer patients. Surgery. 1984 Jan;95(1):71–77. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clerc P., Bensaadi N., Pradel P., Estival A., Clemente F., Vaysse N. Lipid-dependent proliferation of pancreatic cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 1991 Jul 15;51(14):3633–3638. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duffy M. J., Reilly D., O'Sullivan C., O'Higgins N., Fennelly J. J., Andreasen P. Urokinase-plasminogen activator, a new and independent prognostic marker in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 1990 Nov 1;50(21):6827–6829. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUNTER W. M., GREENWOOD F. C. Preparation of iodine-131 labelled human growth hormone of high specific activity. Nature. 1962 May 5;194:495–496. doi: 10.1038/194495a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara S., Kudo I., Inoue K. Augmentation of prostaglandin E2 production by mammalian phospholipase A2 added exogenously. J Biochem. 1991 Aug;110(2):163–165. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a123550. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heinrikson R. L., Krueger E. T., Keim P. S. Amino acid sequence of phospholipase A2-alpha from the venom of Crotalus adamanteus. A new classification of phospholipases A2 based upon structural determinants. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jul 25;252(14):4913–4921. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imagawa W., Bandyopadhyay G. K., Wallace D., Nandi S. Phospholipids containing polyunsaturated fatty acyl groups are mitogenic for normal mouse mammary epithelial cells in serum-free primary cell culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Jun;86(11):4122–4126. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.11.4122. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jänicke F., Schmitt M., Ulm K., Gössner W., Graeff H. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator antigen and early relapse in breast cancer. Lancet. 1989 Oct 28;2(8670):1049–1049. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91070-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kanda A., Ono T., Yoshida N., Tojo H., Okamoto M. The primary structure of a membrane-associated phospholipase A2 from human spleen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1989 Aug 30;163(1):42–48. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(89)92096-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurizaki T., Egami H., Murata K., Kiyohara H., Okazaki S., Yoshida N., Ogawa M. Membrane-associated phospholipase A2 stimulates DNA synthesis in two murine fibroblasts. Res Commun Chem Pathol Pharmacol. 1992 Oct;78(1):39–45. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuda Y., Ogawa M., Sakamoto K., Yamashita S., Kanda A., Kohno M., Yoshida N., Nishijima J., Murata A., Mori T. Development of a radioimmunoassay for human group-II phospholipase A2 and demonstration of postoperative elevation. Enzyme. 1991;45(4):200–208. doi: 10.1159/000468890. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McGuire W. L., De La Garza M., Chamness G. C. Evaluation of estrogen receptor assays in human breast cancer tissue. Cancer Res. 1977 Mar;37(3):637–639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nolan R. D., Danilowicz R. M., Eling T. E. Role of arachidonic acid metabolism in the mitogenic response of BALB/c 3T3 fibroblasts to epidermal growth factor. Mol Pharmacol. 1988 Jun;33(6):650–656. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada F., Hosokawa M., Hasegawa J., Ishikawa M., Chiba I., Nakamura Y., Kobayashi H. Regression mechanisms of mouse fibrosarcoma cells after in vitro exposure to quercetin: diminution of tumorigenicity with a corresponding decrease in the production of prostaglandin E2. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1990;31(6):358–364. doi: 10.1007/BF01741407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seilhamer J. J., Pruzanski W., Vadas P., Plant S., Miller J. A., Kloss J., Johnson L. K. Cloning and recombinant expression of phospholipase A2 present in rheumatoid arthritic synovial fluid. J Biol Chem. 1989 Apr 5;264(10):5335–5338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spyratos F., Maudelonde T., Brouillet J. P., Brunet M., Defrenne A., Andrieu C., Hacene K., Desplaces A., Rouëssé J., Rochefort H. Cathepsin D: an independent prognostic factor for metastasis of breast cancer. Lancet. 1989 Nov 11;2(8672):1115–1118. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(89)91487-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tandon A. K., Clark G. M., Chamness G. C., Chirgwin J. M., McGuire W. L. Cathepsin D and prognosis in breast cancer. N Engl J Med. 1990 Feb 1;322(5):297–302. doi: 10.1056/NEJM199002013220504. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uhl W., Büchler M., Nevalainen T. J., Deller A., Beger H. G. Serum phospholipase A2 in patients with multiple injuries. J Trauma. 1990 Oct;30(10):1285–1290. doi: 10.1097/00005373-199010000-00015. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadas P., Hay J. B. Involvement of circulating phospholipase A2 in the pathogenesis of the hemodynamic changes in endotoxin shock. Can J Physiol Pharmacol. 1983 Jun;61(6):561–566. doi: 10.1139/y83-086. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vadas P., Pruzanski W. Role of secretory phospholipases A2 in the pathobiology of disease. Lab Invest. 1986 Oct;55(4):391–404. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita J., Horiuchi S., Kimura M., Nishimura R., Akagi M. Plasminogen activator as a functional marker for estrogen dependence in human breast cancer cells. Jpn J Cancer Res. 1986 Feb;77(2):177–181. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita J., Ogawa M., Inada K., Yamashita S., Nakashima Y., Saishoji T., Nomura K. Breast cancer prognosis is poor when total plasminogen activator activity is low. Br J Cancer. 1993 Feb;67(2):374–378. doi: 10.1038/bjc.1993.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita S., Yamashita J., Sakamoto K., Inada K., Nakashima Y., Murata K., Saishoji T., Nomura K., Ogawa M. Increased expression of membrane-associated phospholipase A2 shows malignant potential of human breast cancer cells. Cancer. 1993 May 15;71(10):3058–3064. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19930515)71:10<3058::aid-cncr2820711028>3.0.co;2-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Bosch H. Intracellular phospholipases A. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980 Sep 30;604(2):191–246. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(80)90574-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]