Abstract
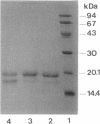
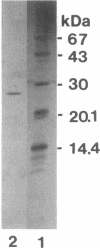
A novel endo-N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase (ENGase), acting on the di-N-acetylchitobiosyl part of N-linked glycans, was characterized in the culture medium of Stigmatella aurantiaca DW4. Purified to homogeneity by ammonium sulfate precipitation, gel filtration, and chromatofocusing, this ENGase presents, upon sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, a molecular mass near 27 kDa. Optimal pH and pI were 4.0 and 6.8, respectively. The enzyme, named ENGase St, exhibits high activity on oligomannoside-type glycoasparagines and glycoproteins and could also hydrolyze hybrid- and complex-type glycoasparagines but does not acts as a murein hydrolase.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Atkinson P. H., Grey A., Carver J. P., Hakimi J., Ceccarini C. Demonstration of heterogeneity of chick ovalbumin glycopeptides using 360-MHz proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy. Biochemistry. 1981 Jul 7;20(14):3979–3986. doi: 10.1021/bi00517a006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgerie S., Berger S., Strecker G., Julien R., Karamanos Y. A fluorescence high-performance liquid chromatography assay for enzymes acting on the di-N-acetylchitobiosyl part of asparagine-linked glycans. J Biochem Biophys Methods. 1994 Jun;28(4):283–293. doi: 10.1016/0165-022x(94)90004-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bourgerie S., Karamanos Y., Berger S., Julien R. Use of resorufin-labelled N-glycopeptide in a high-performance liquid chromatography assay to monitor endoglycosidase activities during cultivation of Flavobacterium meningosepticum. Glycoconj J. 1992 Aug;9(4):162–167. doi: 10.1007/BF00731160. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnosspelius G. Purification and properties of an extracellular protease from Myxococcus virescens. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):17–25. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.17-25.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hartzell P., Kaiser D. Function of MglA, a 22-kilodalton protein essential for gliding in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(23):7615–7624. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.23.7615-7624.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Muramatsu T. Demonstration of an endo-glycosidase acting on a glycoprotein. J Biol Chem. 1971 Sep 10;246(17):5535–5537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Petit F., Guespin-Michel J. F. Production of an extracellular milk-clotting activity during development in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1992 Aug;174(15):5136–5140. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.15.5136-5140.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plamann L., Kuspa A., Kaiser D. Proteins that rescue A-signal-defective mutants of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1992 May;174(10):3311–3318. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.10.3311-3318.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Qualls G. T., Stephens K., White D. Morphogenetic movements and multicellular development in the fruiting Myxobacterium, Stigmatella aurantiaca. Dev Biol. 1978 Sep;66(1):270–274. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90291-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins P. W., Trimble R. B., Wirth D. F., Hering C., Maley F., Maley G. F., Das R., Gibson B. W., Royal N., Biemann K. Primary structure of the Streptomyces enzyme endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase H. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7577–7583. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudd P. M., Scragg I. G., Coghill E., Dwek R. A. Separation and analysis of the glycoform populations of ribonuclease B using capillary electrophoresis. Glycoconj J. 1992 Apr;9(2):86–91. doi: 10.1007/BF00731704. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seko A., Kitajima K., Inoue Y., Inoue S. Peptide:N-glycosidase activity found in the early embryos of Oryzias latipes (Medaka fish). The first demonstration of the occurrence of peptide:N-glycosidase in animal cells and its implication for the presence of a de-N-glycosylation system in living organisms. J Biol Chem. 1991 Nov 25;266(33):22110–22114. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets L. J. Social and developmental biology of the myxobacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Dec;54(4):473–501. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.4.473-501.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sudo S., Dworkin M. Bacteriolytic enzymes produced by Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1972 Apr;110(1):236–245. doi: 10.1128/jb.110.1.236-245.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tai T., Yamashita K., Kobata A. The substrate specificities of endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidases CII and H. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Sep 9;78(1):434–441. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91273-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takegawa K., Mikami B., Iwahara S., Morita Y., Yamamoto K., Tochikura T. Complete amino acid sequence of endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase from Flavobacterium sp. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Nov 15;202(1):175–180. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16359.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarentino A. L., Trimble R. B., Plummer T. H., Jr Enzymatic approaches for studying the structure, synthesis, and processing of glycoproteins. Methods Cell Biol. 1989;32:111–139. doi: 10.1016/s0091-679x(08)61169-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tretter V., Altmann F., März L. Peptide-N4-(N-acetyl-beta-glucosaminyl)asparagine amidase F cannot release glycans with fucose attached alpha 1----3 to the asparagine-linked N-acetylglucosamine residue. Eur J Biochem. 1991 Aug 1;199(3):647–652. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1991.tb16166.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamashita K., Tachibana Y., Kobata A. The structures of the galactose-containing sugar chains of ovalbumin. J Biol Chem. 1978 Jun 10;253(11):3862–3869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]