Abstract
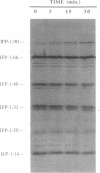
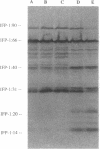
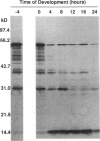
The extracellular matrix fibrils of Myxococcus xanthus are mediators of cell-cell cohesion and as such are required for the maintenance of the social lifestyle characteristic of these prokaryotes. The fibrils have also been implicated as factors involved in contact-mediated cell interactions and in signal exchange. The fibrils are extracellular carbohydrate structures with associated proteins. All of the major proteins associated with the fibrils react with monoclonal antibody 2105 and can be removed from the fibrils only by boiling with sodium dodecyl sulfate (SDS) and beta-mercaptoethanol. For consistency with their integral association with the fibrils, we have designated this class of proteins as integral fibrillar proteins class 1 (IFP-1). IFP-1 comprises five major proteins whose molecular sizes range from 66 to 14 kDa. All of the proteins in IFP-1 have been purified from isolated fibrils by electroelution after size separation on SDS-PAGE gels. Analysis of the purified proteins suggested that the forms with different molecular sizes result from the aggregation of a single small-molecular-size subunit. Fingerprint analysis and amino acid composition profiles confirmed the identity among the different members of IFP-1. The sequence of the 31 amino-terminal amino acids of the 31-kDa form of IFP-1 (IFP-1:31) was determined. There was no significant homology to other known protein sequences. During development there is a dramatic shift in the banding pattern of IFP-1 proteins without any apparent overall loss of total protein.
Full text
PDF


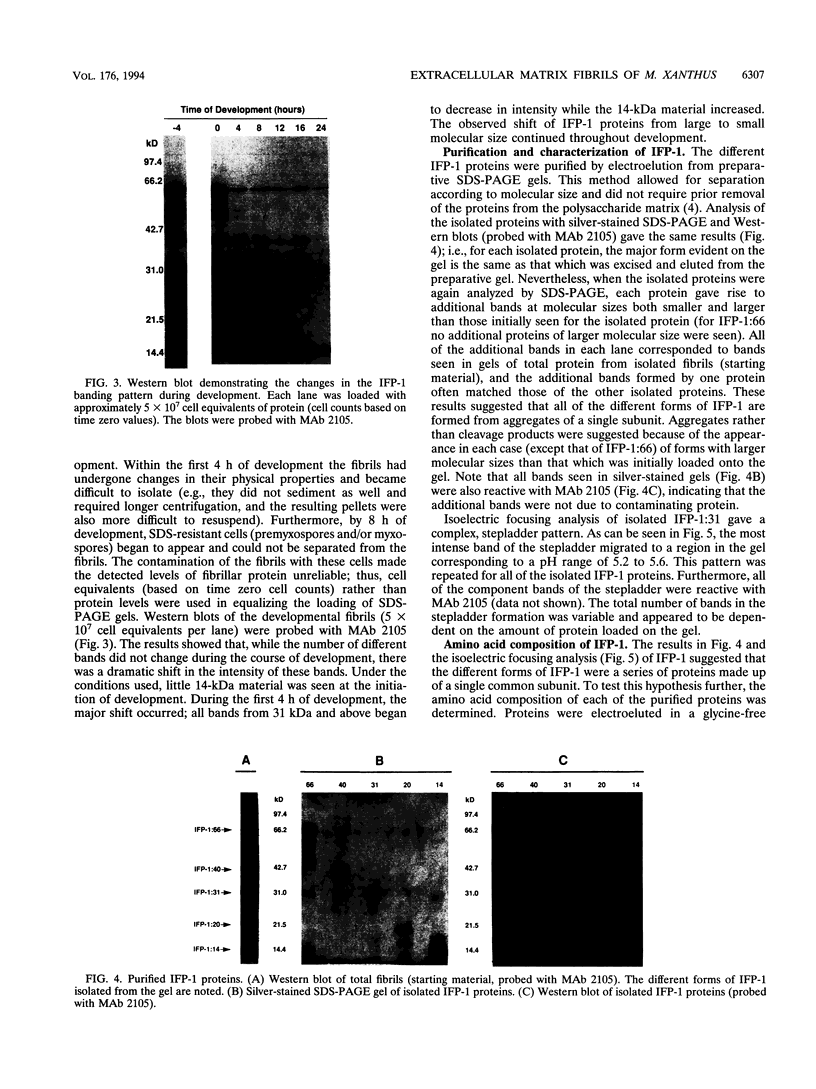
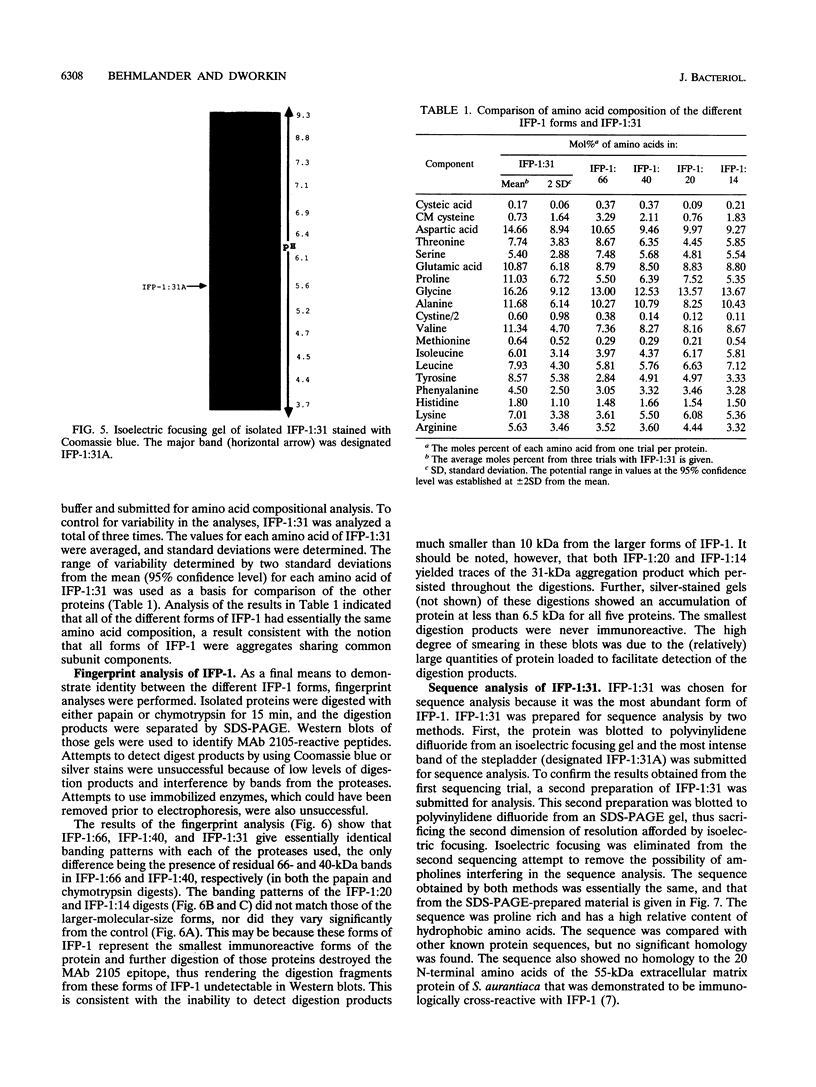
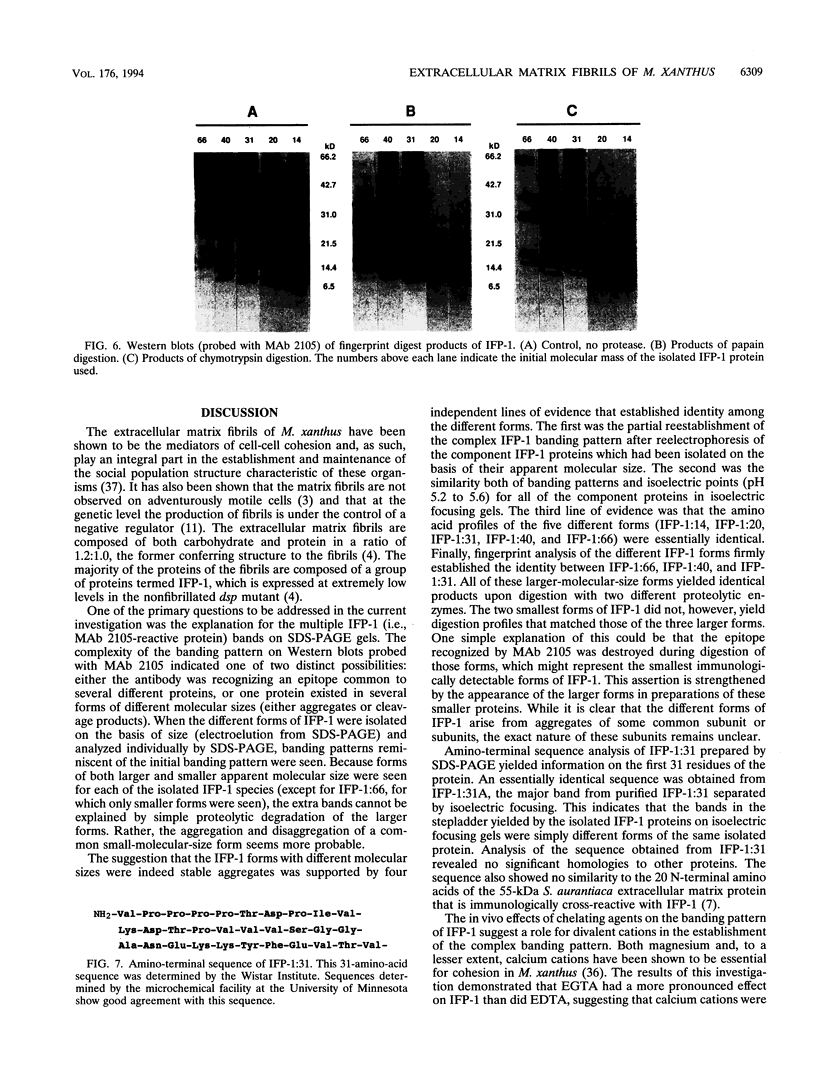


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames G. F., Nikaido K. Two-dimensional gel electrophoresis of membrane proteins. Biochemistry. 1976 Feb 10;15(3):616–623. doi: 10.1021/bi00648a026. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold J. W., Shimkets L. J. Cell surface properties correlated with cohesion in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5771–5777. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5771-5777.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arnold J. W., Shimkets L. J. Inhibition of cell-cell interactions in Myxococcus xanthus by congo red. J Bacteriol. 1988 Dec;170(12):5765–5770. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.12.5765-5770.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Behmlander R. M., Dworkin M. Extracellular fibrils and contact-mediated cell interactions in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(24):7810–7820. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.24.7810-7820.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bretscher A. P., Kaiser D. Nutrition of Myxococcus xanthus, a fruiting myxobacterium. J Bacteriol. 1978 Feb;133(2):763–768. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.2.763-768.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chang B. Y., White D. Cell surface modifications induced by calcium ion in the myxobacterium Stigmatella aurantiaca. J Bacteriol. 1992 Sep;174(18):5780–5787. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.18.5780-5787.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clemans D. L., Chance C. M., Dworkin M. A development-specific protein in Myxococcus xanthus is associated with the extracellular fibrils. J Bacteriol. 1991 Nov;173(21):6749–6759. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.21.6749-6759.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Fischer S. G., Kirschner M. W., Laemmli U. K. Peptide mapping by limited proteolysis in sodium dodecyl sulfate and analysis by gel electrophoresis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):1102–1106. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dana J. R., Shimkets L. J. Regulation of cohesion-dependent cell interactions in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jun;175(11):3636–3647. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.11.3636-3647.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dworkin M., Kaiser D. Cell interactions in myxobacterial growth and development. Science. 1985 Oct 4;230(4721):18–24. doi: 10.1126/science.3929384. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FLUEGEL W. SIMPLE METHOD FOR DEMONSTRATING MYXOBACTERIAL SLIME. J Bacteriol. 1963 May;85:1173–1174. doi: 10.1128/jb.85.5.1173-1174.1963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gill J., Stellwag E., Dworkin M. Monoclonal antibodies against cell-surface antigens of developing cells of Myxococcus xanthus. Ann Inst Pasteur Microbiol. 1985 Jan-Feb;136A(1):11–18. doi: 10.1016/s0769-2609(85)80015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gnosspelius G. Myxobacterial slime and proteolytic activity. Arch Microbiol. 1978 Jan 23;116(1):51–59. doi: 10.1007/BF00408733. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaiser D. Social gliding is correlated with the presence of pili in Myxococcus xanthus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Nov;76(11):5952–5956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.11.5952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kuner J. M., Kaiser D. Fruiting body morphogenesis in submerged cultures of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jul;151(1):458–461. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.1.458-461.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li S. F., Shimkets L. J. Effect of dsp mutations on the cell-to-cell transmission of CsgA in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1993 Jun;175(11):3648–3652. doi: 10.1128/jb.175.11.3648-3652.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacRae T. H., McCurdy D. Evidence for motility-related fimbriae in the gliding microorganism Myxococcus xanthus. Can J Microbiol. 1976 Oct;22(10):1589–1593. doi: 10.1139/m76-234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maeba P. Y. Iodination of Myxococcus xanthus during development. J Bacteriol. 1983 Sep;155(3):1033–1041. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.3.1033-1041.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McIntire F. C., Vatter A. E., Baros J., Arnold J. Mechanism of coaggregation between Actinomyces viscosus T14V and Streptococcus sanguis 34. Infect Immun. 1978 Sep;21(3):978–988. doi: 10.1128/iai.21.3.978-988.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orndorff P. E., Dworkin M. Synthesis of several membrane proteins during developmental aggregation in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jan;149(1):29–39. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.1.29-39.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palva E. T., Hirst T. R., Hardy S. J., Holmgren J., Randall L. Synthesis of a precursor to the B subunit of heat-labile enterotoxin in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1981 Apr;146(1):325–330. doi: 10.1128/jb.146.1.325-330.1981. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenberg E., Keller K. H., Dworkin M. Cell density-dependent growth of Myxococcus xanthus on casein. J Bacteriol. 1977 Feb;129(2):770–777. doi: 10.1128/jb.129.2.770-777.1977. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosenbluh A., Eisenbach M. Effect of mechanical removal of pili on gliding motility of Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1992 Aug;174(16):5406–5413. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.16.5406-5413.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets L. J. Correlation of energy-dependent cell cohesion with social motility in Myxococcus xanthus. J Bacteriol. 1986 Jun;166(3):837–841. doi: 10.1128/jb.166.3.837-841.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets L. J., Rafiee H. CsgA, an extracellular protein essential for Myxococcus xanthus development. J Bacteriol. 1990 Sep;172(9):5299–5306. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.9.5299-5306.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimkets L. J. Social and developmental biology of the myxobacteria. Microbiol Rev. 1990 Dec;54(4):473–501. doi: 10.1128/mr.54.4.473-501.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Silver R. P., Aaronson W., Vann W. F. Translocation of capsular polysaccharides in pathogenic strains of Escherichia coli requires a 60-kilodalton periplasmic protein. J Bacteriol. 1987 Dec;169(12):5489–5495. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.12.5489-5495.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]