Abstract
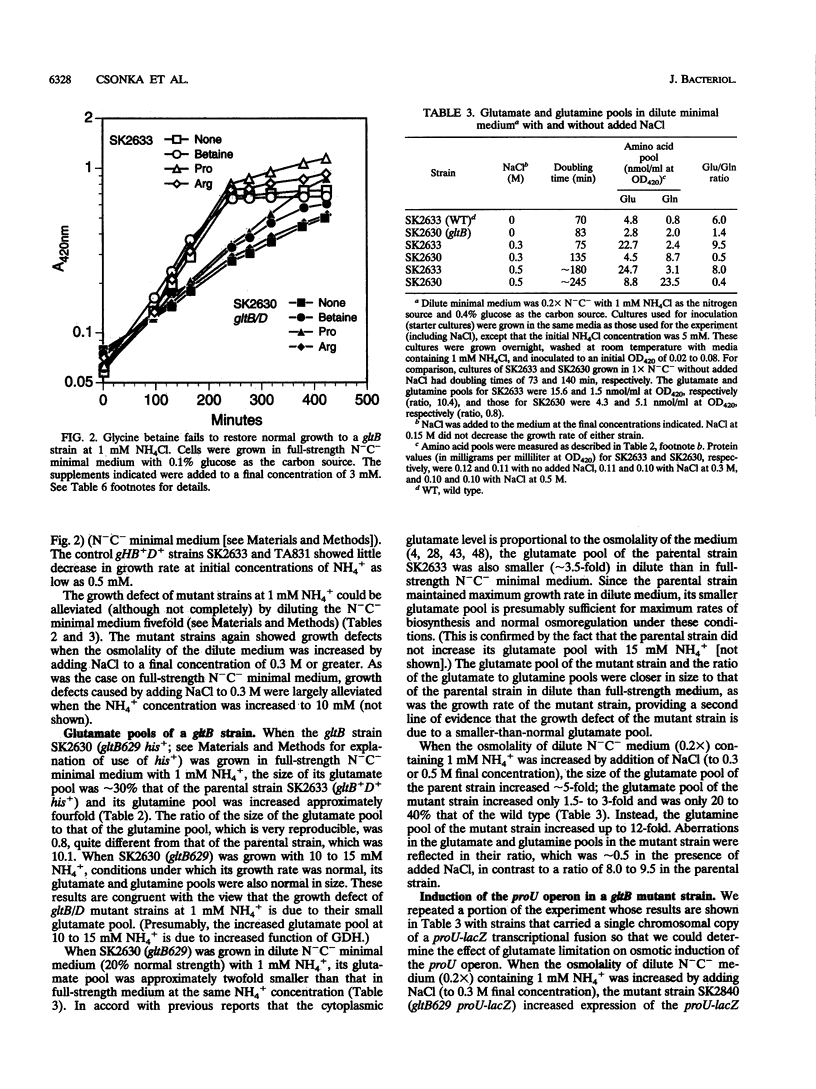
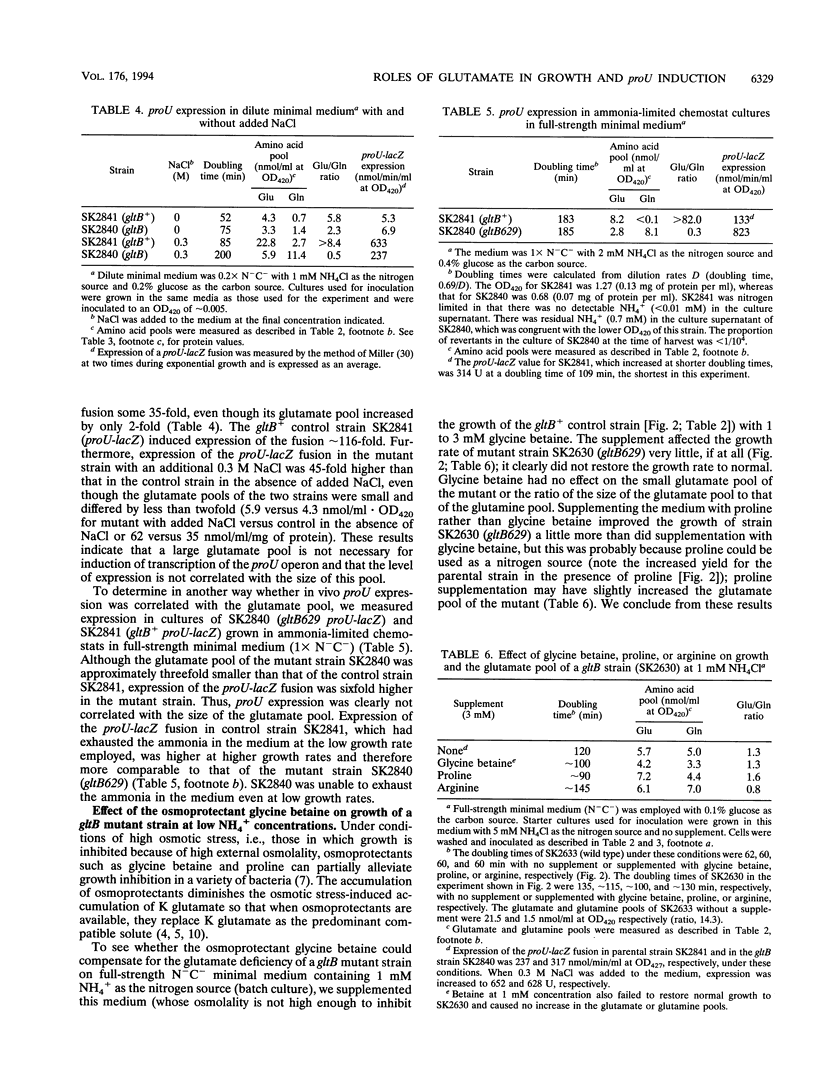
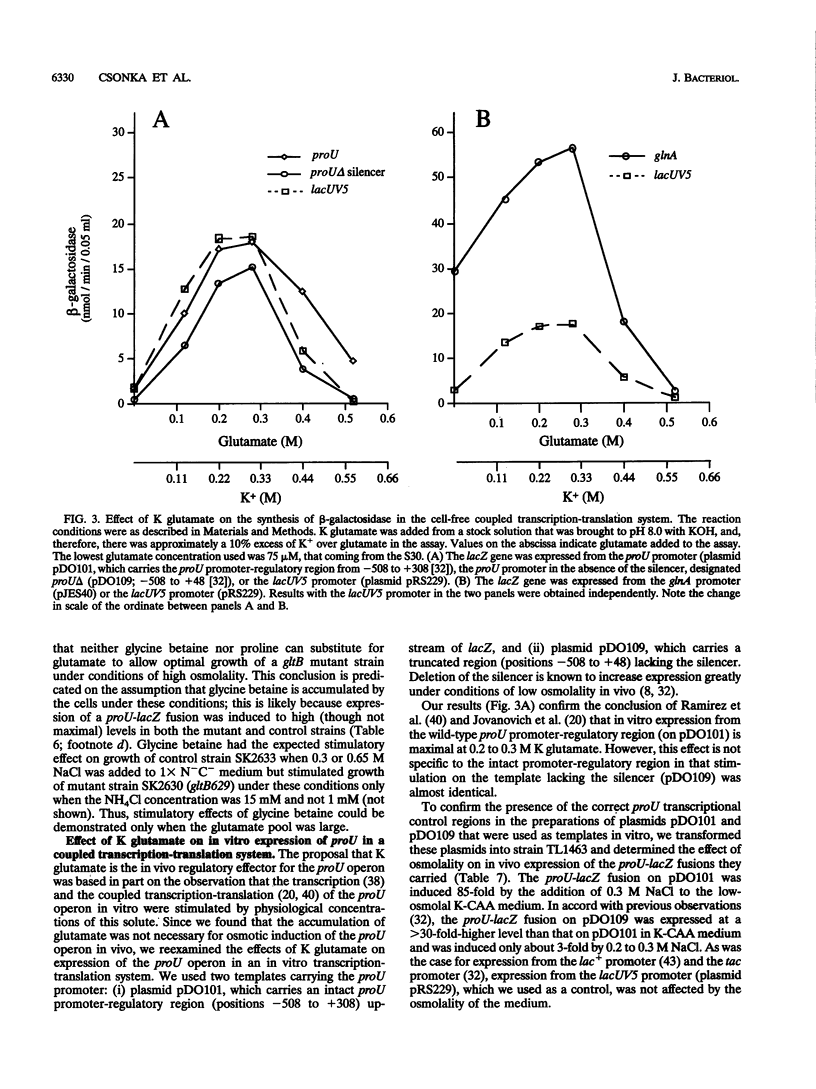
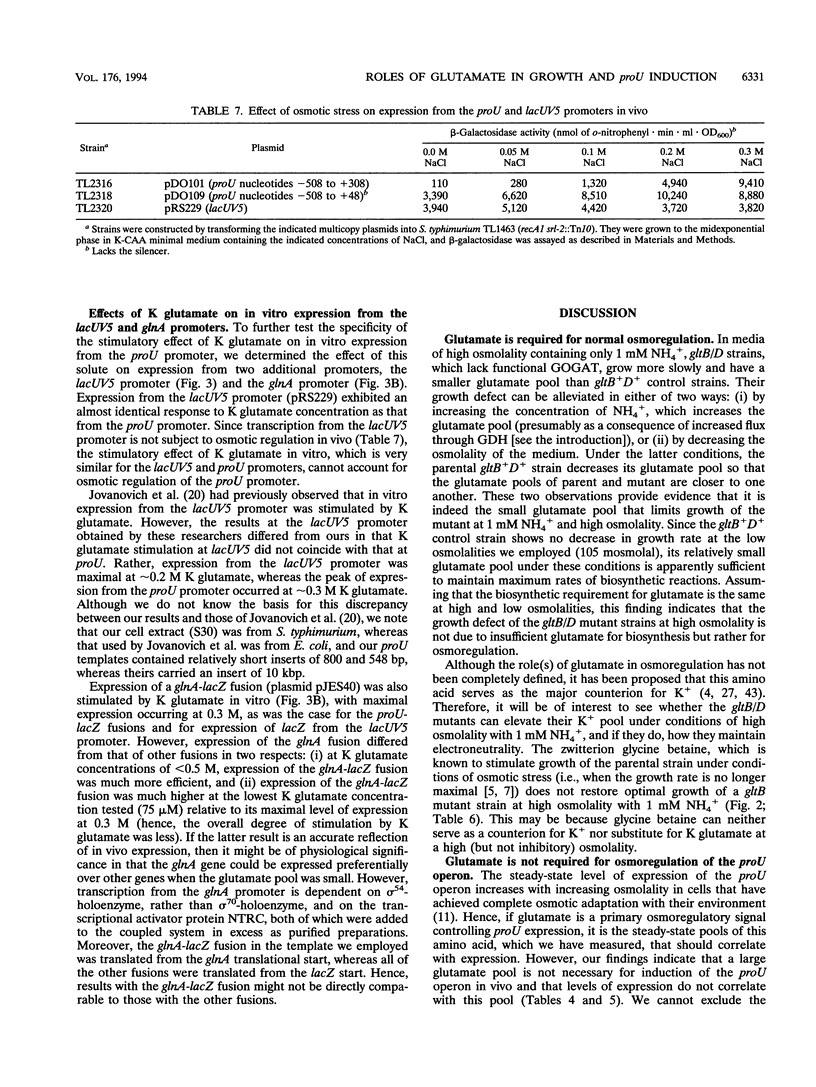
Synthesis of glutamate can be limited in bacterial strains carrying mutations to loss of function of glutamate synthase (2-oxoglutarate:glutamine aminotransferase) by using low concentrations of NH4+ in the growth medium. By using such gltB/D mutant strains of Salmonella typhimurium, we demonstrated that: (i) a large glutamate pool, previously observed to correlate with growth at high external osmolality, is actually required for optimal growth under these conditions; (ii) the osmoprotectant glycine betaine (N,N,N-trimethylglycine) apparently cannot substitute for glutamate; and (iii) accumulation of glutamate is not necessary for high levels of induction of the proU operon in vivo. Expression of the proU operon, which encodes a transport system for the osmoprotectants proline and glycine betaine, is induced > 100-fold in the wild-type strain under conditions of high external osmolality. Ramirez et al. (R. M. Ramirez, W. S. Prince, E. Bremer, and M. Villarejo, Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 86:1153-1157, 1989) observed and we confirmed that in vitro expression of the lacZ gene from the wild-type proU promoter is stimulated by 0.2 to 0.3 M K glutamate. However, we observed a very similar stimulation for lacZ expressed from the lacUV5 promoter and from the proU promoter when an important negative regulatory element downstream of this promoter (the silencer) was deleted. Since the lacUV5 promoter is not osmotically regulated in vivo and osmotic regulation of the proU promoter is largely lost as a result of deletion of the silencer, we conclude that stimulation of proU expression by K glutamate in vitro is not a specific osmoregulatory response but probably a manifestation of the optimization of in vitro transcription-translation at high concentrations of this solute. Our in vitro and in vivo results demonstrate that glutamate is not an obligatory component of the transcriptional regulation of the proU operon.
Full text
PDF





Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames B. N., Whitfield H. J., Jr Frameshift mutagenesis in Salmonella. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1966;31:221–225. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1966.031.01.030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brenchley J. E., Prival M. J., Magasanik B. Regulation of the synthesis of enzymes responsible for glutamate formation in Klebsiella aerogenes. J Biol Chem. 1973 Sep 10;248(17):6122–6128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown A. D., Simpson J. R. Water relations of sugar-tolerant yeasts: the role of intracellular polyols. J Gen Microbiol. 1972 Oct;72(3):589–591. doi: 10.1099/00221287-72-3-589. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cayley S., Lewis B. A., Guttman H. J., Record M. T., Jr Characterization of the cytoplasm of Escherichia coli K-12 as a function of external osmolarity. Implications for protein-DNA interactions in vivo. J Mol Biol. 1991 Nov 20;222(2):281–300. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(91)90212-o. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cayley S., Lewis B. A., Record M. T., Jr Origins of the osmoprotective properties of betaine and proline in Escherichia coli K-12. J Bacteriol. 1992 Mar;174(5):1586–1595. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.5.1586-1595.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Csonka L. N., Hanson A. D. Prokaryotic osmoregulation: genetics and physiology. Annu Rev Microbiol. 1991;45:569–606. doi: 10.1146/annurev.mi.45.100191.003033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dattananda C. S., Rajkumari K., Gowrishankar J. Multiple mechanisms contribute to osmotic inducibility of proU operon expression in Escherichia coli: demonstration of two osmoresponsive promoters and of a negative regulatory element within the first structural gene. J Bacteriol. 1991 Dec;173(23):7481–7490. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.23.7481-7490.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinnbier U., Limpinsel E., Schmid R., Bakker E. P. Transient accumulation of potassium glutamate and its replacement by trehalose during adaptation of growing cells of Escherichia coli K-12 to elevated sodium chloride concentrations. Arch Microbiol. 1988;150(4):348–357. doi: 10.1007/BF00408306. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunlap V. J., Csonka L. N. Osmotic regulation of L-proline transport in Salmonella typhimurium. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jul;163(1):296–304. doi: 10.1128/jb.163.1.296-304.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ENNIS H. L., LUBIN M. Dissociation of ribonucleic acid and protein synthesis in bacteria deprived of potassium. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1961 Jun 24;50:399–402. doi: 10.1016/0006-3002(61)90355-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fuchs R. L., Madonna M. J., Brenchley J. E. Identification of the structural genes for glutamate synthase and genetic characterization of this region of the Salmonella typhimurium chromosome. J Bacteriol. 1982 Mar;149(3):906–915. doi: 10.1128/jb.149.3.906-915.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giaever H. M., Styrvold O. B., Kaasen I., Strøm A. R. Biochemical and genetic characterization of osmoregulatory trehalose synthesis in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2841–2849. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2841-2849.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Griep M. A., McHenry C. S. Glutamate overcomes the salt inhibition of DNA polymerase III holoenzyme. J Biol Chem. 1989 Jul 5;264(19):11294–11301. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gutnick D., Calvo J. M., Klopotowski T., Ames B. N. Compounds which serve as the sole source of carbon or nitrogen for Salmonella typhimurium LT-2. J Bacteriol. 1969 Oct;100(1):215–219. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.1.215-219.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F., Dorman C. J., Stirling D. A., Waddell L., Booth I. R., May G., Bremer E. A physiological role for DNA supercoiling in the osmotic regulation of gene expression in S. typhimurium and E. coli. Cell. 1988 Feb 26;52(4):569–584. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90470-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hulton C. S., Seirafi A., Hinton J. C., Sidebotham J. M., Waddell L., Pavitt G. D., Owen-Hughes T., Spassky A., Buc H., Higgins C. F. Histone-like protein H1 (H-NS), DNA supercoiling, and gene expression in bacteria. Cell. 1990 Nov 2;63(3):631–642. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90458-q. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jovanovich S. B., Record M. T., Jr, Burgess R. R. In an Escherichia coli coupled transcription-translation system, expression of the osmoregulated gene proU is stimulated at elevated potassium concentrations and by an extract from cells grown at high osmolality. J Biol Chem. 1989 May 15;264(14):7821–7825. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kennedy E. P. Osmotic regulation and the biosynthesis of membrane-derived oligosaccharides in Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Feb;79(4):1092–1095. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.4.1092. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kustu S., Hirschman J., Burton D., Jelesko J., Meeks J. C. Covalent modification of bacterial glutamine synthetase: physiological significance. Mol Gen Genet. 1984;197(2):309–317. doi: 10.1007/BF00330979. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Madonna M. J., Fuchs R. L., Brenchley J. E. Fine structure analysis of Salmonella typhimurium glutamate synthase genes. J Bacteriol. 1985 Jan;161(1):353–360. doi: 10.1128/jb.161.1.353-360.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- May G., Dersch P., Haardt M., Middendorf A., Bremer E. The osmZ (bglY) gene encodes the DNA-binding protein H-NS (H1a), a component of the Escherichia coli K12 nucleoid. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Oct;224(1):81–90. doi: 10.1007/BF00259454. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaggan D., Naprstek J., Buurman E. T., Epstein W. Interdependence of K+ and glutamate accumulation during osmotic adaptation of Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1994 Jan 21;269(3):1911–1917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Measures J. C. Role of amino acids in osmoregulation of non-halophilic bacteria. Nature. 1975 Oct 2;257(5525):398–400. doi: 10.1038/257398a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neeley W. E., Phillipson J. Automated enzymatic method for determining ammonia in plasma, with 14-day reagent stability. Clin Chem. 1988 Sep;34(9):1868–1869. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overdier D. G., Csonka L. N. A transcriptional silencer downstream of the promoter in the osmotically controlled proU operon of Salmonella typhimurium. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Apr 1;89(7):3140–3144. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.7.3140. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Owen-Hughes T. A., Pavitt G. D., Santos D. S., Sidebotham J. M., Hulton C. S., Hinton J. C., Higgins C. F. The chromatin-associated protein H-NS interacts with curved DNA to influence DNA topology and gene expression. Cell. 1992 Oct 16;71(2):255–265. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90354-f. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pahel G., Zelenetz A. D., Tyler B. M. gltB gene and regulation of nitrogen metabolism by glutamine synthetase in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1978 Jan;133(1):139–148. doi: 10.1128/jb.133.1.139-148.1978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pestka S. Peptidyl-puromycin synthesis on polyribosomes from Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):624–628. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson G. L. A simplification of the protein assay method of Lowry et al. which is more generally applicable. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):346–356. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90043-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfau J., Youderian P. Transferring plasmid DNA between different bacterial species with electroporation. Nucleic Acids Res. 1990 Oct 25;18(20):6165–6165. doi: 10.1093/nar/18.20.6165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prince W. S., Villarejo M. R. Osmotic control of proU transcription is mediated through direct action of potassium glutamate on the transcription complex. J Biol Chem. 1990 Oct 15;265(29):17673–17679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez R. M., Prince W. S., Bremer E., Villarejo M. In vitro reconstitution of osmoregulated expression of proU of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1153–1157. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1153. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramirez R. M., Villarejo M. Osmotic signal transduction to proU is independent of DNA supercoiling in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jan;173(2):879–885. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.2.879-885.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reiners J. J., Jr, Messenger L. J., Zalkin H. Immunological cross-reactivity of Escherichia coli anthranilate synthetase, glutamate synthase, and other proteins. J Biol Chem. 1978 Feb 25;253(4):1226–1233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Richey B., Cayley D. S., Mossing M. C., Kolka C., Anderson C. F., Farrar T. C., Record M. T., Jr Variability of the intracellular ionic environment of Escherichia coli. Differences between in vitro and in vivo effects of ion concentrations on protein-DNA interactions and gene expression. J Biol Chem. 1987 May 25;262(15):7157–7164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santero E., Hoover T., Keener J., Kustu S. In vitro activity of the nitrogen fixation regulatory protein NIFA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Oct;86(19):7346–7350. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.19.7346. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons R. W., Hoopes B. C., McClure W. R., Kleckner N. Three promoters near the termini of IS10: pIN, pOUT, and pIII. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):673–682. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90400-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Simons R. W., Houman F., Kleckner N. Improved single and multicopy lac-based cloning vectors for protein and operon fusions. Gene. 1987;53(1):85–96. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(87)90095-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tempest D. W., Meers J. L., Brown C. M. Influence of environment on the content and composition of microbial free amino acid pools. J Gen Microbiol. 1970 Dec;64(2):171–185. doi: 10.1099/00221287-64-2-171. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ueguchi C., Mizuno T. The Escherichia coli nucleoid protein H-NS functions directly as a transcriptional repressor. EMBO J. 1993 Mar;12(3):1039–1046. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1993.tb05745.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Anken H. C., Schiphorst M. E. A kinetic determination of ammonia in plasma. Clin Chim Acta. 1974 Oct 30;56(2):151–157. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(74)90223-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



