Abstract
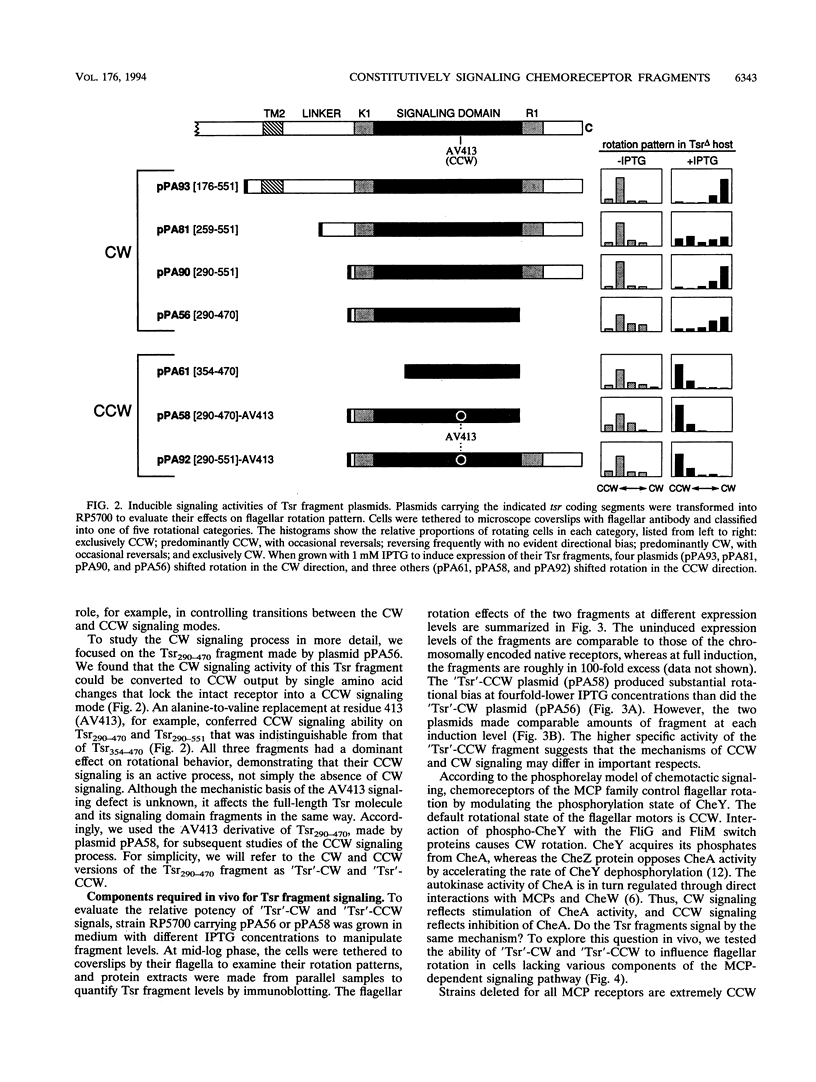
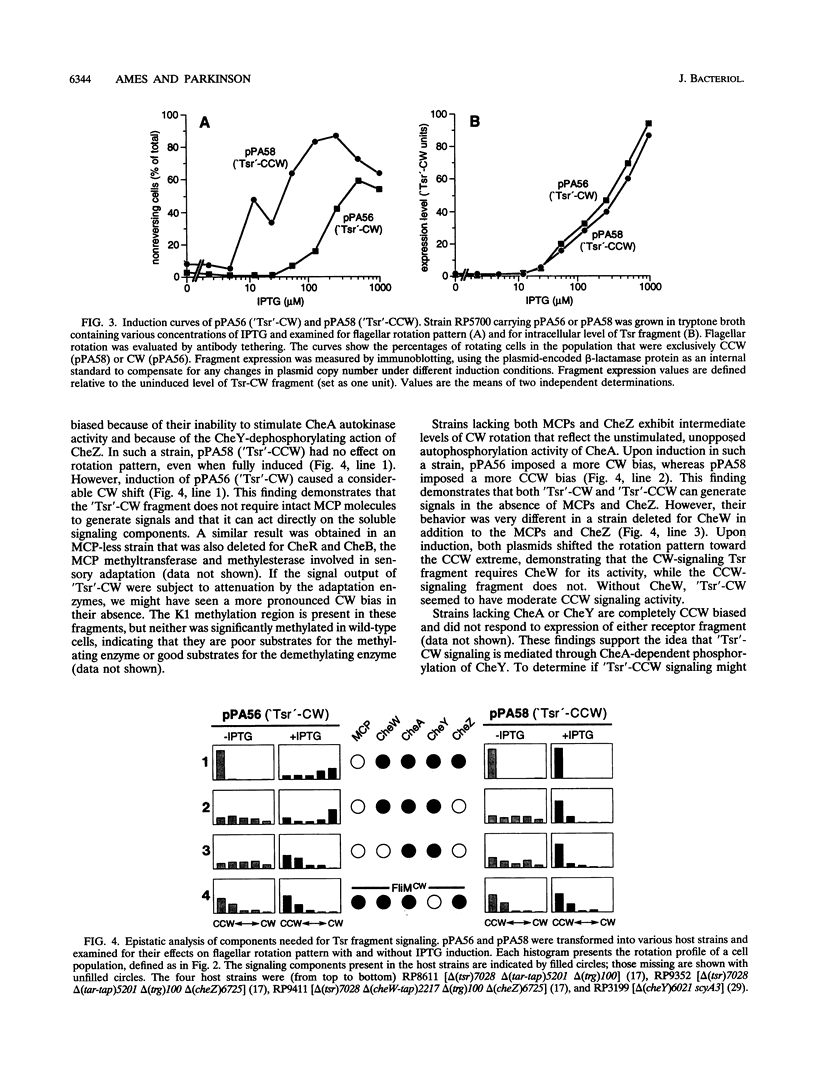
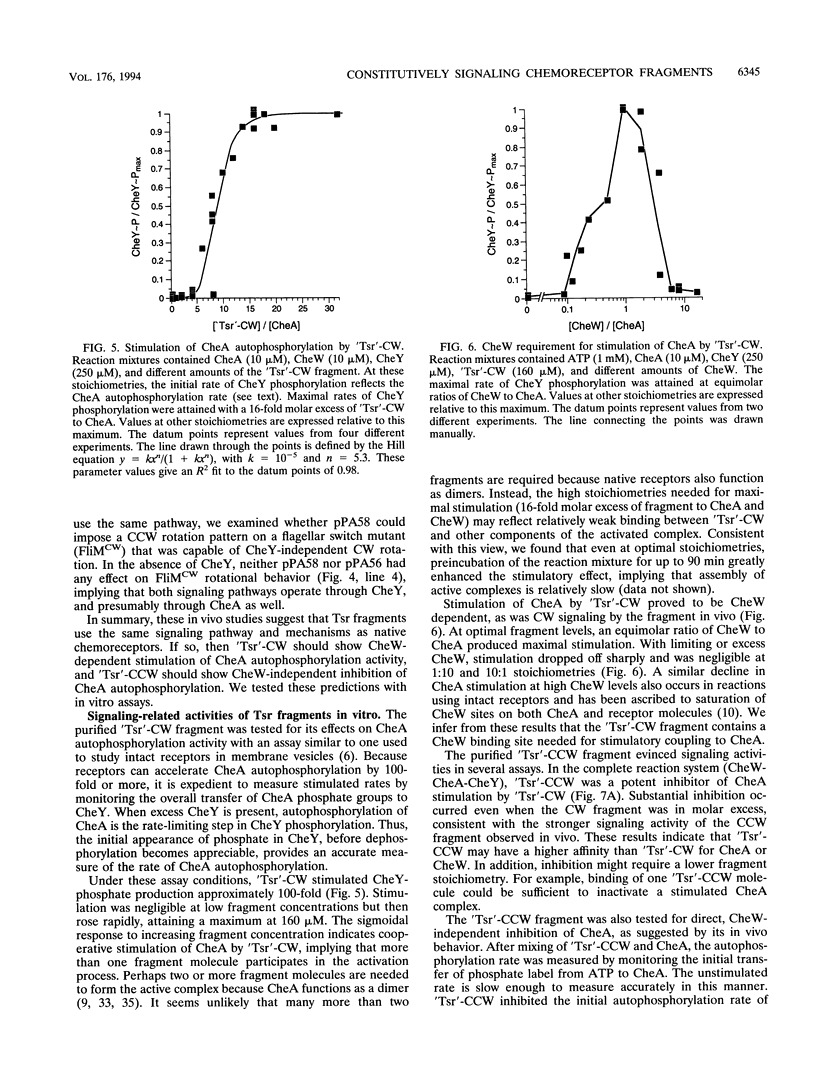
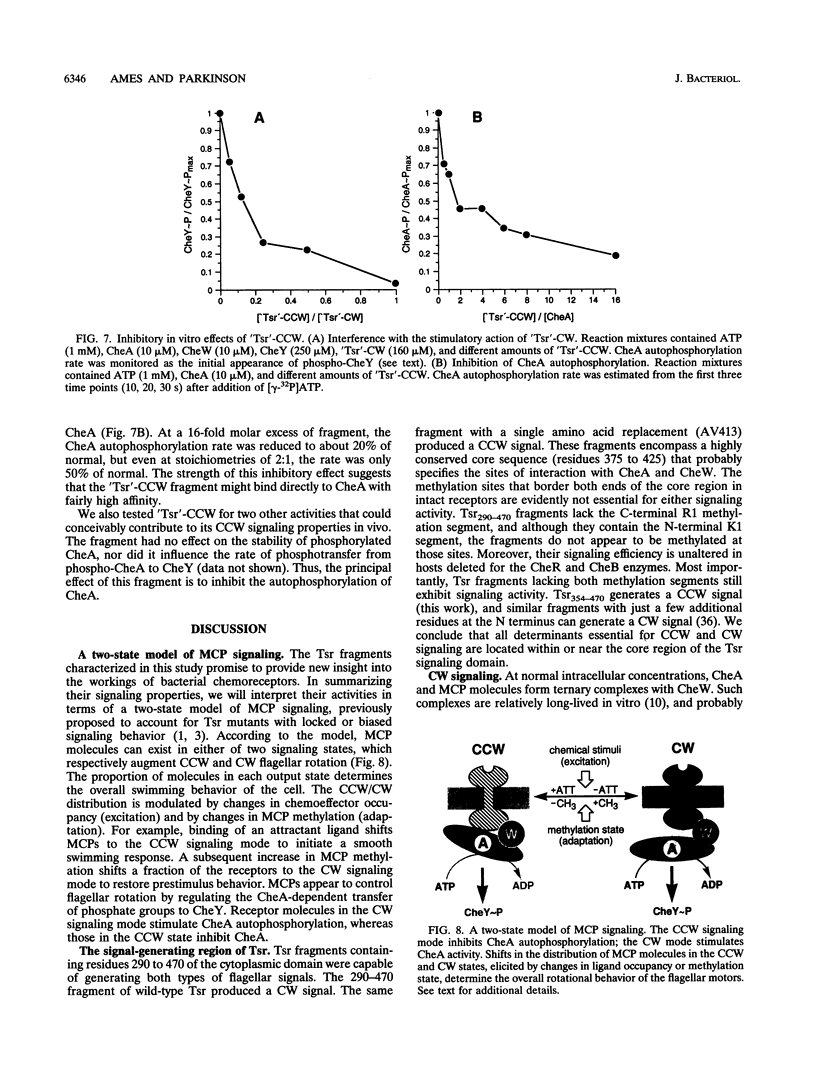
Tsr, the serine chemoreceptor of Escherichia coli, has two signaling modes. One augments clockwise (CW) flagellar rotation, and the other augments counterclockwise (CCW) rotation. To identify the portion of the Tsr molecule responsible for these activities, we isolated soluble fragments of the Tsr cytoplasmic domain that could alter the flagellar rotation patterns of unstimulated wild-type cells. Residues 290 to 470 from wild-type Tsr generated a CW signal, whereas the same fragment with a single amino acid replacement (alanine 413 to valine) produced a CCW signal. The soluble components of the chemotaxis phosphorelay system needed for expression of these Tsr fragment signals were identified by epistasis analysis. Like full-length receptors, the fragments appeared to generate signals through interactions with the CheA autokinase and the CheW coupling factor. CheA was required for both signaling activities, whereas CheW was needed only for CW signaling. Purified Tsr fragments were also examined for effects on CheA autophosphorylation activity in vitro. Consistent with the in vivo findings, the CW fragment stimulated CheA, whereas the CCW fragment inhibited CheA. CheW was required for stimulation but not for inhibition. These findings demonstrate that a 180-residue segment of the Tsr cytoplasmic domain can produce two active signals. The CCW signal involves a direct contact between the receptor and the CheA kinase, whereas the CW signal requires participation of CheW as well. The correlation between the in vitro effects of Tsr signaling fragments on CheA activity and their in vivo behavioral effects lends convincing support to the phosphorelay model of chemotactic signaling.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ames P., Chen J., Wolff C., Parkinson J. S. Structure-function studies of bacterial chemosensors. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1988;53(Pt 1):59–65. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1988.053.01.010. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ames P., Parkinson J. S. Transmembrane signaling by bacterial chemoreceptors: E. coli transducers with locked signal output. Cell. 1988 Dec 2;55(5):817–826. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90137-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barak R., Eisenbach M. Correlation between phosphorylation of the chemotaxis protein CheY and its activity at the flagellar motor. Biochemistry. 1992 Feb 18;31(6):1821–1826. doi: 10.1021/bi00121a034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borkovich K. A., Kaplan N., Hess J. F., Simon M. I. Transmembrane signal transduction in bacterial chemotaxis involves ligand-dependent activation of phosphate group transfer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Feb;86(4):1208–1212. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.4.1208. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borkovich K. A., Simon M. I. The dynamics of protein phosphorylation in bacterial chemotaxis. Cell. 1990 Dec 21;63(6):1339–1348. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(90)90429-i. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Callahan A. M., Frazier B. L., Parkinson J. S. Chemotaxis in Escherichia coli: construction and properties of lambda tsr transducing phage. J Bacteriol. 1987 Mar;169(3):1246–1253. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.3.1246-1253.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engström P., Hazelbauer G. L. Multiple methylation of methyl-accepting chemotaxis proteins during adaptation of E. coli to chemical stimuli. Cell. 1980 May;20(1):165–171. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90244-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gegner J. A., Dahlquist F. W. Signal transduction in bacteria: CheW forms a reversible complex with the protein kinase CheA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Feb 1;88(3):750–754. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.3.750. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gegner J. A., Graham D. R., Roth A. F., Dahlquist F. W. Assembly of an MCP receptor, CheW, and kinase CheA complex in the bacterial chemotaxis signal transduction pathway. Cell. 1992 Sep 18;70(6):975–982. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90247-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess J. F., Oosawa K., Kaplan N., Simon M. I. Phosphorylation of three proteins in the signaling pathway of bacterial chemotaxis. Cell. 1988 Apr 8;53(1):79–87. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90489-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hess J. F., Oosawa K., Matsumura P., Simon M. I. Protein phosphorylation is involved in bacterial chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1987 Nov;84(21):7609–7613. doi: 10.1073/pnas.84.21.7609. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krikos A., Conley M. P., Boyd A., Berg H. C., Simon M. I. Chimeric chemosensory transducers of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Mar;82(5):1326–1330. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.5.1326. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J. D., Parkinson J. S. Genetic evidence for interaction between the CheW and Tsr proteins during chemoreceptor signaling by Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1991 Aug;173(16):4941–4951. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.16.4941-4951.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu J. D., Parkinson J. S. Role of CheW protein in coupling membrane receptors to the intracellular signaling system of bacterial chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Nov;86(22):8703–8707. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.22.8703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lupas A., Stock J. Phosphorylation of an N-terminal regulatory domain activates the CheB methylesterase in bacterial chemotaxis. J Biol Chem. 1989 Oct 15;264(29):17337–17342. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maddock J. R., Shapiro L. Polar location of the chemoreceptor complex in the Escherichia coli cell. Science. 1993 Mar 19;259(5102):1717–1723. doi: 10.1126/science.8456299. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manoil C., Beckwith J. A genetic approach to analyzing membrane protein topology. Science. 1986 Sep 26;233(4771):1403–1408. doi: 10.1126/science.3529391. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsumura P., Rydel J. J., Linzmeier R., Vacante D. Overexpression and sequence of the Escherichia coli cheY gene and biochemical activities of the CheY protein. J Bacteriol. 1984 Oct;160(1):36–41. doi: 10.1128/jb.160.1.36-41.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morrison T. B., Parkinson J. S. Liberation of an interaction domain from the phosphotransfer region of CheA, a signaling kinase of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1994 Jun 7;91(12):5485–5489. doi: 10.1073/pnas.91.12.5485. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mutoh N., Oosawa K., Simon M. I. Characterization of Escherichia coli chemotaxis receptor mutants with null phenotypes. J Bacteriol. 1986 Sep;167(3):992–998. doi: 10.1128/jb.167.3.992-998.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ninfa E. G., Stock A., Mowbray S., Stock J. Reconstitution of the bacterial chemotaxis signal transduction system from purified components. J Biol Chem. 1991 May 25;266(15):9764–9770. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oosawa K., Mutoh N., Simon M. I. Cloning of the C-terminal cytoplasmic fragment of the tar protein and effects of the fragment on chemotaxis of Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2521–2526. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2521-2526.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S., Houts S. E. Isolation and behavior of Escherichia coli deletion mutants lacking chemotaxis functions. J Bacteriol. 1982 Jul;151(1):106–113. doi: 10.1128/jb.151.1.106-113.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S., Parker S. R., Talbert P. B., Houts S. E. Interactions between chemotaxis genes and flagellar genes in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1983 Jul;155(1):265–274. doi: 10.1128/jb.155.1.265-274.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parkinson J. S. cheA, cheB, and cheC genes of Escherichia coli and their role in chemotaxis. J Bacteriol. 1976 May;126(2):758–770. doi: 10.1128/jb.126.2.758-770.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith R. A., Parkinson J. S. Overlapping genes at the cheA locus of Escherichia coli. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5370–5374. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5370. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer M. S., Goy M. F., Adler J. Protein methylation in behavioural control mechanisms and in signal transduction. Nature. 1979 Jul 26;280(5720):279–284. doi: 10.1038/280279a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock A., Mottonen J., Chen T., Stock J. Identification of a possible nucleotide binding site in CheW, a protein required for sensory transduction in bacterial chemotaxis. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jan 15;262(2):535–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson R. V., Bourret R. B., Simon M. I. Intermolecular complementation of the kinase activity of CheA. Mol Microbiol. 1993 May;8(3):435–441. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01588.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welch M., Oosawa K., Aizawa S., Eisenbach M. Phosphorylation-dependent binding of a signal molecule to the flagellar switch of bacteria. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Oct 1;90(19):8787–8791. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.19.8787. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolfe A. J., Stewart R. C. The short form of the CheA protein restores kinase activity and chemotactic ability to kinase-deficient mutants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1993 Feb 15;90(4):1518–1522. doi: 10.1073/pnas.90.4.1518. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]




