Abstract
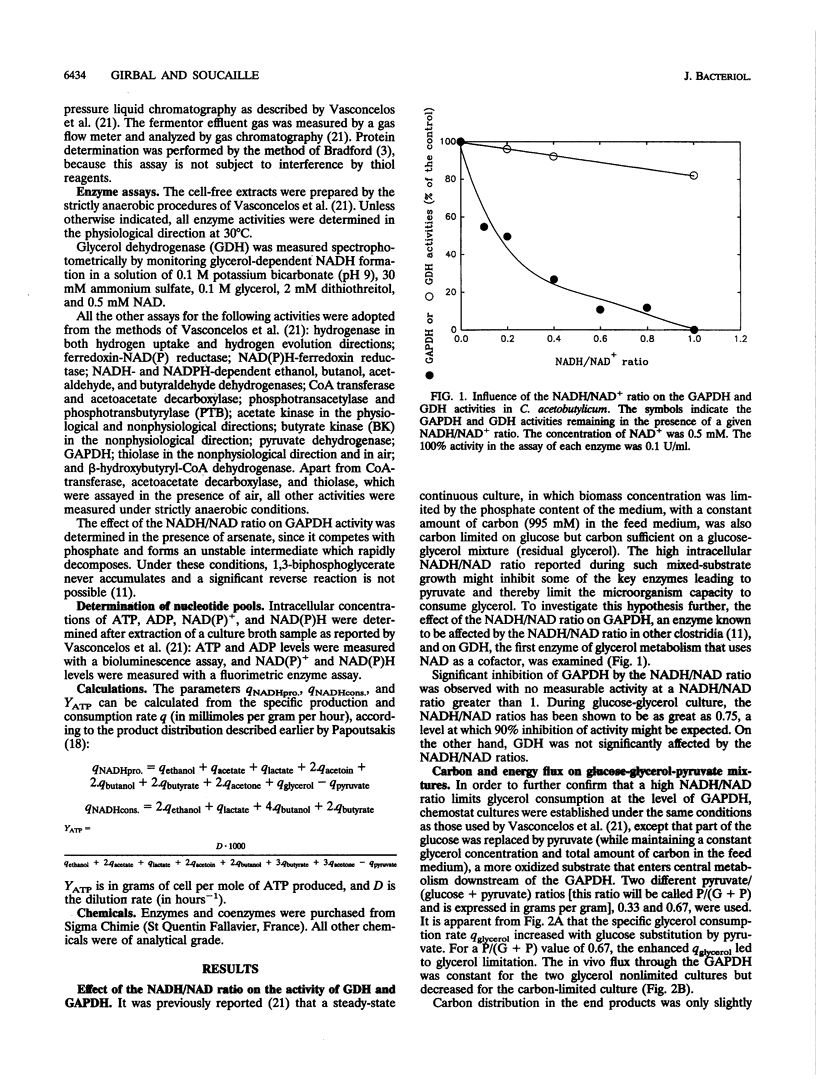
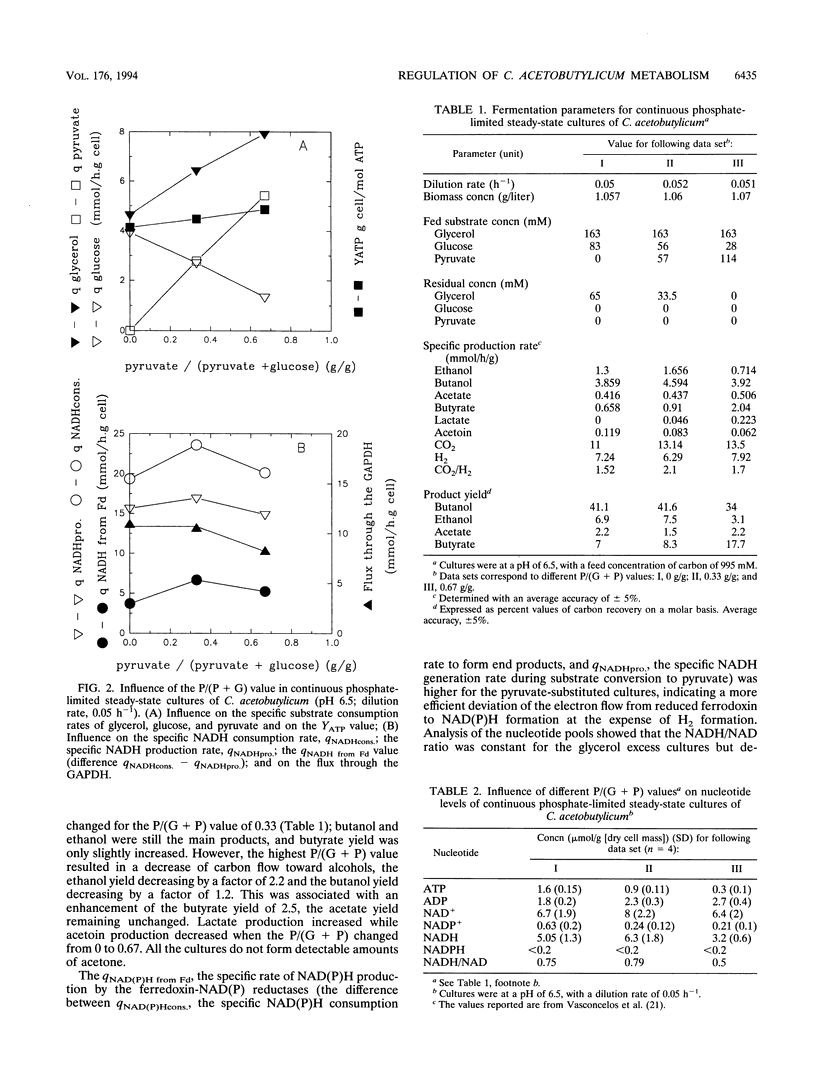
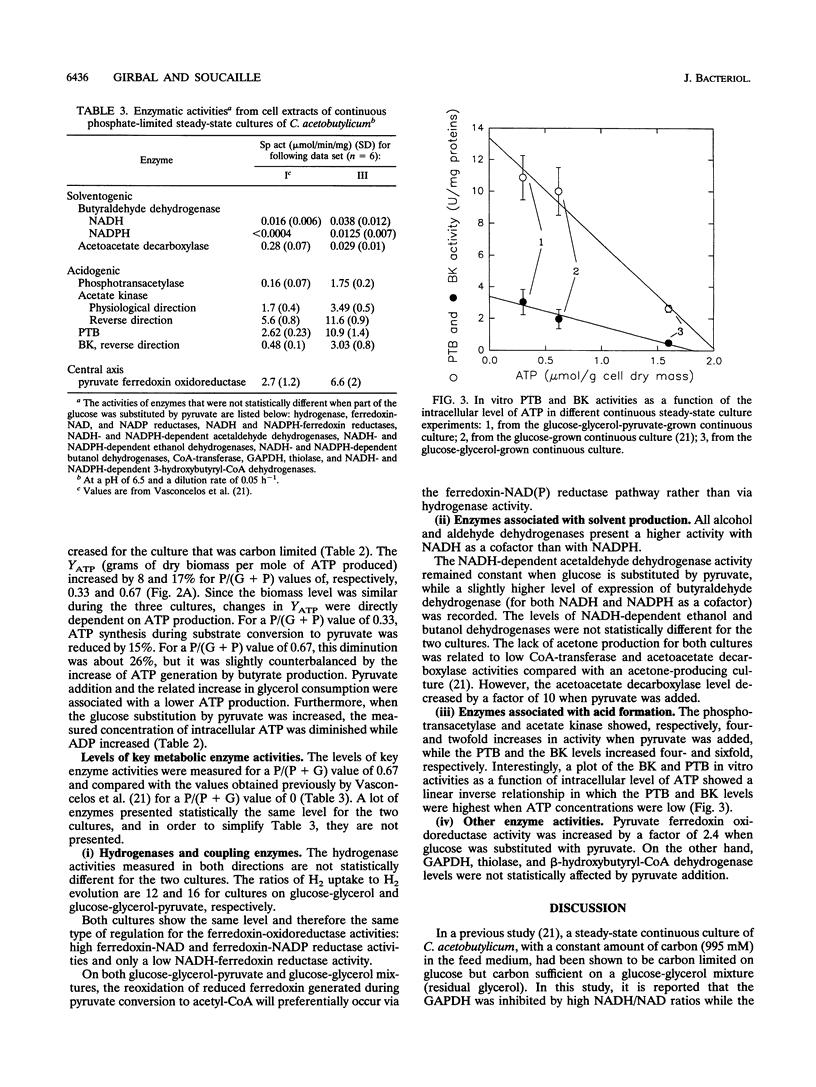
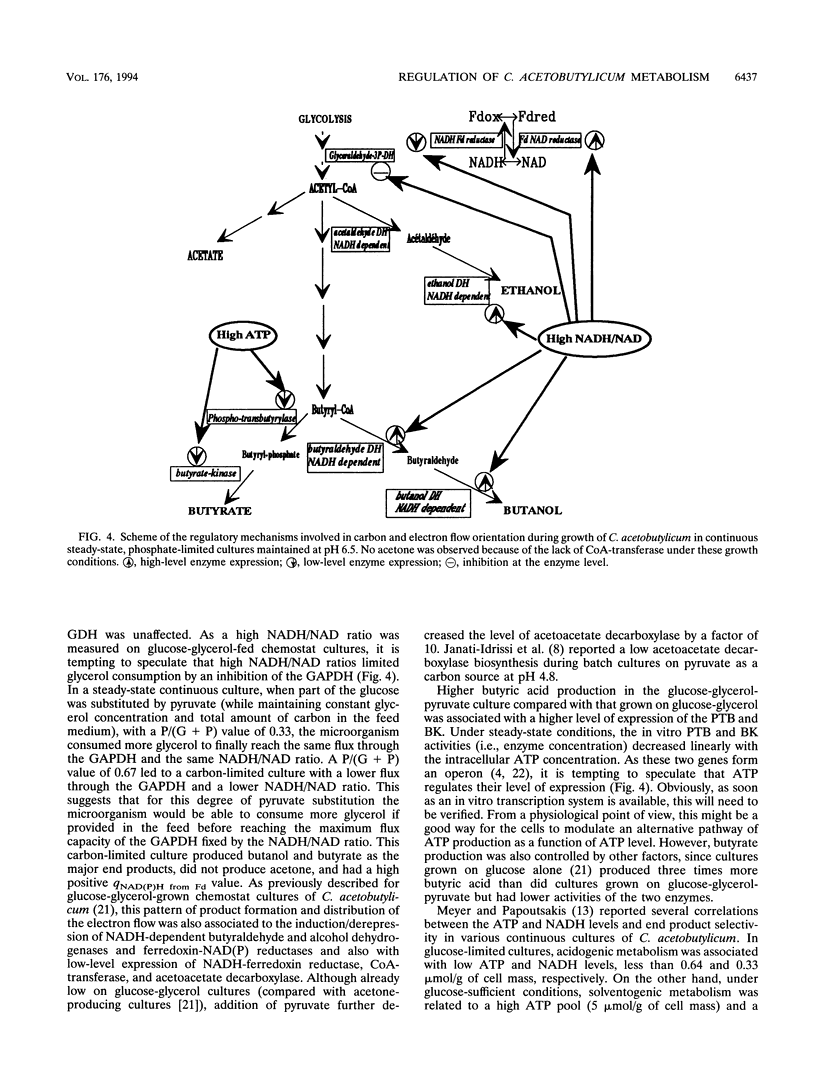
Glycerol-glucose-fed (molar ratio of 2) chemostat cultures of Clostridium acetobutylicum were glucose limited but glycerol sufficient and had a high intracellular NADH/NAD ratio (I. Vasconcelos, L. Girbal, and P. Soucaille, J. Bacteriol. 176:1443-1450, 1994). We report here that the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase, one of the key enzymes of the glycolytic pathway, is inhibited by high NADH/NAD ratios. Partial substitution of glucose by pyruvate while maintaining glycerol concentration at a constant level allowed a higher consumption of glycerol in steady-state continuous cultures. However, glycerol-sufficient cultures had a constant flux through the glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase and a constant NADH/NAD ratio. A high substitution of glucose by pyruvate [P/(G+P) value of 0.67 g/g] provided a carbon-limited culture with butanol and butyrate as the major end products. In this alcohologenic culture, the induction of the NADH-dependent butyraldehyde and the ferredoxin-NAD(P) reductases and the higher expression of alcohol dehydrogenases were related to a high NADH/NAD ratio and a low intracellular ATP concentration. In three different steady-state cultures, the in vitro phosphotransbutyrylase and butyrate-kinase activities decreased with the intracellular ATP concentration, suggesting a transcriptional regulation of these two genes, which are arranged in an operon (K. A. Walter, R. V. Nair, R. V. Carry, G. N. Bennett, and E. T. Papoutsakis, Gene 134:107-111, 1993).
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bahl H., Gottwald M., Kuhn A., Rale V., Andersch W., Gottschalk G. Nutritional Factors Affecting the Ratio of Solvents Produced by Clostridium acetobutylicum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jul;52(1):169–172. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.1.169-172.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradford M. M. A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 1976 May 7;72:248–254. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cary J. W., Petersen D. J., Papoutsakis E. T., Bennett G. N. Cloning and expression of Clostridium acetobutylicum phosphotransbutyrylase and butyrate kinase genes in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1988 Oct;170(10):4613–4618. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.10.4613-4618.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Datta R., Zeikus J. G. Modulation of acetone-butanol-ethanol fermentation by carbon monoxide and organic acids. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1985 Mar;49(3):522–529. doi: 10.1128/aem.49.3.522-529.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grupe H., Gottschalk G. Physiological Events in Clostridium acetobutylicum during the Shift from Acidogenesis to Solventogenesis in Continuous Culture and Presentation of a Model for Shift Induction. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1992 Dec;58(12):3896–3902. doi: 10.1128/aem.58.12.3896-3902.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janati-Idrissi R., Junelles A. M., el Kanouni A., Petitdemange H., Gay R. Pyruvate fermentation by Clostridium acetobutylicum. Biochem Cell Biol. 1989 Oct;67(10):735–739. doi: 10.1139/o89-110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Junelles A. M., Janati-Idrissi R., Petitdemange H., Gay R. Effect of pyruvate on glucose metabolism in Clostridium acetobutylicum. Biochimie. 1987 Nov-Dec;69(11-12):1183–1190. doi: 10.1016/0300-9084(87)90145-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim B. H., Bellows P., Datta R., Zeikus J. G. Control of Carbon and Electron Flow in Clostridium acetobutylicum Fermentations: Utilization of Carbon Monoxide to Inhibit Hydrogen Production and to Enhance Butanol Yields. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1984 Oct;48(4):764–770. doi: 10.1128/aem.48.4.764-770.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lovitt R. W., Shen G. J., Zeikus J. G. Ethanol production by thermophilic bacteria: biochemical basis for ethanol and hydrogen tolerance in Clostridium thermohydrosulfuricum. J Bacteriol. 1988 Jun;170(6):2809–2815. doi: 10.1128/jb.170.6.2809-2815.1988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monot F., Martin J. R., Petitdemange H., Gay R. Acetone and Butanol Production by Clostridium acetobutylicum in a Synthetic Medium. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1982 Dec;44(6):1318–1324. doi: 10.1128/aem.44.6.1318-1324.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terracciano J. S., Kashket E. R. Intracellular Conditions Required for Initiation of Solvent Production by Clostridium acetobutylicum. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1986 Jul;52(1):86–91. doi: 10.1128/aem.52.1.86-91.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vasconcelos I., Girbal L., Soucaille P. Regulation of carbon and electron flow in Clostridium acetobutylicum grown in chemostat culture at neutral pH on mixtures of glucose and glycerol. J Bacteriol. 1994 Mar;176(5):1443–1450. doi: 10.1128/jb.176.5.1443-1450.1994. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walter K. A., Nair R. V., Cary J. W., Bennett G. N., Papoutsakis E. T. Sequence and arrangement of two genes of the butyrate-synthesis pathway of Clostridium acetobutylicum ATCC 824. Gene. 1993 Nov 30;134(1):107–111. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90182-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



