Abstract
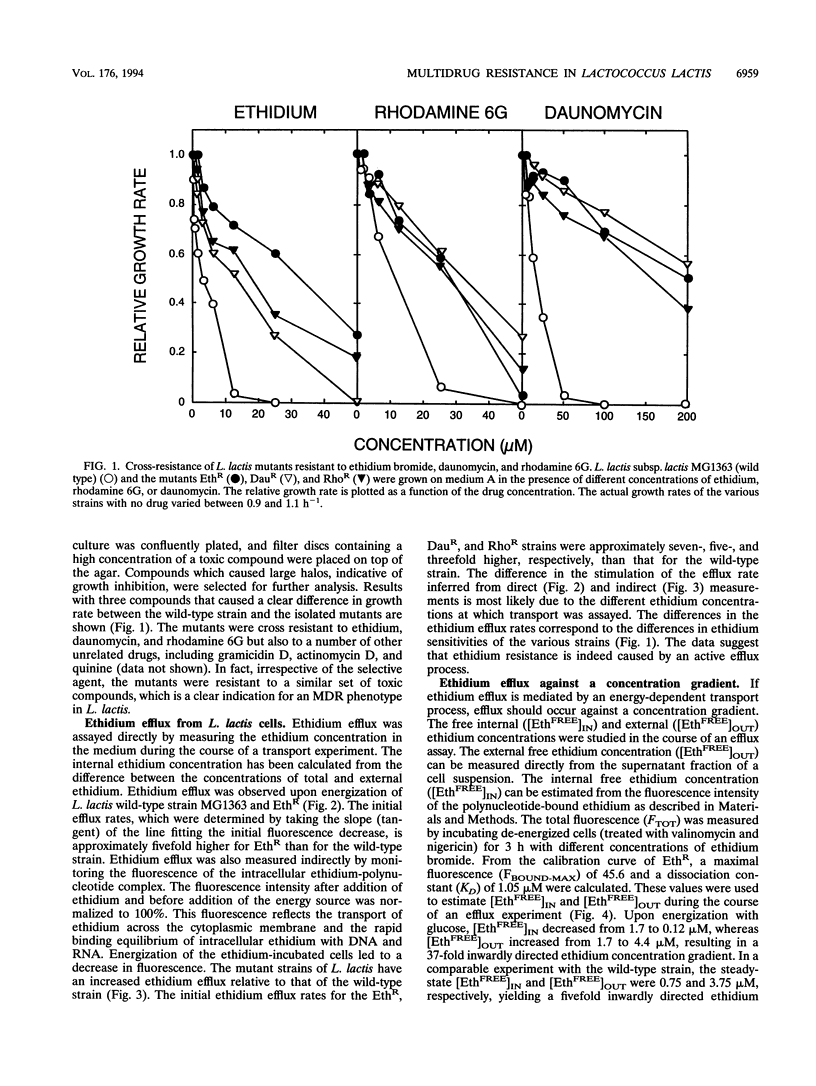
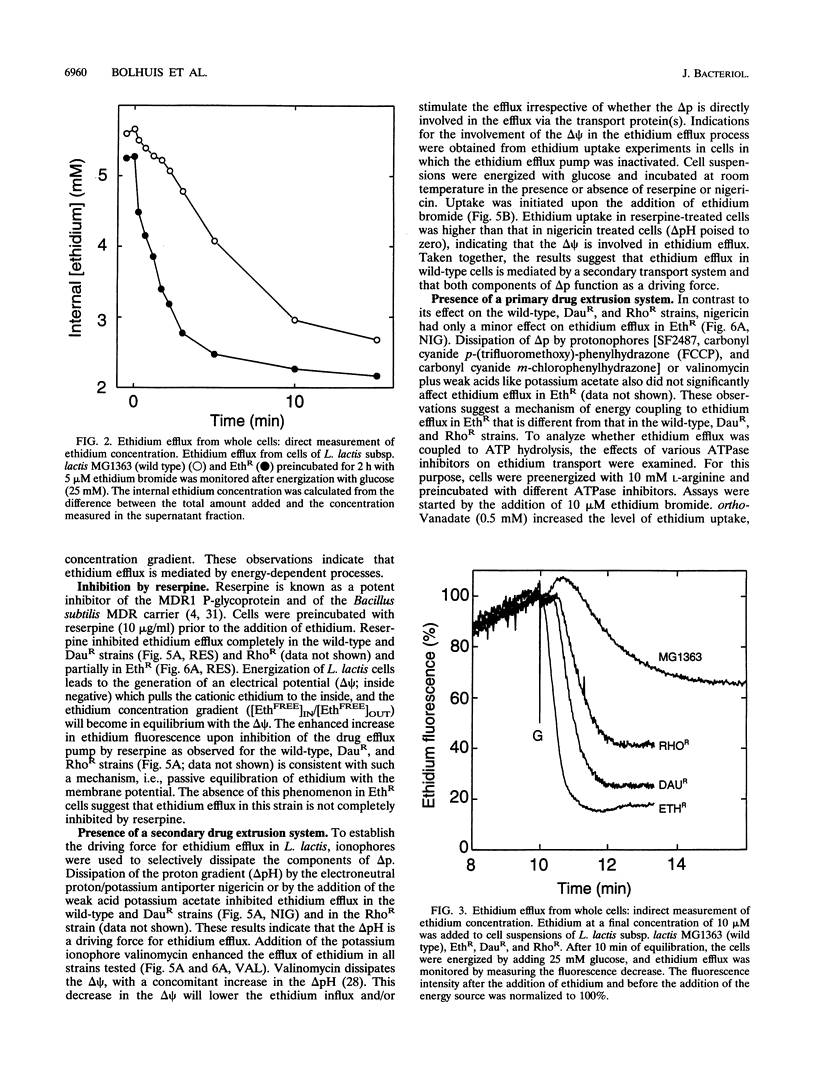
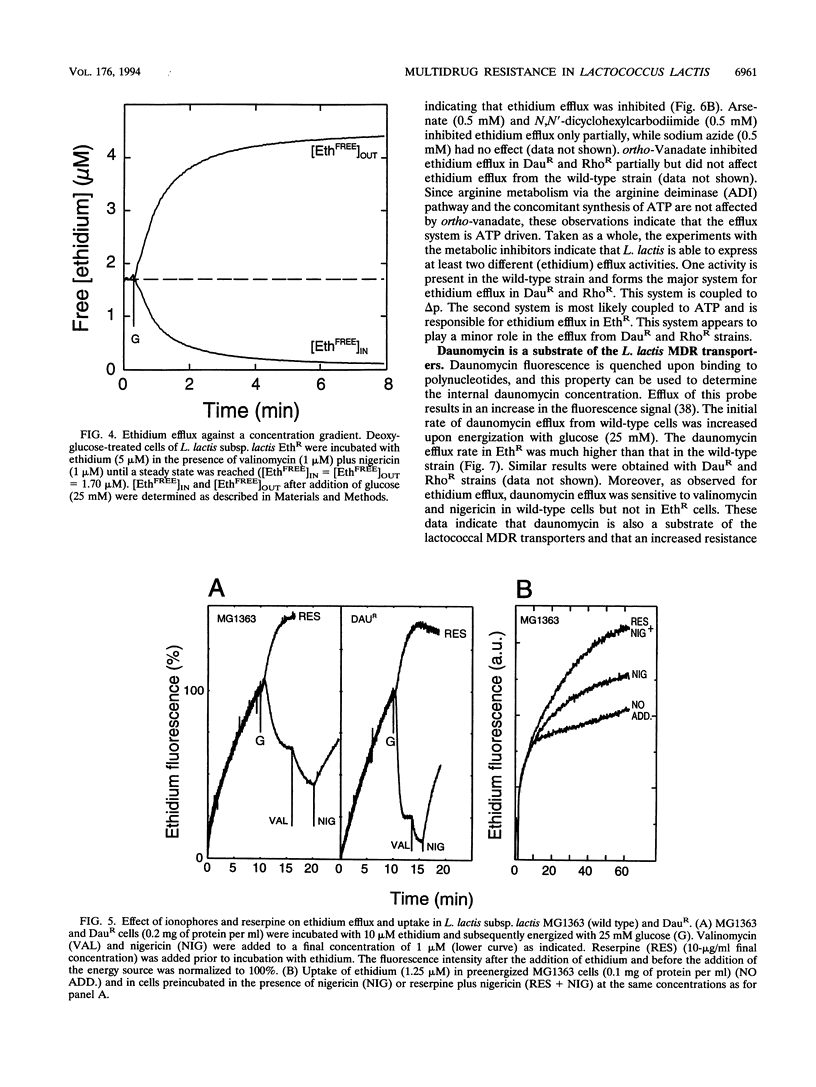
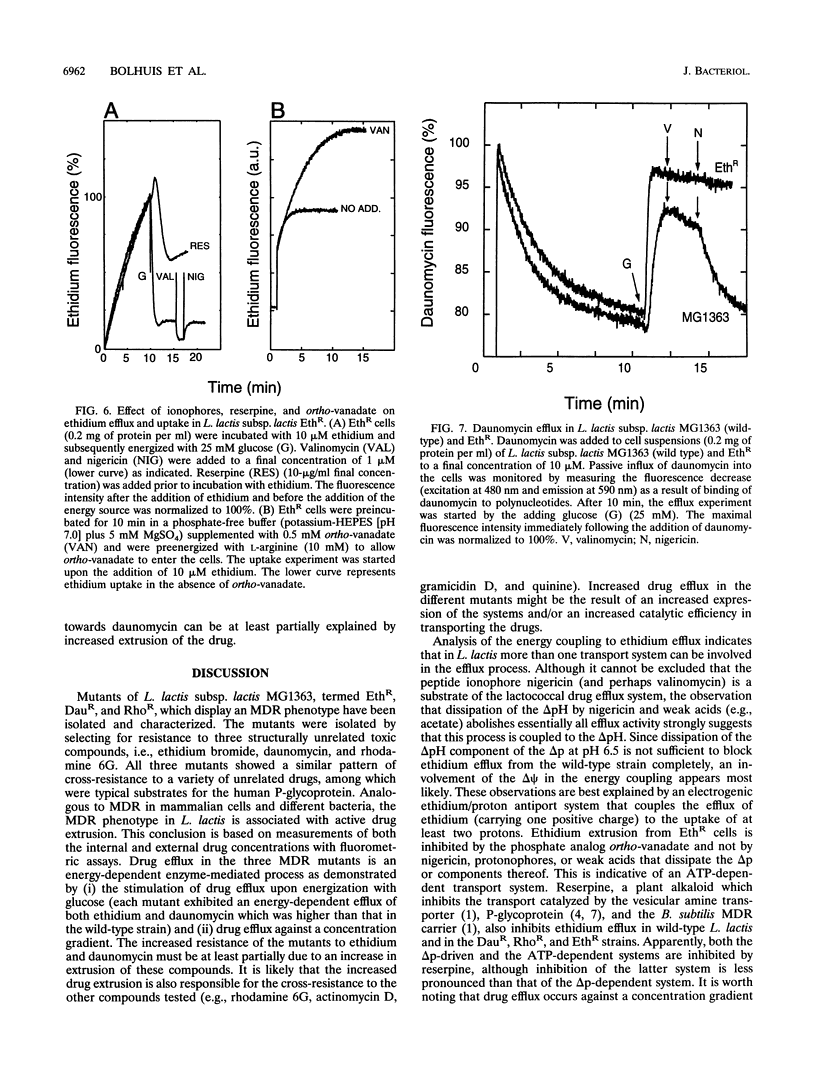
Three mutants of Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis MG1363, termed EthR, DauR, and RhoR, were selected for resistance to high concentrations of ethidium bromide, daunomycin, and rhodamine 6G, respectively. These mutants were found to be cross resistant to a number of structurally and functionally unrelated drugs, among which were typical substrates of the mammalian multidrug transporter (P-glycoprotein) such as daunomycin, quinine, actinomycin D, gramicidin D, and rhodamine 6G. The three multidrug-resistant strains showed an increased rate of energy-dependent ethidium and daunomycin efflux compared with that of the wild-type strain. This suggests that resistance to these toxic compounds is at least partly due to active efflux. Efflux of ethidium from the EthR strain could occur against a 37-fold inwardly directed concentration gradient. In all strains, ethidium efflux was inhibited by reserpine, a well-known inhibitor of P-glycoprotein. Ionophores which selectively dissipate the membrane potential or the pH gradient across the membrane inhibited ethidium and daunomycin efflux in the wild-type strain, corresponding with a proton motive force-driven efflux system. The ethidium efflux system in the EthR strain, on the other hand, was inhibited by ortho-vanadate and not upon dissipation of the proton motive force, which suggests the involvement of ATP in the energization of transport. The partial inhibition of ethidium efflux by ortho-vanadate and nigericin in the DauR and RhoR strains suggest that a proton motive force-dependent and an ATP-dependent system are expressed simultaneously. This is the first report of an ATP-dependent transport system in prokaryotes which confers multidrug resistance to the organism.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahmed M., Borsch C. M., Neyfakh A. A., Schuldiner S. Mutants of the Bacillus subtilis multidrug transporter Bmr with altered sensitivity to the antihypertensive alkaloid reserpine. J Biol Chem. 1993 May 25;268(15):11086–11089. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bissonnette L., Champetier S., Buisson J. P., Roy P. H. Characterization of the nonenzymatic chloramphenicol resistance (cmlA) gene of the In4 integron of Tn1696: similarity of the product to transmembrane transport proteins. J Bacteriol. 1991 Jul;173(14):4493–4502. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.14.4493-4502.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Culliton B. J. Drug-resistant TB may bring epidemic. Nature. 1992 Apr 9;356(6369):473–473. doi: 10.1038/356473a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Endicott J. A., Ling V. The biochemistry of P-glycoprotein-mediated multidrug resistance. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:137–171. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.58.070189.001033. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fath M. J., Kolter R. ABC transporters: bacterial exporters. Microbiol Rev. 1993 Dec;57(4):995–1017. doi: 10.1128/mr.57.4.995-1017.1993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frezard F., Garnier-Suillerot A. DNA-containing liposomes as a model for the study of cell membrane permeation by anthracycline derivatives. Biochemistry. 1991 May 21;30(20):5038–5043. doi: 10.1021/bi00234a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gottesman M. M., Pastan I. Biochemistry of multidrug resistance mediated by the multidrug transporter. Annu Rev Biochem. 1993;62:385–427. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.62.070193.002125. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grinius L., Dreguniene G., Goldberg E. B., Liao C. H., Projan S. J. A staphylococcal multidrug resistance gene product is a member of a new protein family. Plasmid. 1992 Mar;27(2):119–129. doi: 10.1016/0147-619x(92)90012-y. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gros P., Talbot F., Tang-Wai D., Bibi E., Kaback H. R. Lipophilic cations: a group of model substrates for the multidrug-resistance transporter. Biochemistry. 1992 Feb 25;31(7):1992–1998. doi: 10.1021/bi00122a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guilfoile P. G., Hutchinson C. R. A bacterial analog of the mdr gene of mammalian tumor cells is present in Streptomyces peucetius, the producer of daunorubicin and doxorubicin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Oct 1;88(19):8553–8557. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.19.8553. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F. ABC transporters: from microorganisms to man. Annu Rev Cell Biol. 1992;8:67–113. doi: 10.1146/annurev.cb.08.110192.000435. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Higgins C. F., Gottesman M. M. Is the multidrug transporter a flippase? Trends Biochem Sci. 1992 Jan;17(1):18–21. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(92)90419-a. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horio M., Gottesman M. M., Pastan I. ATP-dependent transport of vinblastine in vesicles from human multidrug-resistant cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 May;85(10):3580–3584. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.10.3580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyde S. C., Emsley P., Hartshorn M. J., Mimmack M. M., Gileadi U., Pearce S. R., Gallagher M. P., Gill D. R., Hubbard R. E., Higgins C. F. Structural model of ATP-binding proteins associated with cystic fibrosis, multidrug resistance and bacterial transport. Nature. 1990 Jul 26;346(6282):362–365. doi: 10.1038/346362a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hächler H., Cohen S. P., Levy S. B. marA, a regulated locus which controls expression of chromosomal multiple antibiotic resistance in Escherichia coli. J Bacteriol. 1991 Sep;173(17):5532–5538. doi: 10.1128/jb.173.17.5532-5538.1991. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston L. H., Dyke K. G. Ethidium bromide resistance, a new marker on the staphylococcal penicillinase plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1969 Dec;100(3):1413–1414. doi: 10.1128/jb.100.3.1413-1414.1969. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaatz G. W., Seo S. M., Ruble C. A. Efflux-mediated fluoroquinolone resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1993 May;37(5):1086–1094. doi: 10.1128/aac.37.5.1086. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lambert B., Le Pecq J. B. Effect of mutation, electric membrane potential, and metabolic inhibitors on the accessibility of nucleic acids to ethidium bromide in Escherichia coli cells. Biochemistry. 1984 Jan 3;23(1):166–176. doi: 10.1021/bi00296a027. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LePecq J. B., Paoletti C. A fluorescent complex between ethidium bromide and nucleic acids. Physical-chemical characterization. J Mol Biol. 1967 Jul 14;27(1):87–106. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90353-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy S. B. Active efflux mechanisms for antimicrobial resistance. Antimicrob Agents Chemother. 1992 Apr;36(4):695–703. doi: 10.1128/aac.36.4.695. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu Y., Peter D., Roghani A., Schuldiner S., Privé G. G., Eisenberg D., Brecha N., Edwards R. H. A cDNA that suppresses MPP+ toxicity encodes a vesicular amine transporter. Cell. 1992 Aug 21;70(4):539–551. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(92)90425-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomovskaya O., Lewis K. Emr, an Escherichia coli locus for multidrug resistance. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 1;89(19):8938–8942. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.19.8938. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midgley M. An efflux system for cationic dyes and related compounds in Escherichia coli. Microbiol Sci. 1987 Apr;4(4):125–127. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Midgley M. The phosphonium ion efflux system of Escherichia coli: relationship to the ethidium efflux system and energetic studies. J Gen Microbiol. 1986 Nov;132(11):3187–3193. doi: 10.1099/00221287-132-11-3187. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mimura C. S., Holbrook S. R., Ames G. F. Structural model of the nucleotide-binding conserved component of periplasmic permeases. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jan 1;88(1):84–88. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.1.84. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miyauchi S., Komatsubara M., Kamo N. In archaebacteria, there is a doxorubicin efflux pump similar to mammalian P-glycoprotein. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1992 Oct 5;1110(2):144–150. doi: 10.1016/0005-2736(92)90351-l. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molenaar D., Abee T., Konings W. N. Continuous measurement of the cytoplasmic pH in Lactococcus lactis with a fluorescent pH indicator. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1991 Nov 14;1115(1):75–83. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(91)90014-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molenaar D., Bolhuis H., Abee T., Poolman B., Konings W. N. The efflux of a fluorescent probe is catalyzed by an ATP-driven extrusion system in Lactococcus lactis. J Bacteriol. 1992 May;174(10):3118–3124. doi: 10.1128/jb.174.10.3118-3124.1992. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neyfakh A. A., Bidnenko V. E., Chen L. B. Efflux-mediated multidrug resistance in Bacillus subtilis: similarities and dissimilarities with the mammalian system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Jun 1;88(11):4781–4785. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.11.4781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paulsen I. T., Skurray R. A. Topology, structure and evolution of two families of proteins involved in antibiotic and antiseptic resistance in eukaryotes and prokaryotes--an analysis. Gene. 1993 Feb 14;124(1):1–11. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(93)90755-r. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodríguez A. M., Olano C., Vilches C., Méndez C., Salas J. A. Streptomyces antibioticus contains at least three oleandomycin-resistance determinants, one of which shows similarity with proteins of the ABC-transporter superfamily. Mol Microbiol. 1993 May;8(3):571–582. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1993.tb01601.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross J. I., Eady E. A., Cove J. H., Cunliffe W. J., Baumberg S., Wootton J. C. Inducible erythromycin resistance in staphylococci is encoded by a member of the ATP-binding transport super-gene family. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Jul;4(7):1207–1214. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00696.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosteck P. R., Jr, Reynolds P. A., Hershberger C. L. Homology between proteins controlling Streptomyces fradiae tylosin resistance and ATP-binding transport. Gene. 1991 Jun 15;102(1):27–32. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(91)90533-h. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rouch D. A., Cram D. S., DiBerardino D., Littlejohn T. G., Skurray R. A. Efflux-mediated antiseptic resistance gene qacA from Staphylococcus aureus: common ancestry with tetracycline- and sugar-transport proteins. Mol Microbiol. 1990 Dec;4(12):2051–2062. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.1990.tb00565.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spoelstra E. C., Westerhoff H. V., Dekker H., Lankelma J. Kinetics of daunorubicin transport by P-glycoprotein of intact cancer cells. Eur J Biochem. 1992 Jul 15;207(2):567–579. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1992.tb17083.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tennent J. M., Lyon B. R., Midgley M., Jones I. G., Purewal A. S., Skurray R. A. Physical and biochemical characterization of the qacA gene encoding antiseptic and disinfectant resistance in Staphylococcus aureus. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 Jan;135(1):1–10. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-1-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring M. J. Complex formation between ethidium bromide and nucleic acids. J Mol Biol. 1965 Aug;13(1):269–282. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80096-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamaguchi A., Kimura T., Someya Y., Sawai T. Metal-tetracycline/H+ antiporter of Escherichia coli encoded by transposon Tn10. The structural resemblance and functional difference in the role of the duplicated sequence motif between hydrophobic segments 2 and 3 and segments 8 and 9. J Biol Chem. 1993 Mar 25;268(9):6496–6504. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida H., Bogaki M., Nakamura S., Ubukata K., Konno M. Nucleotide sequence and characterization of the Staphylococcus aureus norA gene, which confers resistance to quinolones. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):6942–6949. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.6942-6949.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwietering M. H., Jongenburger I., Rombouts F. M., van 't Riet K. Modeling of the bacterial growth curve. Appl Environ Microbiol. 1990 Jun;56(6):1875–1881. doi: 10.1128/aem.56.6.1875-1881.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



